Hydrochemical Characteristics Constraints on Evolution of Geothermal Water in Guantang Area on the East Coast of Hainan Island
-
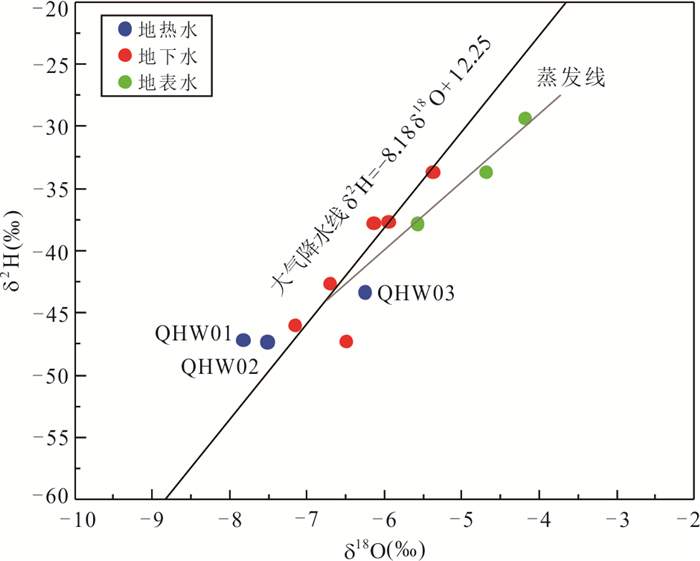
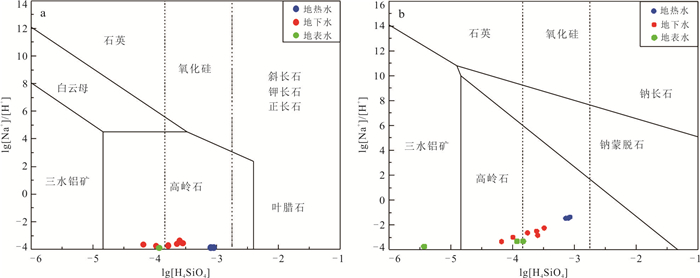
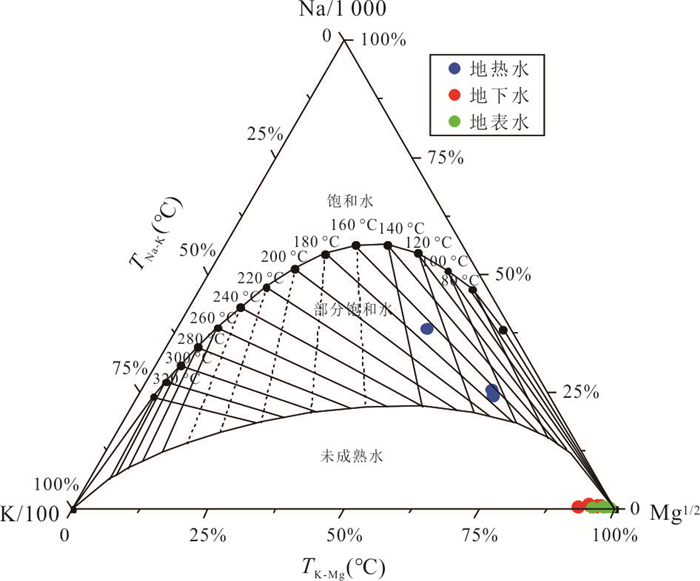
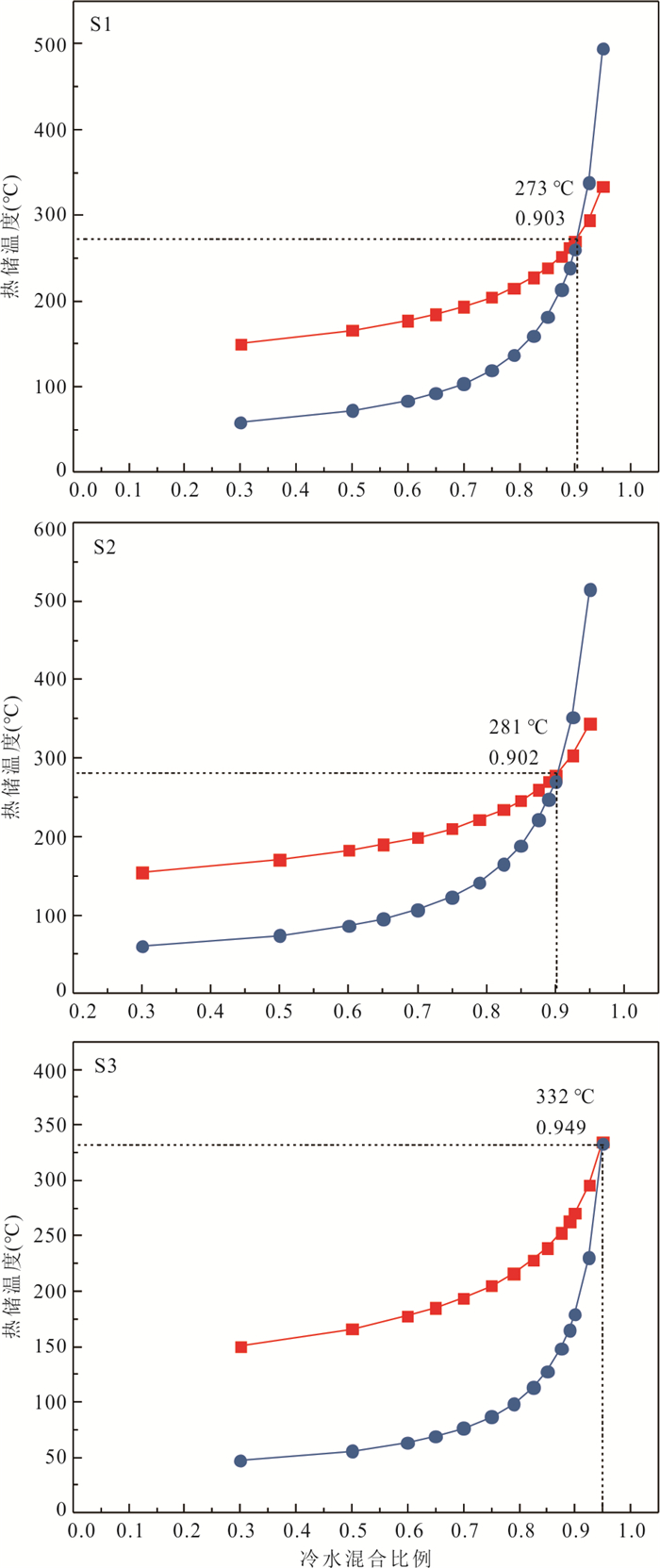
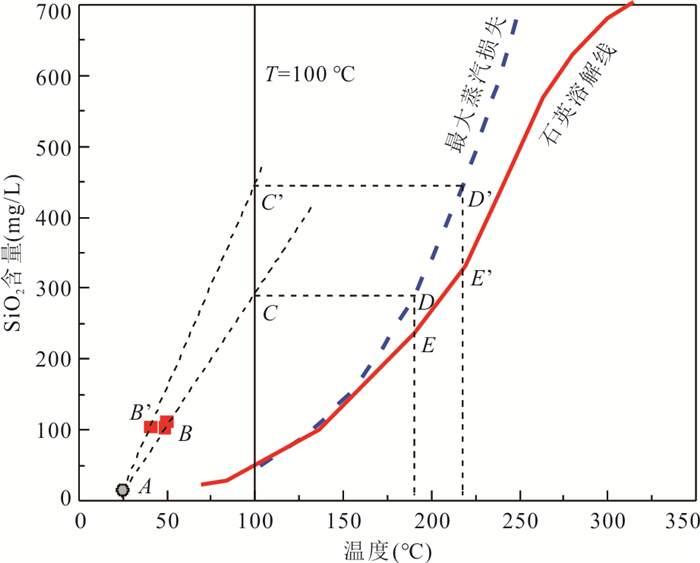
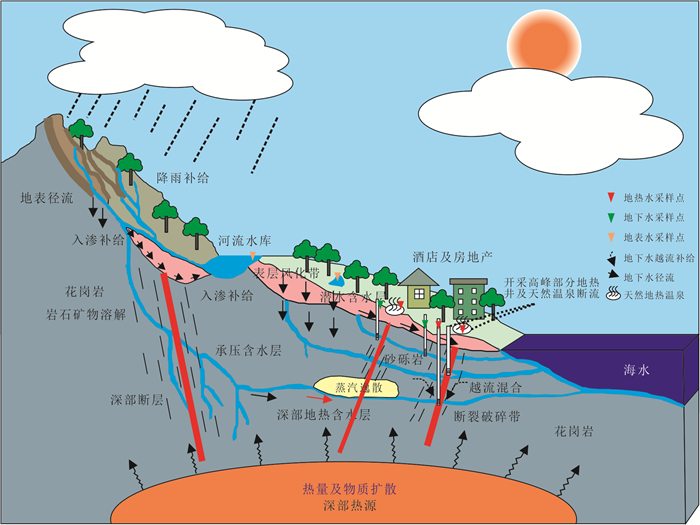
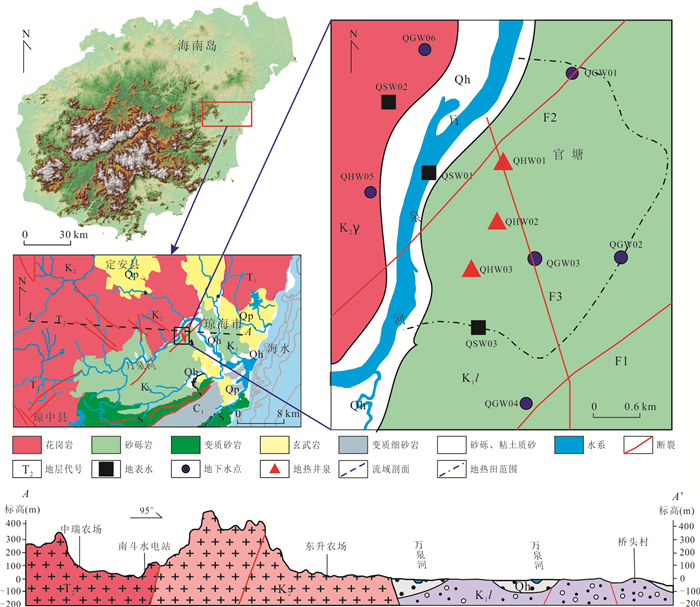
摘要: 地热水资源的形成与演化过程认识是区域地热资源科学合理开发利用的重要基础.运用水化学及同位素分析方法,结合区域地质构造特征,系统揭示了海南东海岸官塘地区地热水水化学特征、地热储温度以及补给来源,构建了官塘地区地热水循环演化概念模型.研究结果表明:该区地热水水化学类型主要为HCO3·SO4-Na型,其组分主要来源于硅酸盐矿物溶解及深部CO2等气体;地热水主要受到大气降水补给,补给海拔约为1 122.2~1 569.4 m,并且地热水上升过程中与浅部地下水之间存在较为显著的混合作用.在考虑混合和蒸汽损失的条件下,深部地热水与冷水混合前蒸汽损失的质量百分比约为18.2%~25.2%,地热水温度为190.4~217.8 ℃,冷水混合比例可达到66.8%~80.8%.该地区地热水开发程度逐年提高,导致地热水水位大幅下降,使得浅部冷水补给量增大,这可能是造成该地区开采地热水温度下降的关键影响因素.Abstract: The understanding of the formation and evolution of geothermal water is an important basis for the scientific and rational utilization of regional geothermal resources. In this paper, the hydrochemical characteristics, geothermal storage temperature and recharge source of geothermal water in Guantang area on the east coast of Hainan were systematically revealed by using hydrochemical and isotopic analysis methods combined with regional geological structure characteristics, and a conceptual model of geothermal water cycle evolution in Guantang area was constructed. The results show that the hydrochemistry of geothermal water was mainly HCO3·SO4-Na type, and its components mainly came from silicate mineral dissolution and deep gas components. Geothermal water was mainly originated from meteoric precipitation, and the recharge area was most likely located at the altitude of 1 122.2-1 569.4 m. There was a significant mixing effect between geothermal water and shallow groundwater. Under the condition of steam loss before mixing, the mass percentage of steam loss from geothermal water was 18.2%-25.2%, and the initial temperature of geothermal water was 190.4-217.8 ℃, and the mass percentage of cold water mixing to geothermal water was 66.8%-80.8%. The geothermal water level decreased greatly with the increasing geothermal water exploration in this area in recent decades, so the increase of shallow groundwater supply may be the crucial process resulting in the decrease of geothermal water temperature in this area.
-
表 1 官塘地区地热水、地下水及地表水水化学及同位素组成
Table 1. Hydrochemistry and isotopic composition of geothermal water, groundwater, and surface water in Guantang area
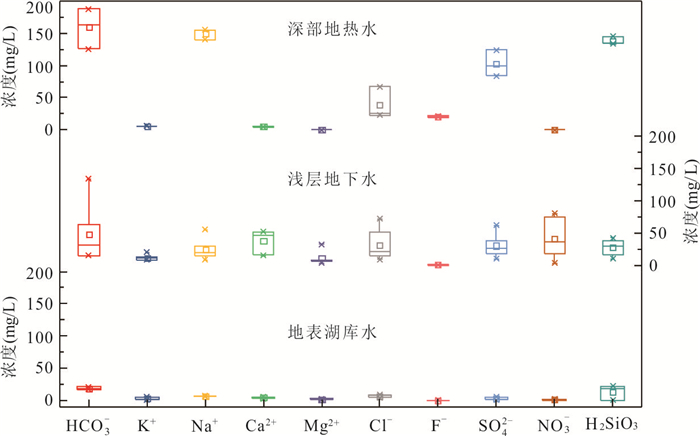
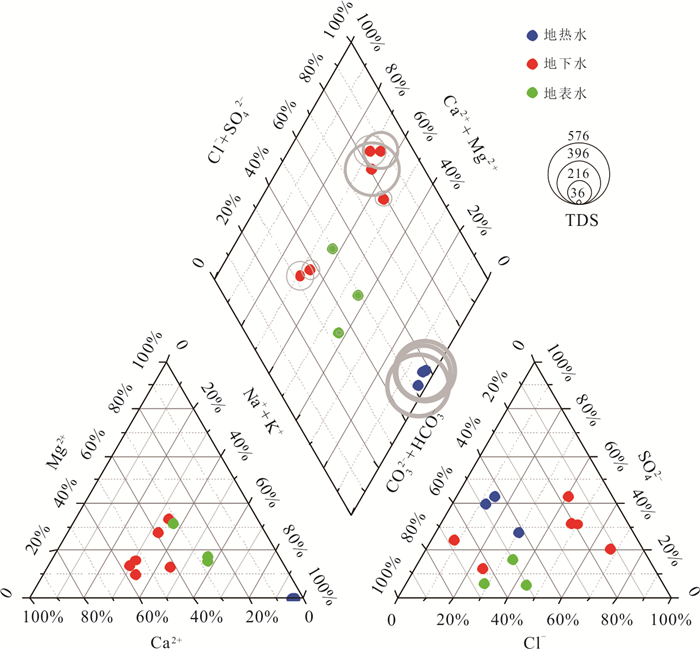
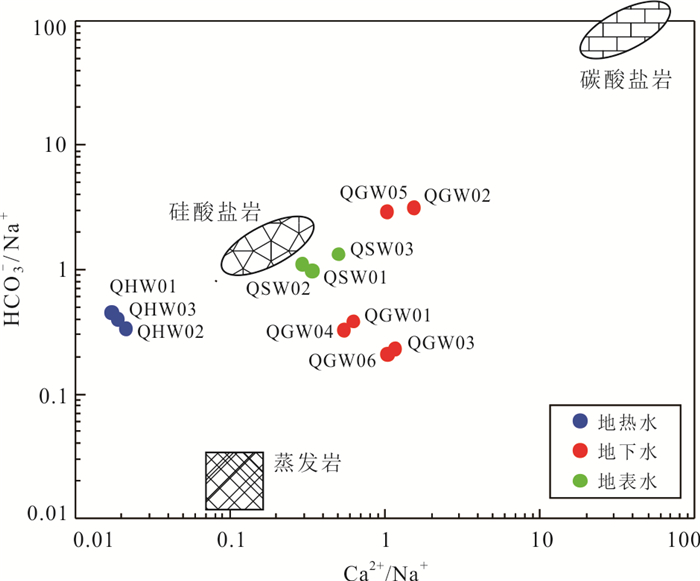
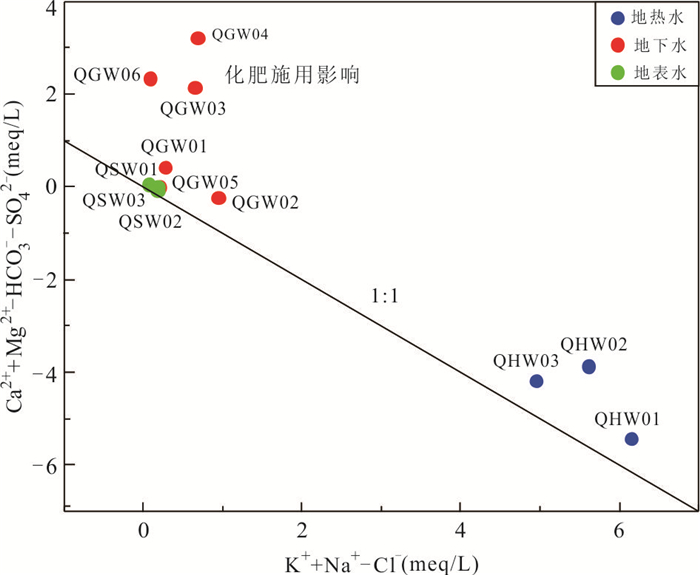
编号 样号 类型 温度(℃) pH TDS HCO3‒ K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl‒ F‒ SO42‒ NO3‒ H2SiO3 δ18O δ2H 水化学类型 (mg/L) (‰) 1 QHW01 地热水 48.5 8.4 585.0 188.0 6.2 155.0 4.6 0.0 26.6 22.2 124.0 0.1 134.0 ‒7.8 ‒47.1 HCO3·SO4‒Na 2 QHW02 49.5 8.3 517.9 126.0 5.9 140.0 5.1 0.1 22.4 19.3 99.3 0.2 145.0 ‒7.5 ‒47.3 HCO3·SO4‒Na 3 QHW03 40.4 8.6 571.3 164.0 6.0 154.0 5.0 0.2 67.5 20.7 84.0 0.2 135.0 ‒6.3 ‒43.3 HCO3·SO4·Cl‒Na 4 QGW01 地下水 29.4 5.6 140.1 15.0 7.7 14.6 15.8 3.0 19.6 0.1 17.7 17.3 16.1 ‒6.7 ‒42.6 Cl·SO4‒Na·Ca 5 QGW02 31.7 6.3 265.9 134.0 19.6 15.9 42.4 7.8 8.9 0.2 38.1 31.0 38.5 ‒6.0 ‒37.6 HCO3·SO4‒Ca 6 QGW03 31.0 6.4 293.2 15.0 8.2 24.3 48.7 7.4 21.8 0.2 31.6 41.3 25.2 ‒6.1 ‒37.8 SO4·Cl‒Ca·Na 7 QGW04 28.7 6.5 512.6 48.0 12.5 55.1 51.9 32.4 72.2 0.4 62.1 3.4 42.8 ‒5.4 ‒33.6 Cl·SO4‒Na·Ca·Mg 8 QGW05 27.0 4.1 170.4 63.0 9.8 8.1 14.5 6.2 14.1 0.3 10.1 80.1 10.0 ‒6.5 ‒47.2 HCO3·Cl‒Ca·Na·Mg 9 QGW06 28.8 6.0 338.5 16.0 11.0 28.8 52.0 5.6 51.6 0.1 22.0 74.2 34.9 ‒7.2 ‒46.0 Cl‒Ca·Na 10 QSW01 地表水 27.5 7.7 57.7 18.0 5.3 6.9 4.1 1.7 9.0 0.2 1.5 2.2 18.2 ‒4.2 ‒29.3 HCO3·Cl‒Na·Ca 11 QSW02 28.3 6.4 36.6 17.0 2.0 5.8 2.9 1.0 4.2 0.1 1.3 0.4 21.8 ‒5.6 ‒37.8 HCO3·Cl‒Na·Ca 12 QSW03 22.2 7.4 56.7 21.0 1.5 5.9 5.1 3.1 8.0 0.0 5.3 0.0 0.5 ‒4.7 ‒33.6 HCO3·Cl‒Na·Ca·Mg 表 2 地热水14C年龄计算校正结果
Table 2. Correction 14C dating results of geothermal water
样品编号 14CpMC δ13C(‰) 表观年龄(a) Vogel(a) Pearson(a) Tamers(a) Gonfiantinie(a) Mook(a) 平均值(a) 1 1.85±0.04 ‒9.2 32 050 31 140 24 721 26 813 25 747 27 222 27 129 2 8.19±0.07 ‒8.9 20 100 18 841 12 148 14 231 13 189 14 938 14 669 3 7.25±0.06 ‒8.1 21 694 19 849 12 478 14 581 13 519 15 944 15 274 注:14CpMC为现代碳元素百分比. 表 3 琼海官塘地区不同水体中不同矿物的饱和指数
Table 3. Saturation Indices of minerals in the water samples in Guantang area
样号 方解石 白云石 硬石膏 石膏 玉髓 石英 滑石 萤石 盐岩 QHW01 0.10 ‒1.45 ‒2.76 ‒2.68 0.21 0.57 0.32 0.2 ‒7.02 QHW02 ‒0.06 ‒1.21 ‒2.75 ‒2.68 0.24 0.6 1.99 0.16 ‒7.13 QHW03 0.25 ‒0.57 ‒2.94 ‒2.80 0.28 0.66 3.14 0.27 ‒6.60 QGW01 ‒3.23 ‒6.79 ‒3.00 ‒2.80 ‒0.48 ‒0.06 ‒15.17 ‒4.40 ‒8.10 QGW02 ‒1.20 ‒2.71 ‒2.36 ‒2.17 ‒0.13 0.28 ‒8.15 ‒2.87 ‒8.43 QGW03 ‒2.03 ‒4.47 ‒2.37 ‒2.18 ‒0.30 0.11 ‒8.68 ‒2.78 ‒7.86 QGW04 ‒1.44 ‒2.71 ‒2.16 ‒1.96 ‒0.05 0.37 ‒5.40 ‒1.96 ‒6.99 QGW05 ‒4.18 ‒8.37 ‒3.36 ‒3.15 ‒0.66 ‒0.23 ‒24.35 ‒2.94 ‒8.51 QGW06 ‒2.35 ‒5.28 ‒2.54 ‒2.33 ‒0.14 0.28 ‒10.73 ‒3.39 ‒7.41 QSW01 ‒1.64 ‒3.29 ‒4.55 ‒4.34 ‒0.41 0.01 ‒3.36 ‒3.57 ‒8.74 QSW02 ‒3.09 ‒6.24 ‒4.76 ‒4.55 ‒0.34 0.08 ‒11.36 ‒4.33 ‒9.14 QSW03 ‒1.81 ‒3.53 ‒3.95 ‒3.72 ‒1.90 ‒1.46 ‒10.91 ‒4.72 ‒8.84 -
Awaleh, M. O., Hoch, F. B., Boschetti, T., et al., 2015. The Geothermal Resources of the Republic of Djibouti—Ⅱ: Geochemical Study of the Lake Abhe Geothermal Field. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 159: 129-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.08.011 Chen, L. Z., Ma, T., Du, Y., et al., 2016. Hydrochemical and Isotopic (2H, 18O and 37Cl) Constraints on Evolution of Geothermal Water in Coastal Plain of Southwestern Guangdong Province, China. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 318: 45-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.03.003 Chen, Y. M., 2008. Present Situation of Geothermal Resource in Hainan Island and Suggestions for Development and Exploitation. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources, 25(6): 61-65 (in Chinese with English abstract). Clark, I. D., Fritz, P., 1997. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. CRC Press, Boca Raton. Dotsika, E., Poutoukis, D., Raco, B., 2010. Fluid Geochemistry of the Methana Peninsula and Loutraki Geothermal Area, Greece. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 104(3): 97-104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.01.001 Fournier, R. O., 1977. Chemical Geothermometers and Mixing Models for Geothermal Systems. Geothermics, 5(1-4): 41-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(77)90007-4 Fournier, R. O., Truesdell, A. H., 1974. Geochemical Indicators of Subsurface Temperature; Part Ⅱ, Estimate of Temperature and Fractions of Hot Water Mixed with Cold Water. Journal of Research of the U. S. Geological Survey, 2(3): 263-270. Fournier, R. O., White, D. E., Truesdell, A. H., 1974. Geochemical Indicators of Subsurface Temperature; Part Ⅰ, Basic assumptions. Journal of Research of the U. S. Geological Survey, 2(3): 259-262. Giggenbach, W. F., 1988. Geothermal Solute Equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca Geoindicators. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12): 2749-2765. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3 Guo, J., Mao, X. M., Tong, S., et al., 2016. Using Hydrochemical Geothermometers Calculate Exchange Temperature of Deep Geothermal System in West Coastal Area of Guangdong Province. Earth Science, 41(12): 2075-2087 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, Q. H., 2012. Hydrogeochemistry of High-Temperature Geothermal Systems in China: A Review. Applied Geochemistry, 27(10): 1887-1898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.07.006 Gurav, T., Singh, H. K., Chandrasekharam, D., 2015. Major and Trace Element Concentrations in the Geothermal Springs along the West Coast of Maharashtra, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(1): 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2139-2 Jiang, Y., Li, J., Xing, Y. F., et al., 2023. Evaluation of Geochemical Geothermometers with Borehole Geothermal Measurements: A Case Study of the Xiong'an New Area. Earth Science, 48(3): 958-972 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kaown, D., Koh, D. C., Mayer, B., et al., 2009. Identification of Nitrate and Sulfate Sources in Groundwater Using Dual Stable Isotope Approaches for an Agricultural Area with Different Land Use (Chuncheon, Mid-Eastern Korea). Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 132(3-4): 223-231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.04.004 Li, C. S., Wu, X. C., Sun, B., et al., 2018. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Geothermal Water in Northern Ji'nan. Earth Science, 43(S1): 313-325 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, J. L., Gao, B., Dong, Y. H., et al., 2017. Sources of Geothermal Water in Jiangxi Province, SE-China: Evidences from Hydrochemistry and Isotopic Composition. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 17: 837-840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2017.01.057 Li, Q. H., Zhang, Y. P., Chen, W., et al., 2018. The Integrated Impacts of Natural Processes and Human Activities on Groundwater Salinization in the Coastal Aquifers of Beihai, Southern China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(5): 1513-1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1756-8 Lund, J. W., Toth, A. N., 2021. Direct Utilization of Geothermal Energy 2020 Worldwide Review. Geothermics, 90: 101915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101915 Luo, J., Li, Y. M., Tian, J., et al., 2022. Geochemistry of Geothermal Fluid with Implications on Circulation and Evolution in Fengshun-Tangkeng Geothermal Field, South China. Geothermics, 100: 102323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102323 Merkel, B. J., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2008. Groundwater Geochemistry. In: Nordstrom, D. K., ed., A Practical Guide to Modelling of Natural and Contaminated Aquatic Systems (2nd Edition). Springer, New York. Najafi, G., Ghobadian, B., 2011. Geothermal Resources in Iran: The Sustainable Future. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(8): 3946-3951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.032 Song, X. F., Liu, X. C., Xia, J., et al., 2007. Study on the Transformation Relationship between Surface Water and Groundwater in Huaisha River Basin Based on Environmental Isotope Technology. Science in China (Series D), 37(1): 102-110 (in Chinese). Stefánsson, A., Arnórsson, S., Sveinbjörnsdóttir, Á. E., et al., 2019. Isotope (δD, δ18O, 3H, δ13C, 14C) and Chemical (B, Cl) Constrains on Water Origin, Mixing, Water-Rock Interaction and Age of Low-Temperature Geothermal Water. Applied Geochemistry, 108: 104380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104380 Sun, H. Y., Sun, X. M., Wei, X. F., et al., 2023. Geochemical Characteristics and Origin of Nuanquanzi Geothermal Water in Yudaokou, Chengde, Hebei, North China. Journal of Earth Science, 34(3): 838-856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1635-z Truesdell, A. H., Fournier, R. O., 1977. Procedure for Estimating the Temperature of a Hot-Water Component in a Mixed Water by Using a Plot of Dissolved Silica Versus Enthalpy. Journal of Research of the U. S. Geological Survey, 5: 49-52. Wang, J. Y., Pang, Z. H., Hu, S. B., et al., 2015. Geothermics and Its Applications. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Wang, X. A., Lu, G. P., Hu, B. X., 2018. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Geothermometry Applications of Thermal Waters in Coastal Xinzhou and Shenzao Geothermal Fields, Guangdong, China. Geofluids, 2018: 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8715080 Wang, X. C., Zhou, X., 2019. Geothermometry and Circulation Behavior of the Hot Springs in Yunlong County of Yunnan in Southwest China. Geofluids, 2019: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8432496 Wang, X. L., Zeng, W. T., Yang, Y. P., et al., 2018. Geological and Hydrochemical Characteristics of Longmuwan Geothermal Field in Ledong, Hainan. West-China Exploration Engineering, 30(9): 111-112, 117 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, C., Wu, X., Mu, W. P., et al., 2020. Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China. Water, 12(5): 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051467 Wu, G. W., Wang, P., Wang, X. F., et al., 2015. Hydro-Geochemical Type and Main Components Origin Analysis of the Geothermal Water in Tongren. Ground Water, 37(4): 4-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, Y. J., Chen, C. X., Yuan, F., 2021. Temporal-Spatial Distribution Regularities of Kaolin Deposits in China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 42(5): 628-640 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, Y., Wang, Y. X., 2014. Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater Salinity at Basin Scale: A Case Study from Datong Basin, Northern China. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts, 16(6): 1469-1479. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4em00019f Yang, F., Ruan, M., Zhang, D. Q., et al., 2018. Study on the Geochemical Characteristics of Hot Mineral Water Isotope in Haipo District, Sanya City, Hainan Province. Ground Water, 40(4): 15-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yokochi, R., Purtschert, R., Suda, Y., et al., 2021. Chemical and Isotopic Constraints on Hydrological Processes in Unzen Volcanic Geothermal System. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 419: 107353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2021.107353 Yuan, J. F., Xu, F., Zheng, T. L., 2022. The Genesis of Saline Geothermal Groundwater in the Coastal Area of Guangdong Province: Insight from Hydrochemical and Isotopic Analysis. Journal of Hydrology, 605: 127345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127345 Zeng, T. R., 2019. Research on Basic Characteristics of 2H, 18O and 14C in Geothermal Fluid in Guangdong Province, China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 7(1): 42-52. https://doi.org/10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2019.01.004 Zhang, J. Y., 2012. Geochemical Studies of the Mineralization by Weathering of Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks in North Hainan Island (Dissertation). China University of Geoscience, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X. B., Guo, Q. H., Zhang, M. Z., et al., 2023. Geochemical Behavior and Indicative Effect of REEs in Carbonate Geothermal Reservoir: A Case of Shidian Geothermal System. Earth Science, 48(3): 908-922 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y. H., Xu, M., Li, X. A., et al., 2018. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water, 10(1): 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010080 Zhang, Y., 2019. A Study of the Characteristics and Formation of the Hot Springs in Hainan Island (Dissertation). China University of Geoscience, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y., Yu, Q., Shi, C. W., et al., 2023. Environmental Isotopes and Cl/Br Ratios Evidences for Delineating Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer System of the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Journal of Earth Science, 34(2): 571-579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1096-1 陈颖民, 2008. 海南岛地热资源现状及勘查开发利用建议. 国土资源科技管理, 25(6): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKG200806014.htm 郭静, 毛绪美, 童晟, 等, 2016. 水化学温度计估算粤西沿海深部地热系统热交换温度. 地球科学, 41(12): 2075-2087. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2016.144 姜颖, 李捷, 邢一飞, 等, 2023. 基于钻孔测温的地球化学温度计适宜性评价: 以雄安新区为例. 地球科学, 48(3): 958-972. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.385 李常锁, 武显仓, 孙斌, 等, 2018. 济南北部地热水水化学特征及其形成机理. 地球科学, 43(S1): 313-325. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.206 宋献方, 刘相超, 夏军, 等, 2007. 基于环境同位素技术的怀沙河流域地表水和地下水转化关系研究. 中国科学(D辑), 37(1): 102-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200701011.htm 汪集暘, 庞中和, 胡圣标, 等, 2015. 地热学及其应用. 北京: 科学出版社. 王晓林, 曾维特, 杨永鹏, 等, 2018. 海南乐东龙沐湾地热田地质及水化学特征分析. 西部探矿工程, 30(9): 111-112, 117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBTK201809038.htm 吴桂武, 王鹏, 王晓峰, 等, 2015. 铜仁市地热水水化学类型及主要组分成因分析. 地下水, 37(4): 4-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201504003.htm 吴宇杰, 陈从喜, 袁峰, 2021. 中国高岭土矿床时空分布规律. 地球学报, 42(5): 628-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202105005.htm 杨峰, 阮明, 张东强, 等, 2018. 海南省三亚市海坡地区热矿水同位素地球化学特征研究. 地下水, 40(4): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201804004.htm 张家友, 2012. 海南岛北部新生代火山岩风化成矿作用地球化学研究(博士学位论文). 武汉: 中国地质大学. 张晓博, 郭清海, 张梦昭, 等, 2023. 碳酸盐岩热储中稀土元素的地球化学行为及其指示意义: 以施甸地热系统为例. 地球科学, 48(3): 908-922. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.323 张颖, 2019. 海南岛温泉特征及成因研究(硕士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. -









 下载:
下载: