Constrained Inversion of Audio Magnetotelluric for Identifying Strata: A Case Study in Hami Basin
-
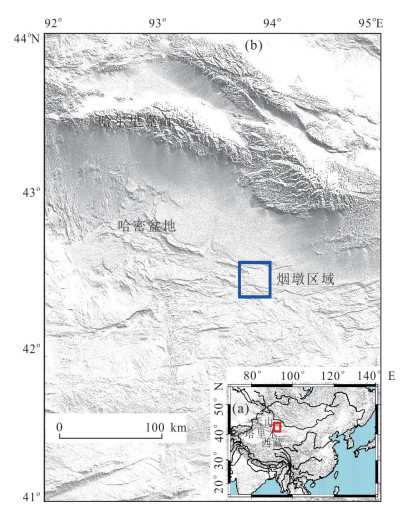
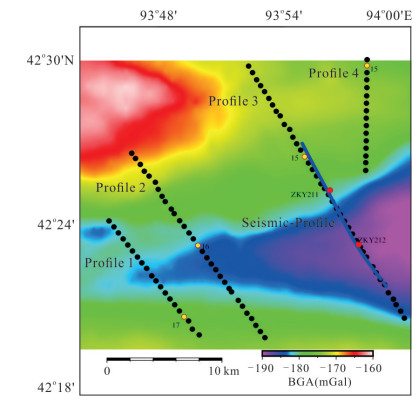
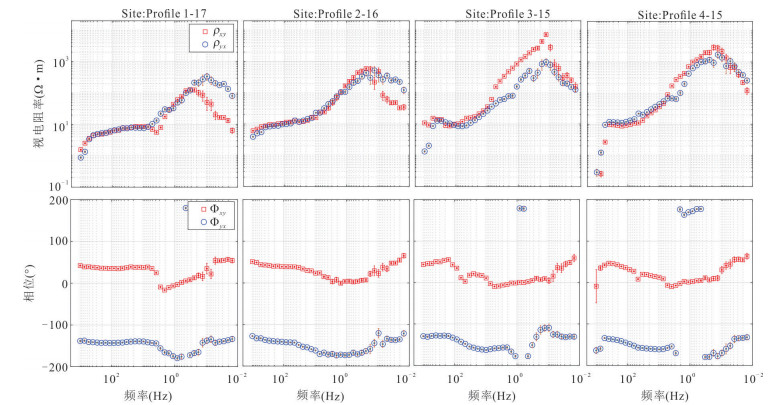
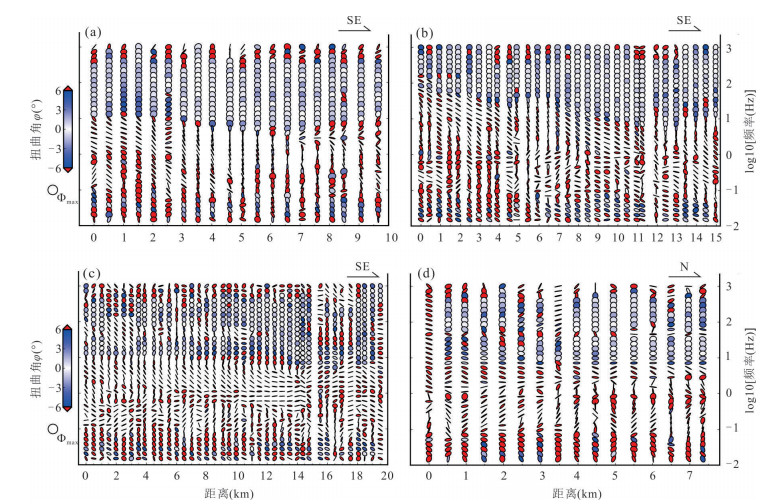
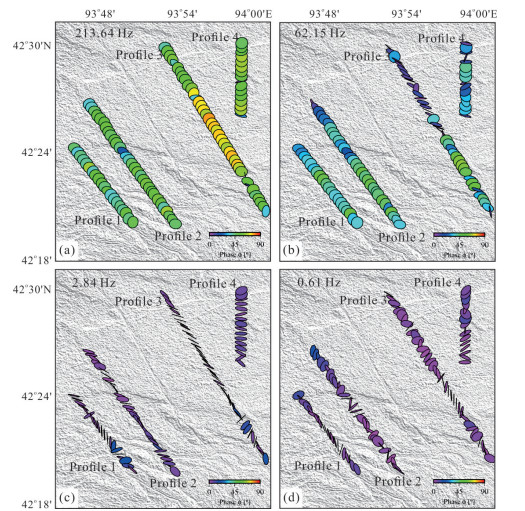
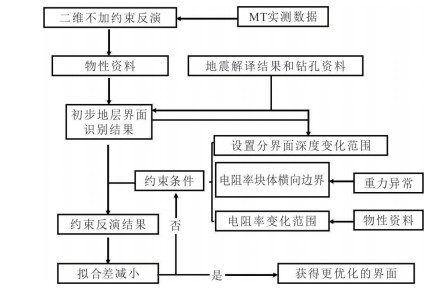
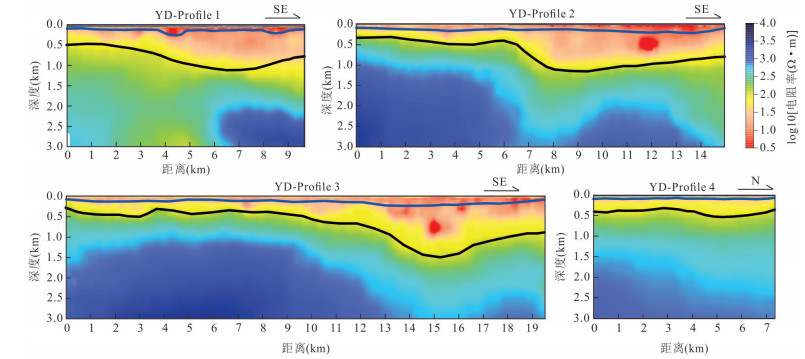
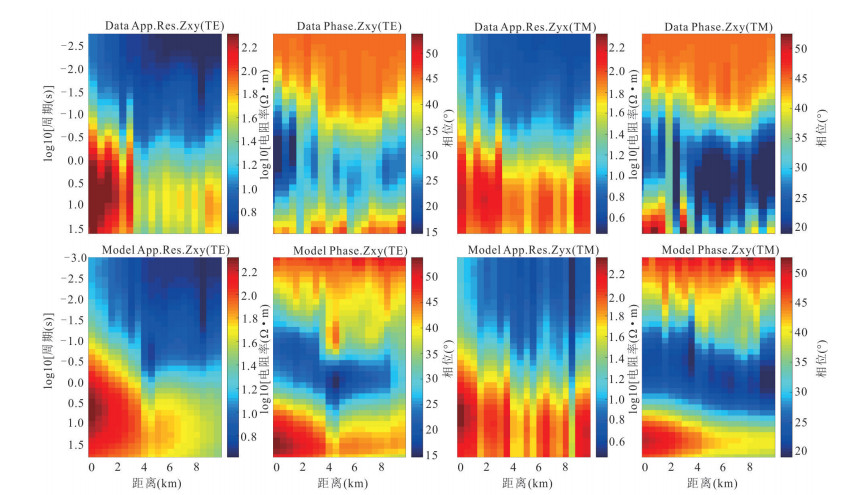
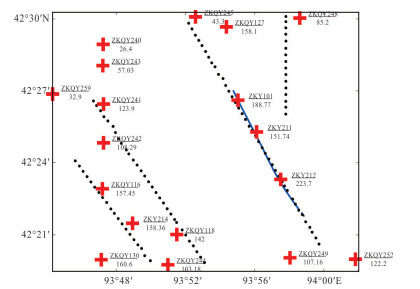
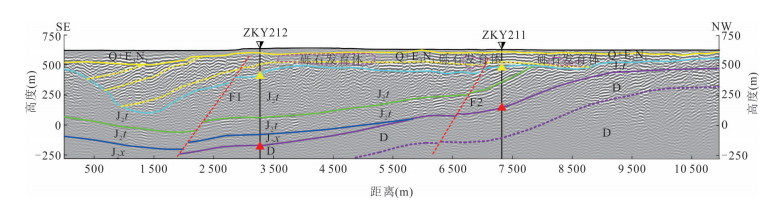
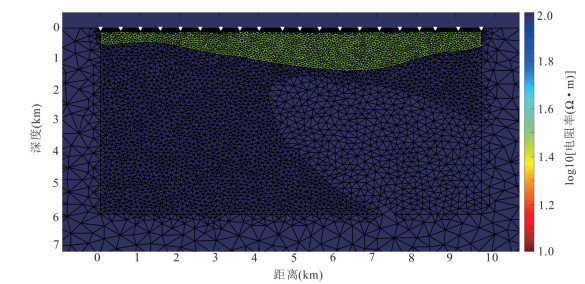
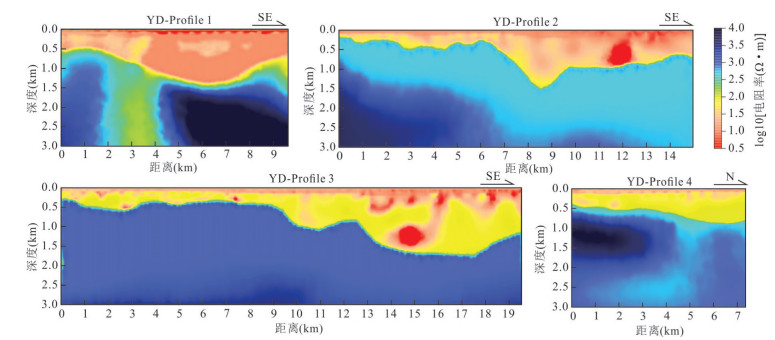
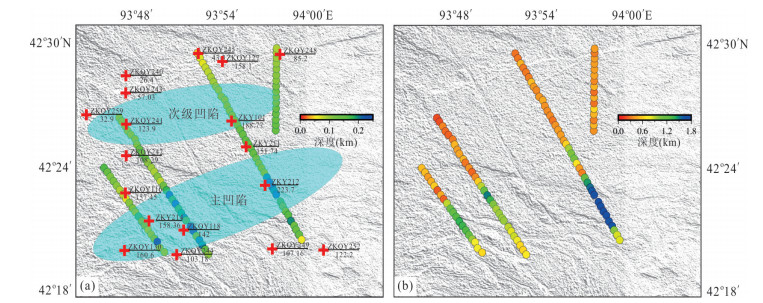
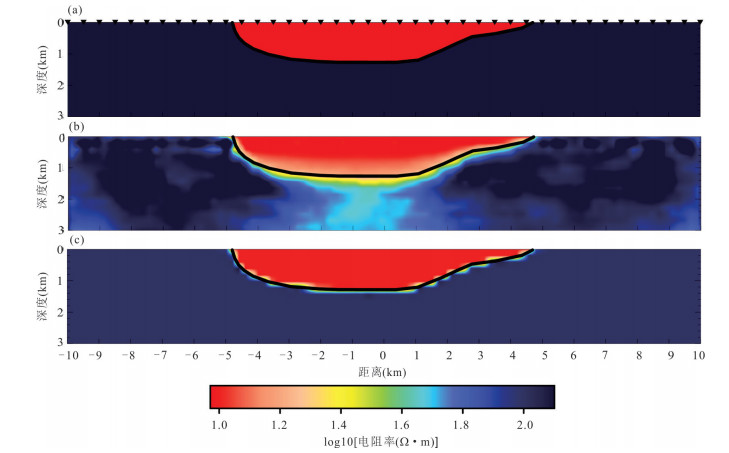
摘要: 覆盖区地质填图是新时期地质填图的重要方向.音频大地电磁法(AMT)是覆盖区地质填图的重要地球物理方法之一,可以为地层和基岩面的刻画提供电性参数的约束.然而,常规的AMT反演无法精确刻画电性异常体的边界,且当缺乏其他地质与地球物理资料约束时,难以进行地质解译.针对此问题,基于数值模拟结果的可行性,利用哈密烟墩戈壁覆盖区的4条实测AMT剖面探讨了AMT约束反演在地层识别中的应用效果.相位张量分析指示研究区浅部(> 1 Hz)电性结构表现为二维特征,深部受三维结构影响;浅部为低阻,深部电阻率逐渐升高.采用不加约束二维反演获得了4条剖面的地下(< 3 km)电性结构.基于研究区的重力异常、地震解译结果、物性和钻孔资料,在二维反演结果上初步划分了渐新统-中新统和侏罗系地层的底界面;进而以这两个界面建立先验模型,并根据物性资料设置电阻率变化范围,进行AMT约束反演,获得了更优化的反演结果以及清晰可靠的渐新统-中新统和侏罗系的底界面.结果显示,研究区渐新统-中新统地层电阻率值略小于10 Ω•m,其底界面平均埋深为120 m;侏罗系电阻率值为10~100Ω•m,其底界面最深可达2 km.基岩面(侏罗系底界面)埋深整体上呈现为东南深、西北浅,这指示哈密烟墩地区中生代以来的沉积中心在东南部;此外,侏罗系地层与下伏的古生界地层存在角度不整合.研究表明,哈密烟墩地区新生代以来可能受到了近南北向应力挤压,在研究区中部形成近东西或北东东向的侏罗系隆凹相间的构造地貌格局.而渐新统-中新统地层底部的不整合面可能反映了后期褶皱构造的影响,这种隆凹作用相伴的褶皱构造可能具有同沉积性质.Abstract: Geological mapping on covered area is a crucial research of new geological mapping. Audio magnetotelluric (AMT) is one of effective geophysical methods for geological mapping on covered area, which can provide the constraint of electrical parameters for depicting strata and bedrocks. However, conventional AMT inversion cannot accurately describe the boundaries of electrical anomalies, and it is difficult to perform geological interpretation when there is no other geological and geophysical data constraints. Based on the feasibility of numerical simulation results and four AMT profiles in the Gobi desert area of Hami Yandun, it tries to investigate the availability of constrained AMT inversion in strata identification. Phase tensor analyses indicate that the shallow (< 1 Hz) electrical structure is mainly two-dimensional (2D), while the deep is affected by 3D structure. The resistivity is low in the shallow and gradually increases in the deep. The underground electrical structures of four profiles were obtained by 2D unconstrained inversion. Based on gravity anomalies, seismic interpretation results, physical properties of rocks and borehole data in the research area, the bottom interfaces of Oligocene-Miocene and Jurassic strata were preliminarily divided from the 2D inversion results. Furthermore, a prior model was established using the two interfaces, where the resistivity change ranges were set according to physical property data. Then, constrained AMT inversion was carried out. The better inversion results and the clear and reliable bottom interfaces of Oligocene-Miocene and Jurassic were obtained. Research results show that the resistivity of Oligocene-Miocene stratum is slightly smaller than 10 Ω•m and the bottom interface is shallow with an average depth of 120 m. The resistivity of Jurassic stratum is about 10-100 Ω•m and the bottom interface is deep up to 2 km. The buried depth of bedrock surface (Jurassic bottom interface) is deep in the southeast but shallow in the northwest, which indicates that the sedimentary center since Mesozoic is in the southeast of Hami Yandun area. Moreover, an angular unconformity exists between Jurassic and underlying Paleozoic strata. The study supports that Hami Yandun area may go through the extrusion from nearly NS compression stress since Cenozoic, resulting in the morphotectonic pattern of Jurassic uplift and depression with nearly EW or NEE direction in the central part. Besides, the angular unconformity beneath the Oligocene-Miocene strata may reflect the influence of later fold structure. This kind of fold structure along with uplift and depression might have the synsedimentary property.
-
表 1 烟墩地区岩石电阻率按地层划分的统计结果
Table 1. Statistic results of rock resistivity by stratification in Yandun area
系/统 地层代号 岩性 电阻率统计级别 渐新统‒中新统 E3N1 泥质砂岩 低阻(< 20 Ω•m) 侏罗系 J 砂岩 中阻(> 100 Ω•m) 泥盆系 D 闪长玢岩/花岗岩 高阻(> 1 000 Ω•m) -
Booker, J.R., 2014. The Magnetotelluric Phase Tensor: A Critical Review. Surveys in Geophysics, 35(1): 7-40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-013-9234-2 Caldwell, T.G., Bibby, H.M., Brown, C., 2004. The Magnetotelluric Phase Tensor. Geophysical Journal International, 158(2): 457-469. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.2004.02281.x Cao, R., Muhetaer, Z., Wang, D.K., et al., 2016. Structural Characteristics and Plate Boundary Properties of the Kangguertage Fault Zone in Jueluotage Orogenic Belt, Eastern Tianshan. Northwestern Geology, 49(3): 28-38 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.03.003 Charvet, J., Shu, L.S., Laurent-Charvet, S., et al., 2011. Palaeozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Tianshan Belt, NW China. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(2): 166-184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-4138-1 Chen, C., Xu, S.F., Wang, G.C., et al., 2021. Comprehensive Geophysical Survey and Practice in Geological Investigation of Gobi Desert Covered Area. Earth Science, 46(8): 3028-3038 (in Chinese with English abstract). De Groot-Hedlin, C., Constable, S., 2004. Inversion of Magnetotelluric Data for 2D Structure with Sharp Resistivity-Contrast. Geophysics, 69(1): 78-86. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1649377 Egbert, G.D., Booker, J.R., 1986. Robust Estimation of Geomagnetic Transfer Functions. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 87(1): 173-194. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1986.tb04552.x Gamble, T.D., Goubau, W.M., Clarke, J., 1979. Magnetotellurics with a Remote Magnetic Reference. Geophysics, 44(1): 53-68. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1440923 Garcia, X., Jones, A.G., 2002. Atmospheric Sources for Audio-Magnetotelluric (AMT) Sounding. Geophysics, 67(2): 448-458. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1468604 Han, B.F., Ji, J.Q., Song, B., et al., 2006. Late Paleozoic Vertical Growth of Continental Crust around the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China(PartⅠ): Timing of Post-Collisional Plutonism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1077-1086 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hetzel, R., Tao, M.X., Stokes, S., et al., 2004. Late Pleistocene/Holocene Slip Rate of the Zhangye Thrust (Qilian Shan, China) and Implications for the Active Growth of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 23(6): TC6006. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004tc001653 Jegen, M.D., Hobbs, R.W., Tarits, P., et al., 2009. Joint Inversion of Marine Magnetotelluric and Gravity Data Incorporating Seismic Constraints: Preliminary Results of Sub-Basalt Imaging off the Faroe Shelf. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 282(1-4): 47-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.02.018 Key, K., 2016. MARE2DEM: A 2-D Inversion Code for Controlled-Source Electromagnetic and Magnetotelluric Data. Geophysical Journal International, 207(1): 571-588. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw290 Kim, H.J., Song, Y., Lee, K.H., 1999. Inequality Constraint in Least-Squares Inversion of Geophysical Data. Earth, Planets and Space, 51(4): 255-259. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352229 Li, W.Q., 2005. Research on Ancient Arc-Basain System of Kangguertage in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang(Dissertation). Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y., Hu, D.G., Xu, S.F., et al., 2020. Electrical Anisotropic Structure in the Quaternary Volcanic Region of North Hainan Island and Its Geological Implications. Earth Science, 45(1): 330-340 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/332316432_Electrical_Anisotropic_Structure_in_the_Quaternary_Volcanic_Region_of_North_Hainan_Island_and_Its_Geological_Implication Liu, Y., Liu, J.P., Chen, C., et al., 2020. The Application of Audio Magnetotelluric for 3D Geological Mapping in the Gobi Desert Area. Geological Journal, 55(11): 7335-7345. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3627 Musil, M., Maurer, H.R., Green, A.G., 2003. Discrete Tomography and Joint Inversion for Loosely Connected or Unconnected Physical Properties: Application to Crosshole Seismic and Georadar Data Sets. Geophysical Journal International, 153(2): 389-402. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01887.x Portniaguine, O., Zhdanov, M.S., 1999. Focusing Geophysical Inversion Images. Geophysics, 64(3): 874-887. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444596 Sternberg, T., Paillou, P., 2015. Mapping Potential Shallow Groundwater in the Gobi Desert Using Remote Sensing: Lake Ulaan Nuur. Journal of Arid Environments, 118: 21-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2015.02.020 Tao, M.X., 2010. The Two Kinds of Tectonic Unit Systems in Turpan-Hami Basin, Xinjiang, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(S1): 297-304 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, G.C., Shen, T.Y., Chen, C., et al., 2020. Basin-Range Coupling and Tectonic Topography Analysis during Geological Mapping on Covered Area: A Case Study of Turpan-Hami Basin, Eastern Tianshan. Earth Science, 45(12): 4313-4331 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, G.C., Xu, Y, X., Chen, X, J., et al., 2015. Three-Dimensional Geological Mapping and Visualization of Complex Orogenic Belts. Earth Science, 40(3): 397-406 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiao, F., Wang, Z.H., 2017. Geological Interpretation of Bouguer Gravity and Aeromagnetic Data from the Gobi-Desert Covered Area, Eastern Tianshan, China: Implications for Porphyry Cu-Mo Polymetallic Deposits Exploration. Ore Geology Reviews, 80: 1042-1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.08.034 Xiao, M., Wu, S.T., Yuan, X.J., et al., 2021. Conglomerate Reservoir Pore Evolution Characteristics and Favorable Area Prediction: A Case Study of the Lower Triassic Baikouquan Formation in the Northwest Margin of the Junggar Basin, China. Journal of Earth Science, 32(4): 998-1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1083-6 Yang, Z., Gulibahaer, A., Muhetaer, Z., et al., 2015. Geochemistry Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of the Igneous Rocks from the Eastern Tianshan Mountains. Northwestern Geology, 48(2): 104-111 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.02.010 Yu, J.J., Wang, G.C., Xu, Y.X., et al., 2015. Constraining Deep Geological Structures in Three-Dimensional Geological Mapping of Complicated Orogenic Belts: A Case Study from Karamay Region, Western Junggar. Earth Science, 40(3): 407-418, 424 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, D.L., Xu, Z.H., Niu, X.J., 2006. Using 3D Seismic Prospecting to Find out Complicated Structures in Gobi and Desert Areas. Coal Geology of China, 184): 59-61(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, S.J., Huang, Q.H., 2018. Two-Dimensional Sharp Boundary Magnetotelluric Inversion Using Bayesian Theory. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(8): 3420-3434 (in Chinese with English abstract). 曹锐, 木合塔尔·扎日, 王敦科, 等, 2016. 东天山觉罗塔格造山带康古尔塔格断裂带构造特征及边界属性研究. 西北地质, 49(3): 28-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.03.003 陈超, 许顺芳, 王国灿, 等, 2021. 戈壁荒漠覆盖区地质调查中综合地球物理方法与实践. 地球科学, 46(8): 3028-3038. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.386 韩宝福, 季建清, 宋彪, 等, 2006. 新疆准噶尔晚古生代陆壳垂向生长(Ⅰ): 后碰撞深成岩浆活动的时限. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1077-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605003.htm 李文铅, 2005. 新疆东天山康古尔塔格地区古弧-盆系统研究(博士学位论文). 广州: 中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所). 刘营, 胡道功, 许顺芳, 等, 2020. 琼北第四纪火山区电各向异性结构及其地质意义. 地球科学, 45(1): 330-340. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.336 陶明信, 2010. 论新疆吐哈盆地的两种构造单元体系. 地质通报, 29(增刊1): 297-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2010Z1015.htm 王国灿, 申添毅, 陈超, 等, 2020. 覆盖区地质调查中的盆山构造地貌关系研究: 以东天山-吐哈盆地为例. 地球科学, 45(12): 4313-4331. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.300 王国灿, 徐义贤, 陈旭军, 等, 2015. 基于地表地质调查剖面网络基础上的复杂造山带三维地质调查与建模方法. 地球科学, 40(3): 397-406. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.031 杨震, 古力巴哈尔·阿布都热西提, 木合塔尔·扎日, 等, 2015. 东天山觉罗塔格一带晚古生代岩浆岩地球化学特征及构造意义. 西北地质, 48(2): 104-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201502010.htm 郁军建, 王国灿, 徐义贤, 等, 2015. 复杂造山带地区三维地质填图中深部地质结构的约束方法: 西准噶尔克拉玛依后山地区三维地质填图实践. 地球科学, 40(3): 407-418, 424. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.032 张灯亮, 徐忠华, 牛小军, 2006. 利用三维地震在戈壁沙漠区解决复杂地质构造问题. 中国煤田地质, 18(4): 59-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200604021.htm 周思杰, 黄清华, 2018. 基于贝叶斯方法的二维大地电磁尖锐边界反演研究. 地球物理学报, 61(8): 3420-3434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201808027.htm -









 下载:
下载: