Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Dissolved Carbon Export from an Alpine Catchment underlain by Seasonal Frost in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai-Xizang Plateau
-
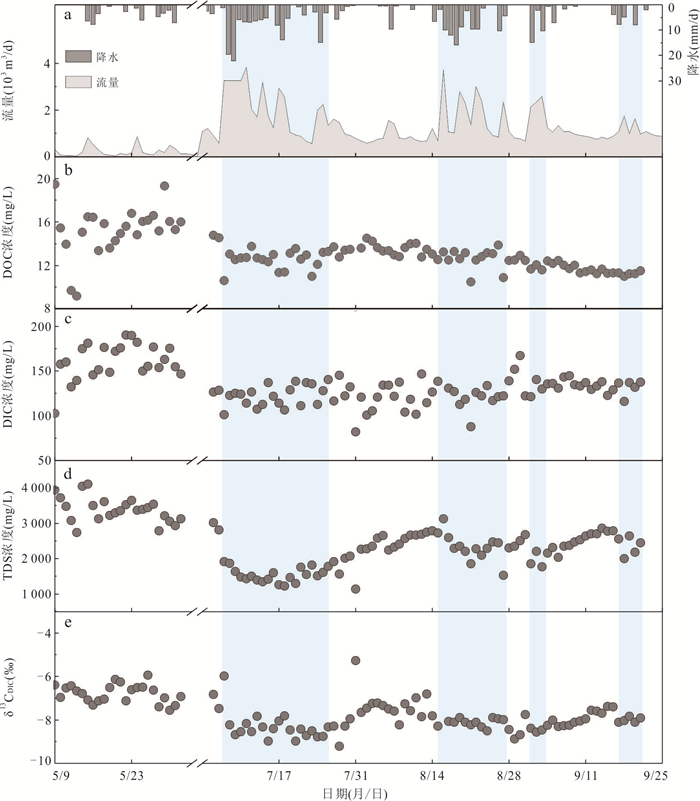
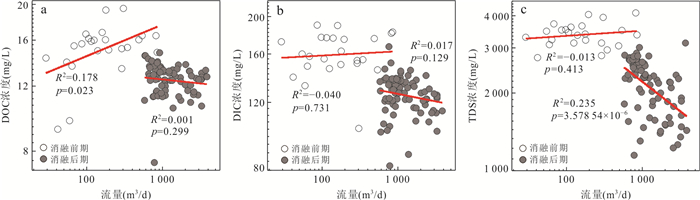
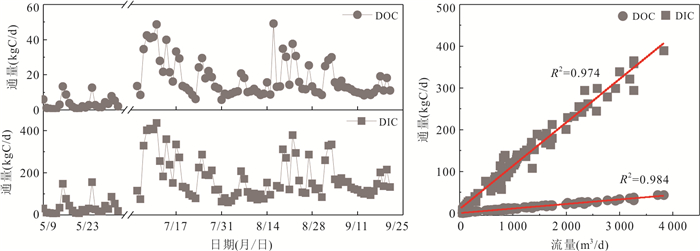
摘要: 高寒山区土壤碳是全球冻土碳库的重要组成部分,以溶解相从陆地侧向输出到河流是该地区土壤碳输出的重要途径,而以往研究主要集中在多年冻土区,对季节冻土区关注较少.为探讨季节冻土区河流溶解性碳的输出规律、影响因素及其作用机制,以位于青藏高原祁连山北麓黑河上游的季节冻土山区——红泥沟小流域为研究区,通过对河水中溶解性有机碳(DOC)和溶解性无机碳(DIC)浓度与通量的连续观测,结合河水中稳定同位素丰度及流域内气象、水文、地温等观测数据,发现在冻土消融前期(春末),流域出口河水中DOC和DIC浓度较高但通量较低;在冻土消融后期(夏季),河水中DOC和DIC浓度较低但通量较高;河水中DOC和DIC浓度在消融后期总体呈下降趋势,但低流量期的浓度比高流量期略有上升.研究表明:对以红泥沟小流域为代表的季节冻土山区,消融前期溶解性碳输出的主控因素仍是冻土特征及动态,但在消融后期则变为水文输入特征主控,以细粒残坡积物为主的薄层含水层和广泛发育的冻融扰动地貌也对其有重要影响,导致河流中DOC浓度高于青藏高原其他地区的报道值.Abstract: Soil carbon storage in alpine regions is an important component of the global frost carbon pool. Lateral carbon export from terrestrial ecosystems to rivers in dissolved phase is an important pathway for soil carbon export from alpine catchments. Previous studies on dissolved carbon export from alpine catchments have focused on permafrost areas, and less attention has been paid to seasonal frost areas. To explore the patterns, influencing factors and mechanisms of dissolved carbon export through rivers in seasonal frost areas, we selected the Hongnigou catchment at the northern flank of the Qilian Mountains on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau as the study area, and we made continuous observations of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) concentrations and fluxes in river water. Combining the observed data of stable isotope abundance in river water and meteorology, hydrology, and ground temperature in the catchment, it is found that: (1) during the early thawing period in late spring, the riverine DOC and DIC at the outlet of the catchment were high in concentration but low in flux; (2) during the late thawing period in summer, the riverine DOC and DIC were low in concentration but high in flux; and (3) both DOC and DIC concentrations in the river showed an overall decreasing trend in summer, but slightly increased during low flow periods compared to high flow periods. The study shows that for the alpine catchments underlaid by seasonal frost, represented by the Hongnigou catchment, the dissolved carbon export is mainly influenced by frost characteristics and dynamics during the early thawing period. However, during the late thawing period in summer, it becomes dominated by hydrological input characteristics. During this period, the thin aquifers consisting mainly of fine-grained residual deposits and the widespread freeze-thaw disturbed landforms also have significant impacts, resulting in a higher riverine DOC concentration than that reported in other areas of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau.
-
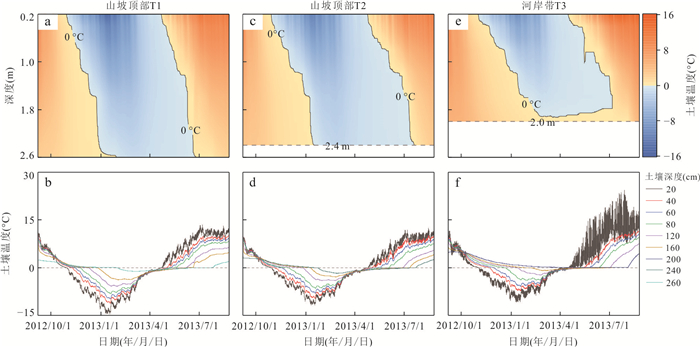
表 1 土壤温度监测剖面的位置及监测深度
Table 1. Location and monitoring depths of three soil temperature monitoring profiles
土壤温度监测剖面 海拔
(m)土壤温度监测深度
(cm)T1(山坡顶部) 3 172 20、40、60、80、120、160、260 T2(山坡中部) 3 159 20、40、60、80、120、160、240 T3(山坡底部河岸带) 3 144 20、40、60、80、120、160、200 表 2 红泥沟小流域出口河水水化学及溶解性碳输出的统计特征
Table 2. Statistical characteristics of stream water chemistry and dissolved carbon export at the outlet of the Hongnigou catchment
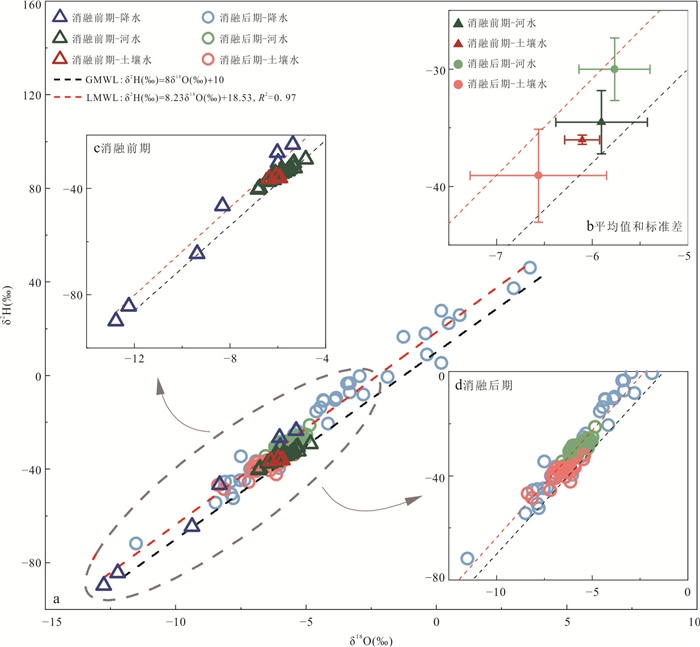
参数 单位 消融前期(2013年5月9日至6月1日) 消融后期(2013年7月5日至9月21日) 最小值 最大值 平均值±
标准差最小值 最大值 平均值±
标准差δ2H ‰ ‒40.45 ‒29.19 ‒34.53±2.71 ‒37.90 ‒21.25 ‒30.03±2.67 δ18O ‰ ‒6.81 ‒4.83 ‒5.90±0.48 ‒6.60 ‒4.85 ‒5.77±0.37 TDS mg/L 2 743.67 4 106.81 3 387.07±348.87 1 147.41 3 128.59 2 167.64±491.50 DOC mg/L 9.19 19.48 15.23±2.30 7.46 14.78 12.52±1.13 DOC
通量kgC/d 0.38 13.49 3.69±3.58 5.83 49.21 18.00±10.66 DIC mg/L 102.70 190.31 160.74±19.78 82.09 167.42 125.98±13.97 DIC
通量kgC/d 4.96 155.41 38.34±39.89 59.22 436.38 175.94±96.56 δ13CDIC ‰ ‒7.55 ‒5.94 ‒6.78±0.41 ‒9.22 ‒5.27 ‒8.00±0.63 -
Amankwah, S. K., Ireson, A. M., Maulé, C., et al., 2021. A Model for the Soil Freezing Characteristic Curve that Represents the Dominant Role of Salt Exclusion. Water Resources Research, 57(8): e2021WR030070. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR030070 An, Z. H., Sun, Z. Y., Hu, Y. L., et al., 2018. Export of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Streams Draining PermafrostDominated Areas: A Review. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(1): 204-211 (in Chinese with English abstract). Buffam, I., Laudon, H., Temnerud, J., et al., 2007. LandscapeScale Variability of Acidity and Dissolved Organic Carbon during Spring Flood in a Boreal Stream Network. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 112: G01022. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006jg000218 Chang, Q. X., Ma, R., Sun, Z. Y., et al., 2018. Using Isotopic and Geochemical Tracers to Determine the Contribution of GlacierSnow Meltwater to Streamflow in a Partly Glacierized AlpineGorge Catchment in Northeastern QinghaiTibet Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 123(18): 10037-10056. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jd028683 Chen, R., Liu, J., Kang, E., et al., 2015. Precipitation Measurement Intercomparison in the Qilian Mountains, NorthEastern Tibetan Plateau. The Cryosphere, 9(5): 1995-2008. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc919952015 Cheng, G. D., Jin, H. J., 2013. Groundwater in the Permafrost Regions on the QinghaiTibet Plateau and it Changes. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 40(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract). Dornblaser, M. M., Striegl, R. G., 2015. Switching Predominance of Organic Versus Inorganic Carbon Exports from an IntermediateSize Subarctic Watershed. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(2): 386-394. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014gl062349 Lloret, E., Dessert, C., Pastor, L., et al., 2013. Dynamic of Particulate and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Small Volcanic Mountainous Tropical Watersheds. Chemical Geology, 351: 229-244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.023 Evans, S. G., Ge, S. M., 2017. Contrasting Hydrogeologic Responses to Warming in Permafrost and Seasonally Frozen Ground Hillslopes. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(4): 1803-1813. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016gl072009 Gao, T. G., Kang, S. C., Chen, R. S., et al., 2019. Riverine Dissolved Organic Carbon and Its Optical Properties in a Permafrost Region of the Upper Heihe River Basin in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 686: 370-381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.478 Hirst, C., Mauclet, E., Monhonval, A., et al., 2022. Seasonal Changes in Hydrology and Permafrost Degradation Control Mineral ElementBound DOC Transport from Permafrost Soils to Streams. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 36(2): e2021GB007105. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GB007105 Ireson, A. M., van der Kamp, G., Ferguson, G., et al., 2013. Hydrogeological Processes in Seasonally Frozen Northern Latitudes: Understanding, Gaps and Challenges. Hydrogeology Journal, 21(1): 53-66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1004001209165 Jencso, K. G., McGlynn, B. L., Gooseff, M. N., et al., 2009. Hydrologic Connectivity between Landscapes and Streams: Transferring Reach and PlotScale Understanding to the Catchment Scale. Water Resources Research, 45(4): W04428. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008wr007225 Liu, Z. W., Chen, R. S., Song, Y. X., et al., 2012. Characteristics of Rainfall Interception for Four Typical Shrubs in Qilian Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(4): 333-342 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mao, N., Liu, G. M., Li, L. S., et al., 2022. Methane Fluxes and Their Relationships with MethaneRelated Microbes in Permafrost Regions of the Qilian Mountains. Earth Science, 47(2): 556-567 (in Chinese with English abstract). McGuire, A. D., Anderson, L. G., Christensen, T. R., et al., 2009. Sensitivity of the Carbon Cycle in the Arctic to Climate Change. Ecological Monographs, 79(4): 523-555. https://doi.org/10.1890/082025.1 Mu, C. C., Zhang, T. J., Cao, B., et al., 2013. Study of the Organic Carbon Storage in the Active Layer of Permafrost over the Eboling Mountain in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River in the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 35(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mu, C., Zhang, T., Wu, Q., et al., 2015. Editorial: Organic Carbon Pools in Permafrost Regions on the QinghaiXizang (Tibetan) Plateau. The Cryosphere, 9(2): 479-486. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc94792015 Mu, C. C., Abbott, B. W., Wu, X. D., et al., 2017. Thaw Depth Determines Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentration and Biodegradability on the Northern QinghaiTibetan Plateau. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(18): 9389-9399. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017gl075067 Pan, Z., Sun, Z. Y., Ma, R., et al., 2018. Isotopic Investigation of RainfallRunoff Generation in an Alpine Catchment in Headwater Regions of Heihe River, Northeast QinghaiTibet Plateau. Earth Science, 43(11): 4226-4236 (in Chinese with English abstract). Plaza, C., Pegoraro, E., Bracho, R., et al., 2019. Direct Observation of Permafrost Degradation and Rapid Soil Carbon Loss in Tundra. Nature Geoscience, 12(8): 627-631. https://doi.org/10.1038/s4156101903876 Prokushkin, A. S., Pokrovsky, O. S., Shirokova, L. S., et al., 2011. Sources and the Flux Pattern of Dissolved Carbon in Rivers of the Yenisey Basin Draining the Central Siberian Plateau. Environmental Research Letters, 6(4): 045212. https://doi.org/10.1088/17489326/6/4/045212 Song, C. L., Wang, G. X., Mao, T. X., et al., 2019. Importance of Active Layer FreezeThaw Cycles on the Riverine Dissolved Carbon Export on the QinghaiTibet Plateau Permafrost Region. PeerJ, 7: e7146. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7146 Stein, R., MacDonald, R., 2004. The Organic Carbon Cycle in the Arctic Ocean. SpringerVerlag, Berlin. Striegl, R. G., Aiken, G. R., Dornblaser, M. M., et al., 2005. A Decrease in DischargeNormalized DOC Export by the Yukon River during Summer through Autumn. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(21): L21413. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gl024413 Walvoord, M. A., Voss, C. I., Wellman, T. P., 2012. Influence of Permafrost Distribution on Groundwater Flow in the Context of ClimateDriven Permafrost Thaw: Example from Yukon Flats Basin, Alaska, United States. Water Resources Research, 48(7): W07524. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011wr011595 Wan, H. L., Bian, J. M., Zhang, H., et al., 2021. Assessment of Future Climate Change Impacts on WaterHeatSalt Migration in Unsaturated Frozen Soil Using CoupModel. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 15(1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1178302013025 Wang, D., Wu, T. H., Zhao, L., et al., 2021a. A 1 km Resolution Soil Organic Carbon Dataset for Frozen Ground in the Third Pole. Earth System Science Data, 13(7): 3453-3465. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd1334532021 Wang, S., Sun, Z. Y., Hu, Y. L., et al., 2017. IntraAnnual Variation of Dissolved Organic Carbon Export through Stream from an Typical Alpine Catchment in QinghaiTibet Plateau: Patterns and Hydrological Controls. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 24(2): 1-7, 15 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, X., Liu, T., Wang, L., et al., 2021b. SpatialTemporal Variations in Riverine Carbon Strongly Influenced by Local Hydrological Events in an Alpine Catchment. Biogeosciences, 18(10): 3015-3028. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg1830152021 Wild, B., Andersson, A., Bröder, L., et al., 2019. Rivers across the Siberian Arctic Unearth the Patterns of Carbon Release from Thawing Permafrost. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(21): 10280-10285. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1811797116 Woo, M. K., Kane, D. L., Carey, S. K., et al., 2008. Progress in Permafrost Hydrology in the New Millennium. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 19(2): 237-254. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.613 You, X. N., Li, X. Y., 2021. Seasonal Variations in Dissolved Organic Carbon in the Source Region of the Yellow River on the Tibetan Plateau. Water, 13(20): 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202901 Zhang, D. F., Zheng, Q. H., Dong, Z. Y., 2005. Mechanism of Soil SaltMoisture Transfer under Freeze Thawing Condition. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(6): 14-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, F., Jin, Z. D., Li, F. C., et al., 2013. Controls on Seasonal Variations of Silicate Weathering and CO2 Consumption in Two River Catchments on the NE Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 62: 547-560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.004 Zhang, S. X., Sun, Z. Y., Pan, Y. X., et al., 2023. Using Temperature to Trace RiverGroundwater Interactions in Alpine Regions: A Case Study in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 42(4): 95-106 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, T., Barry, R. G., Knowles, K., et al., 2003. Distribution of Seasonally and Perennially Frozen Ground in the Northern Hemisphere. In: Guglielmin, M., Balks, M., Paetzold, R., eds., Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Permafrost. A.A. Balkema Publishers, Amsterdam. Zou, D. F., Zhao, L., Sheng, Y., et al., 2017. A New Map of Permafrost Distribution on the Tibetan Plateau. The Cryosphere, 11(6): 2527-2542. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc1125272017 安志宏, 孙自永, 胡雅璐, 等, 2018. 多年冻土区河流溶解性有机碳输出的研究进展. 地质科技情报, 37(1): 204-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201801028.htm 程国栋, 金会军, 2013. 青藏高原多年冻土区地下水及其变化. 水文地质工程地质, 40(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201301007.htm 刘章文, 陈仁升, 宋耀选, 等, 2012. 祁连山典型灌丛降雨截留特征. 生态学报, 32(4): 333-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201204036.htm 毛楠, 刘桂民, 李莉莎, 等, 2022. 祁连山多年冻土区甲烷通量与甲烷微生物群落组成的关系. 地球科学, 47(2): 556-567. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.037 牟翠翠, 张廷军, 曹斌, 等, 2013. 祁连山区黑河上游俄博岭多年冻土区活动层碳储量研究. 冰川冻土, 35(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201301002.htm 潘钊, 孙自永, 马瑞, 等, 2018. 黑河上游高寒山区降雨‒径流形成过程的同位素示踪. 地球科学, 43(11): 4226-4236. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.552 王烁, 孙自永, 胡雅璐, 等, 2017. 高寒山区典型小流域河流溶解性有机碳输出的年内变化及其成因. 安全与环境工程, 24(2): 1-7, 15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201702001.htm 张殿发, 郑琦宏, 董志颖, 2005. 冻融条件下土壤中水盐运移机理探讨. 水土保持通报, 25(6): 14-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB200506004.htm 张淑勋, 孙自永, 潘艳喜, 等, 2023. 基于温度示踪的高寒地区河水与地下水相互作用: 以黑河上游流域为例. 地质科技通报, 42(4): 95-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202304010.htm -










 下载:
下载: