Preparation of Fly Ash Modified with Manganese Dioxide to Enhance As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) Adsorption from Groundwater
-
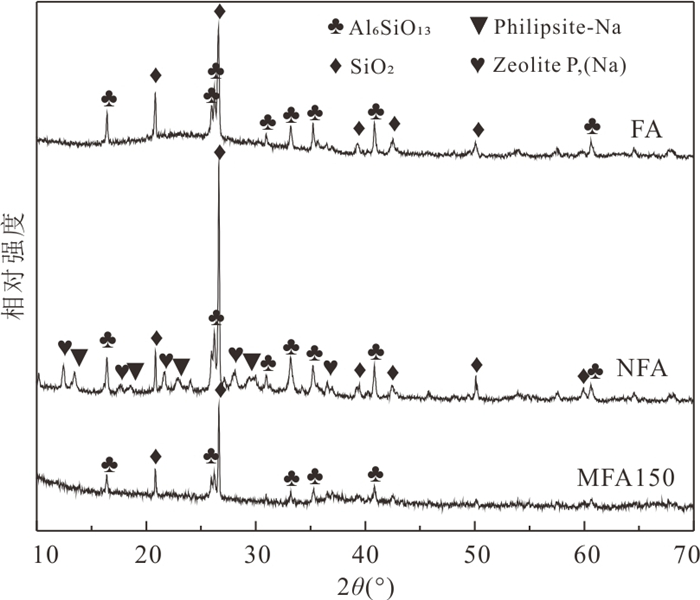
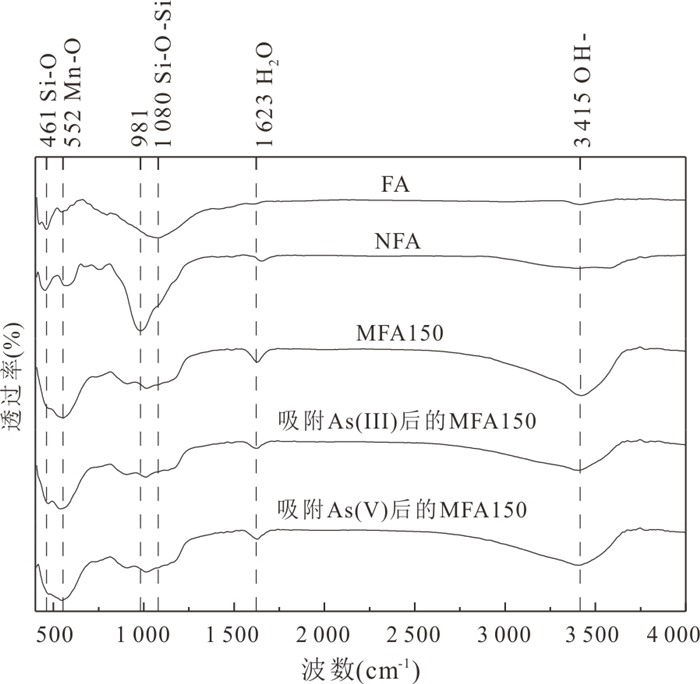
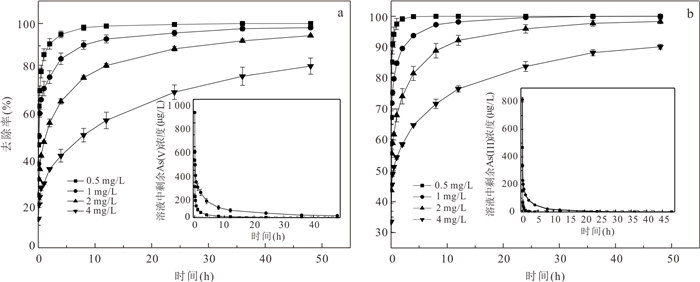
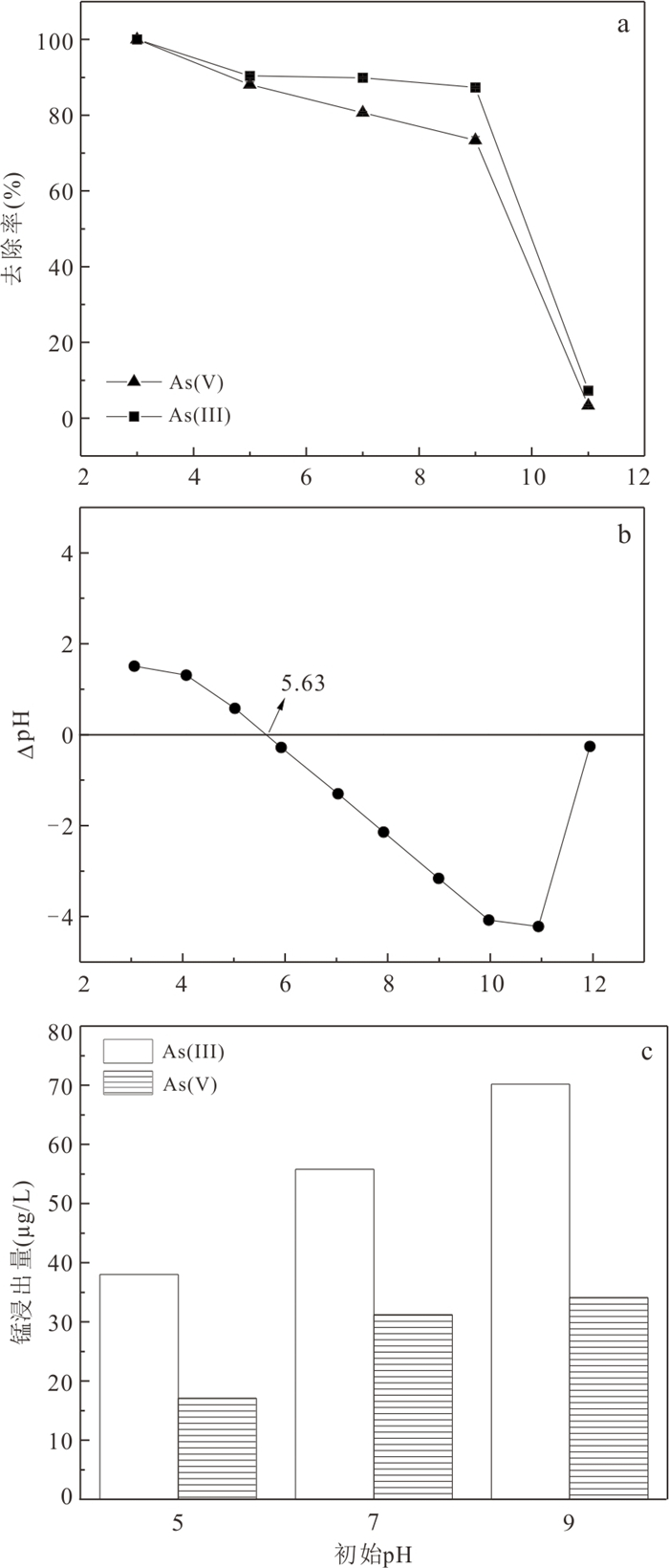
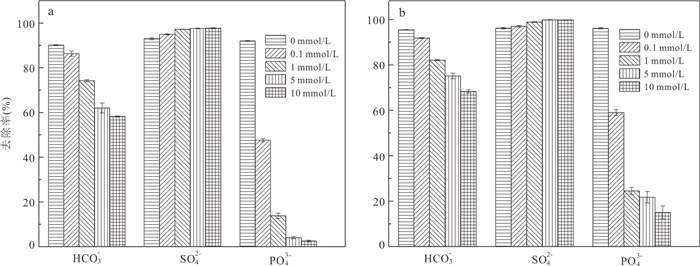
摘要: 高砷地下水在我国广泛分布,开发绿色高效的除砷材料对于促进地区发展和保障居民饮用水安全具有重要意义.采用共沉淀法结合NaOH水热处理技术制备了二氧化锰改性粉煤灰吸附材料MFA150,并研究其对地下水中As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附特性.结果表明,NaOH水热处理破坏了原始粉煤灰的玻璃体结构,且在这一过程中生成沸石相,粉煤灰比表面积由1.30 m2/g增加至40.26 m2/g.在负载MnO2后,MFA150比表面积达到148.82 m2/g.此外,吸附材料表面-OH的含量显著增加,为As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)提供了更多的吸附活性位点.MFA150对As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附过程符合Elovich模型和Freundlich模型.在中性条件下MFA150对As(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅲ)的吸附量分别达到2.55 mg/g和9.71 mg/g,酸性条件更有利于吸附.溶液中共存的HCO3‒和PO43‒会抑制As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附,而SO42‒对As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的去除具有轻微促进作用.在模拟地下水中,MFA150对总砷的去除率达到91.90%.MFA150制备方法简单,制备原料廉价易得,吸附性能好有望用于含砷地下水处理.Abstract: High arsenic groundwater is widely distributed in China, and it is of great significance to develop green and efficient arsenic removal materials for the sake of regional development and safety of drinking water for residents. In this study, the fly ash modified with manganese dioxide (MFA150) was prepared using co-precipitation method combined with NaOH hydrothermal process, to investigate its adsorption of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) in groundwater. The results show that the vitreous structure of the raw fly ash was destroyed to generate zeolite phase in NaOH hydrothermal process, and the specific surface area of fly ash increased from 1.30 m2/g to 40.26 m2/g. After loading MnO2, the specific surface area of the adsorbent further increased to 148.82 m2/g, and the content of -OH on the surface was significantly increased to provide more adsorption sites for As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ). The adsorption of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) was in accordance with the Elovich model and the Freundlich model. The adsorption capacities of MFA150 for As(Ⅴ) and As(Ⅲ) under neutral condition were 2.55 mg/g and 9.71 mg/g, respectively, and showed stronger adsorption ability under acidic condition. Coexisting HCO3‒ and PO43‒ inhibited the adsorption of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ), while SO42‒ slightly promoted the removal of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ). In simulated groundwater, the removal rate of total As reached 91.90% by MFA150. Since preparation of MFA150 is simple and the raw material is cheap and easy to obtain, MFA150 is expected to be used in the treatment of the high arsenic groundwater owing to the better adsorption performance for As(Ⅴ) and As(Ⅲ).
-
Key words:
- high arsenic /
- groundwater /
- fly ash /
- manganese oxide /
- adsorption /
- resource utilization /
- environmental geology
-
表 1 粉煤灰重金属元素浸出量
Table 1. Leaching amount of heavy metals from fly ash
元素 Cr Ni Cu Zn As Cd Hg Pb 浸出量(μg/g) 1.330 0.034 0.003 0.009 0.044 0.004 0.019 0.008 表 2 FA、NFA和MFA150的比表面积和孔结构参数
Table 2. Specific surface area and pore structure parameters of FA, NFA and MFA150
材料 BET比表面积(m2/g) 孔容(cm3/g) 平均孔径(nm) FA 1.30 6.14×10‒3 28.47 NFA 40.26 1.59×10‒1 10.78 MFA150 148.82 2.00×10‒1 7.82 表 3 MFA150吸附As(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅲ)的动力学拟合参数
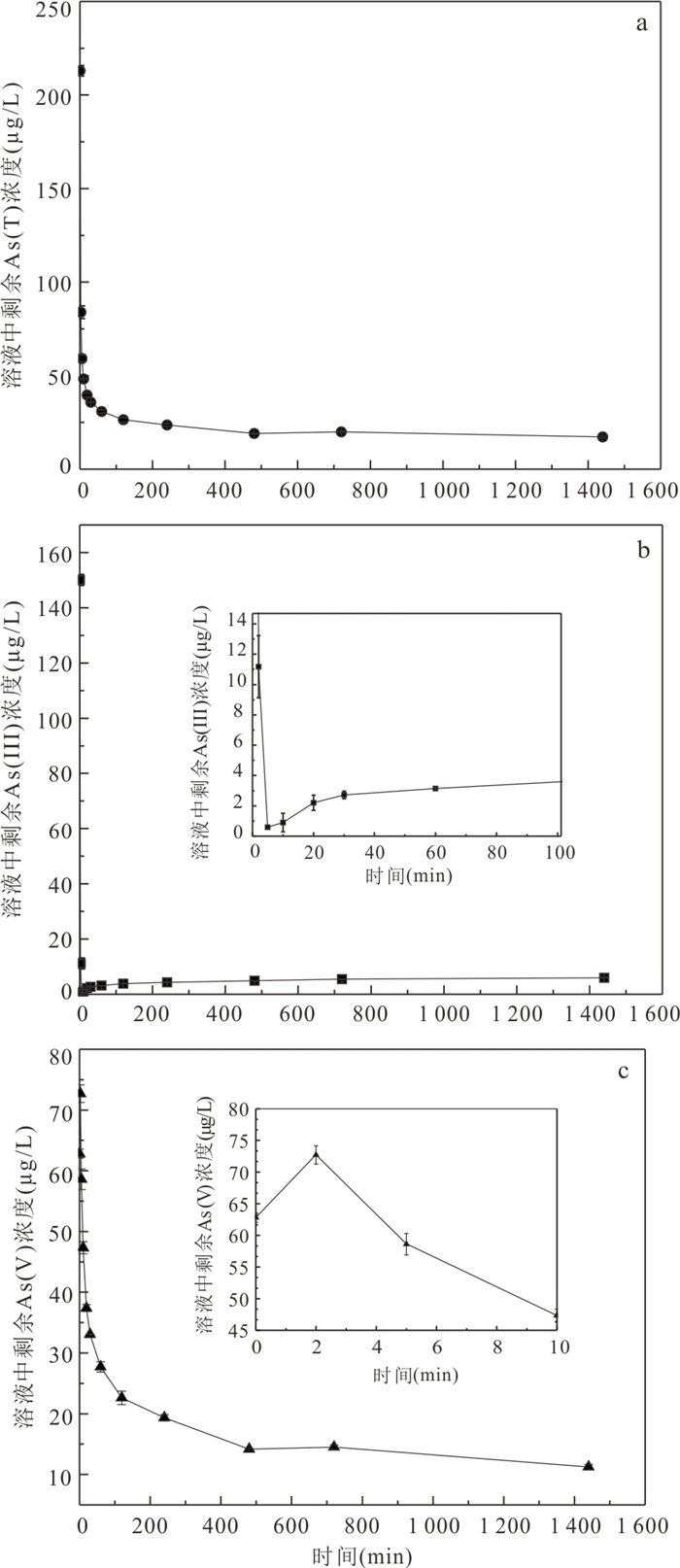
Table 3. The kinetic parameters of adsorption As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) over MFA150
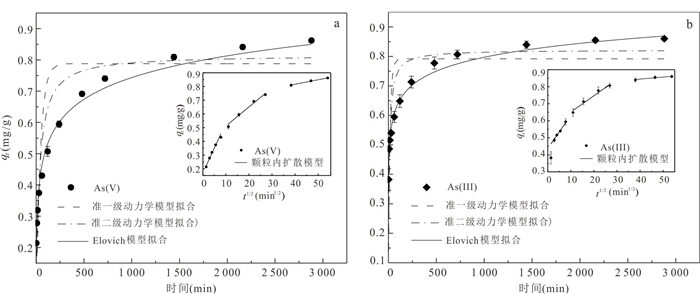
qe, exp 准一级动力学模型 准二级动力学模型 Elovich模型 qe, cal k1 R2 qe, cal k1 R2 α β R2 As(Ⅲ) 0.86 0.79 0.062 0.6557 0.82 0.124 0.8603 8.290 14.690 0.9928 As(Ⅴ) 0.86 0.79 0.023 0.7900 0.82 0.038 0.8616 0.164 9.953 0.9800 颗粒内扩散模型 第一阶段 第二阶段 第三阶段 kd1 C1 R12 kd2 C2 R22 kd3 C3 R32 As(Ⅲ) 0.020 0.437 0.8834 0.010 0.556 0.9757 0.001 0.797 0.9257 As(Ⅴ) 0.037 0.171 0.9842 0.014 0.374 0.9804 0.003 0.687 0.9949 表 4 MFA150吸附As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)吸附等温线拟合参数
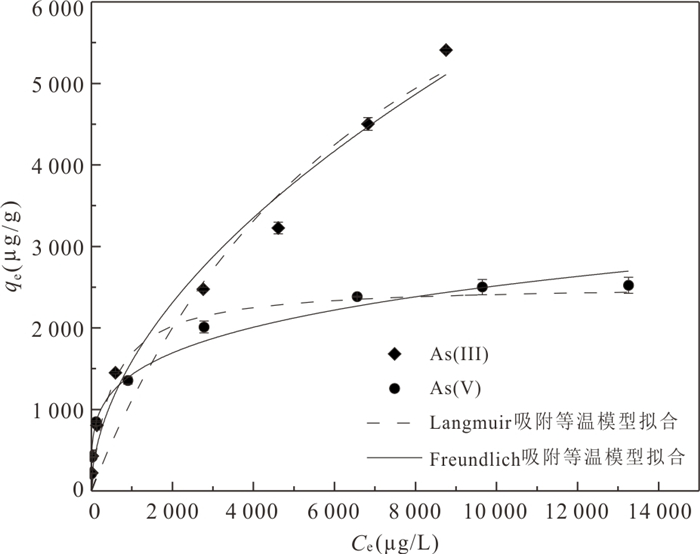
Table 4. The Langmuir and Freundlich parameters of adsorption As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) over MFA150
Langmuir Freundlich qmax(μg/g) KL(L/μg) R2 1/n Kf(μg/g) R2 As(Ⅲ) 9 713.9 0.000 1 0.945 9 0.246 9 262.68 0.986 3 As(Ⅴ) 2 545.1 0.002 1 0.944 1 0.537 7 38.77 0.980 4 -
Algoufi, Y. T., Hameed, B. H., 2014. Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate by Transesterification of Glycerol with Dimethyl Carbonate over K⁃Zeolite Derived from Coal Fly Ash. Fuel Processing Technology, 126: 5-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.04.004 Asl, S. M. H., Javadian, H., Khavarpour, M., et al., 2019. Porous Adsorbents Derived from Coal Fly Ash as Cost⁃Effective and Environmentally⁃Friendly Sources of Aluminosilicate for Sequestration of Aqueous and Gaseous Pollutants: A Review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208: 1131-1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.186 Cuong, D. V., Wu, P. C., Chen, L. I., et al., 2021. Active MnO2/Biochar Composite for Efficient As(Ⅲ) Removal: Insight into the Mechanisms of Redox Transformation and Adsorption. Water Research, 188: 116495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116495 Deschamps, E., Ciminelli, V. S. T., Höll, W. H., 2005. Removal of As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) from Water Using a Natural Fe and Mn Enriched Sample. Water Research, 39(20): 5212-5220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.007 Fendorf, S., Michael, H. A., van Geen, A., 2010. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Groundwater Arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science, 328(5982): 1123-1127. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1172974 Feng, W. L., Lü, X. B., Xiong, J., et al., 2021. Research Progress of High Added Value Utilization of Coal Fly Ash. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 53(4): 25-31 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ferguson, J. F., Gavis, J., 1972. A Review of the Arsenic Cycle in Natural Waters. Water Research, 6(11): 1259-1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043⁃1354(72)90052⁃8 Gollakota, A. R. K., Volli, V., Shu, C. M., 2019. Progressive Utilisation Prospects of Coal Fly Ash: A Review. Science of the Total Environment, 672: 951-989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.337 Ho, Y. S., 2006. Review of Second⁃Order Models for Adsorption Systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3): 681-689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043 Huang, X. R., Zhao, H. H., Hu, X. F., et al., 2020a. Optimization of Preparation Technology for Modified Coal Fly Ash and Its Adsorption Properties for Cd2+. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 392: 122461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122461 Huang, X. R., Zhao, H. H., Zhang, G. B., et al., 2020b. Potential of Removing Cd(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) from Contaminated Water Using a Newly Modified Fly Ash. Chemosphere, 242: 125148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125148 Jiang, L., 2020. Comprehensiveutilization Situation of Fly Ash in Coal⁃Fired Power Plants and Its Development Suggestions. Clean Coal Technology, 26(4): 31-39 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, L., Chen, J. Y., Li, X. M., et al., 2011. Adsorption of Phosphate from Wastewater by Fly Ash Ceramsite. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(7): 1413-1420 (in Chinese with English abstract). Karanac, M., Đolić, M., Veljović, Đ., et al., 2018. The Removal of Zn2+, Pb2+, and As(Ⅴ) Ions by Lime Activated Fly Ash and Valorization of the Exhausted Adsorbent. Waste Management, 78: 366-378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.052 Liang, J., Li, X. M., Yu, Z. G., et al., 2017. Amorphous MnO2 Modified Biochar Derived from Aerobically Composted Swine Manure for Adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ) and Cd(Ⅱ). ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5(6): 5049-5058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00434 Lou, Z. M., Cao, Z., Xu, J., et al., 2017. Enhanced Removal of As(Ⅲ)/(Ⅴ) from Water by Simultaneously Supported and Stabilized Fe⁃Mn Binary Oxide Nanohybrids. Chemical Engineering Journal, 322: 710-721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.079 Manning, B. A., Fendorf, S. E., Bostick, B., et al., 2002. Arsenic(Ⅲ) Oxidation and Arsenic(Ⅴ) Adsorption Reactions on Synthetic Birnessite. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(5): 976-981. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0110170 Min, X. Z., Han, C. Y., Yang, L., et al., 2021. Enhancing As(Ⅴ) and As(Ⅲ) Adsorption Performance of Low Alumina Fly Ash with Ferric Citrate Modification: Role of FeSiO3 and Monosodium Citrate. Journal of Environmental Management, 287: 112302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112302 Pengthamkeerati, P., Satapanajaru, T., Chatsatapattayakul, N., et al., 2010. Alkaline Treatment of Biomass Fly Ash for Reactive Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution. Desalination, 261(1-2): 34-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.050 Qiu, R. F., Cheng, F. Q., Huang, H. M., 2018. Removal of Cd2+ from Aqueous Solution Using Hydrothermally Modified Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash Resulting from Coal Gangue Power Plant. Journal of Cleaner Production, 172: 1918-1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.236 Rathi, B. S., Kumar, P. S., 2021. A Review on Sources, Identification and Treatment Strategies for the Removal of Toxic Arsenic from Water System. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 418: 126299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126299 Rubinos, D. A., Iglesias, L., Díaz⁃Fierros, F., et al., 2011. Interacting Effect of pH, Phosphate and Time on the Release of Arsenic from Polluted River Sediments (Anllóns River, Spain). Aquatic Geochemistry, 17(3): 281-306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498⁃011⁃9135⁃2 Sağ, Y., Aktay, Y., 2002. Kinetic Studies on Sorption of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cu(Ⅱ) Ions by Chitin, Chitosan and Rhizopus Arrhizus. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 12(2): 143-153. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369⁃703X(02)00068⁃2 Salam, M. A., Al⁃Zhrani, G., Kosa, S. A., 2014. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Multi⁃Walled Carbon Nanotubes Modified with 8⁃Hydroxyquinoline: Kinetic Study. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(2): 572-580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.05.016 Shen, Q. B., Wang, Z. Y., Yu, Q., et al., 2020. Removal of Tetracycline from an Aqueous Solution Using Manganese Dioxide Modified Biochar Derived from Chinese Herbal Medicine Residues. Environmental Research, 183: 109195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109195 Shen, Z. L., Guo, H. M., Xu, G., et al., 2010. Abnormal Groundwater Chemistry and Endemic Disease. Chinese Journal of Nature, 32(2): 83-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). Su, Y., Cui, H., Li, Q., et al., 2013. Strong Adsorption of Phosphate by Amorphous Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles. Water Research, 47(14): 5018-5026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.044 Teng, H., Hsieh, C. T., 1999. Activation Energy for Oxygen Chemisorption on Carbon at Low Temperatures. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 38(1): 292-297. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie980107j Tiwari, M. K., Bajpai, S., Dewangan, U. K., et al., 2015. Suitability of Leaching Test Methods for Fly Ash and Slag: A Review. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 8(4): 523-537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.003 Tournassat, C., Charlet, L., Bosbach, D., et al., 2002. Arsenic(Ⅲ) Oxidation by Birnessite and Precipitation of Manganese(Ⅱ) Arsenate. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(3): 493-500. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0109500 Wang, Y. L., Liu, H. P., Wang, S. F., et al., 2020. Simultaneous Removal and Oxidation of Arsenic from Water by δ⁃MnO2 Modified Activated Carbon. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 94: 147-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.006 Wu, D. Y., Sui, Y. M., Chen, X. C., et al., 2008. Changes of Mineralogical⁃Chemical Composition, Cation Exchange Capacity, and Phosphate Immobilization Capacity during the Hydrothermal Conversion Process of Coal Fly Ash into Zeolite. Fuel, 87(10-11): 2194-2200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.10.028 Wu, K., Wang, M., Li, A. Z., et al., 2021. The Enhanced As(Ⅲ) Removal by Fe⁃Mn⁃Cu Ternary Oxide via Synergistic Oxidation: Performances and Mechanisms. Chemical Engineering Journal, 406: 126739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126739 Xie, X. J., Lu, C., Xu, R., et al., 2022. Arsenic Removal by Manganese⁃Doped Mesoporous Iron Oxides from Groundwater: Performance and Mechanism. Science of the Total Environment, 806: 150615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150615 Xiyili, H., Çetintaş, S., Bingöl, D., 2017. Removal of Some Heavy Metals onto Mechanically Activated Fly Ash: Modeling Approach for Optimization, Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 109: 288-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.012 Zhang, G. S., Qu, J. H., Liu, H. J., et al., 2007. Removal Mechanism of As(Ⅲ) by a Novel Fe⁃Mn Binary Oxide Adsorbent: Oxidation and Sorption. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(13): 4613-4619. https://doi.org/10.1021/es063010u Zhang, K. H., Zhang, D. X., Zhang, K., 2016. Arsenic Removal from Water Using a Novel Amorphous Adsorbent Developed from Coal Fly Ash. Water Science and Technology: A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 73(8): 1954-1962. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.028 Zhao, X., Zhao, H. H., Huang, X. R., et al., 2021. Effect and Mechanisms of Synthesis Conditions on the Cadmium Adsorption Capacity of Modified Fly Ash. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 223: 112550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112550 冯文丽, 吕学斌, 熊健, 等, 2021. 粉煤灰高附加值利用研究进展. 无机盐工业, 53(4): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJYG202104005.htm 姜龙, 2020. 燃煤电厂粉煤灰综合利用现状及发展建议. 洁净煤技术, 26(4): 31-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJMS202004004.htm 蒋丽, 谌建宇, 李小明, 等, 2011. 粉煤灰陶粒对废水中磷酸盐的吸附试验研究. 环境科学学报, 31(7): 1413-1420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201107011.htm 沈照理, 郭华明, 徐刚, 等, 2010. 地下水化学异常与地方病. 自然杂志, 32(2): 83-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ201002006.htm -









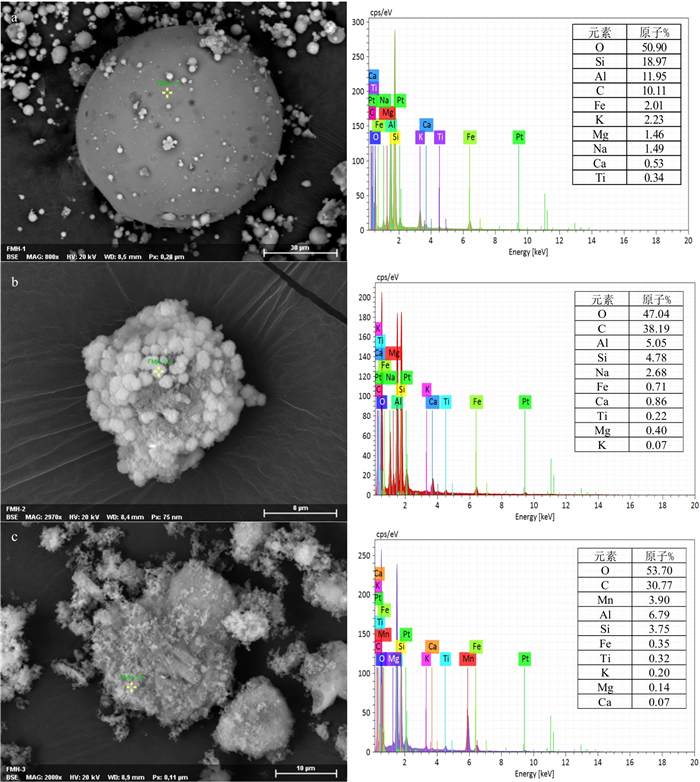
 下载:
下载: