Meteorological Early Warning of Landslide Based on I⁃D⁃R Threshold Model
-
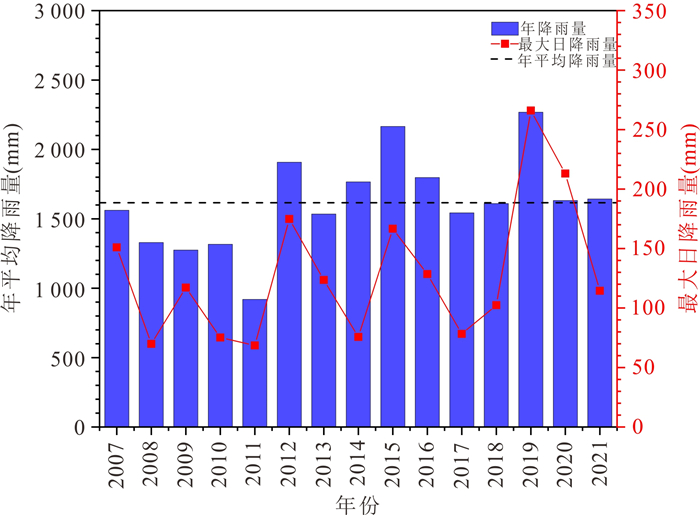
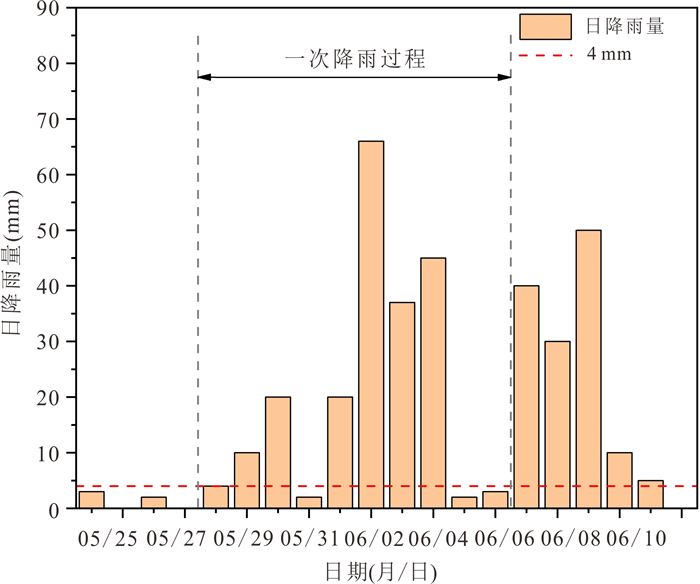
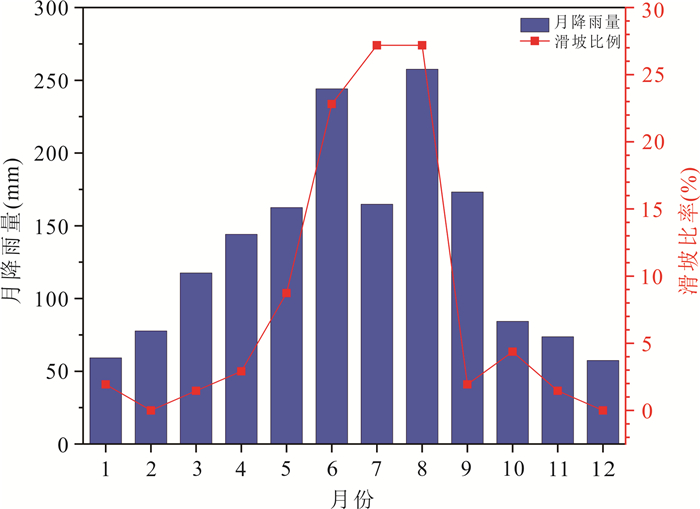
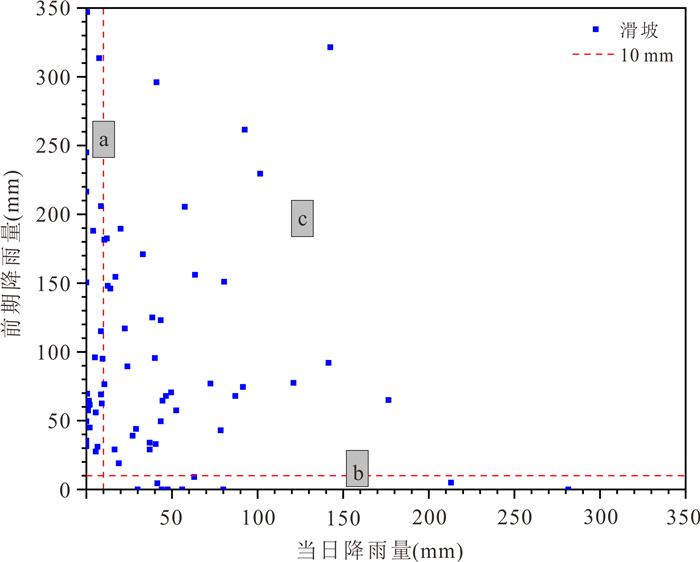
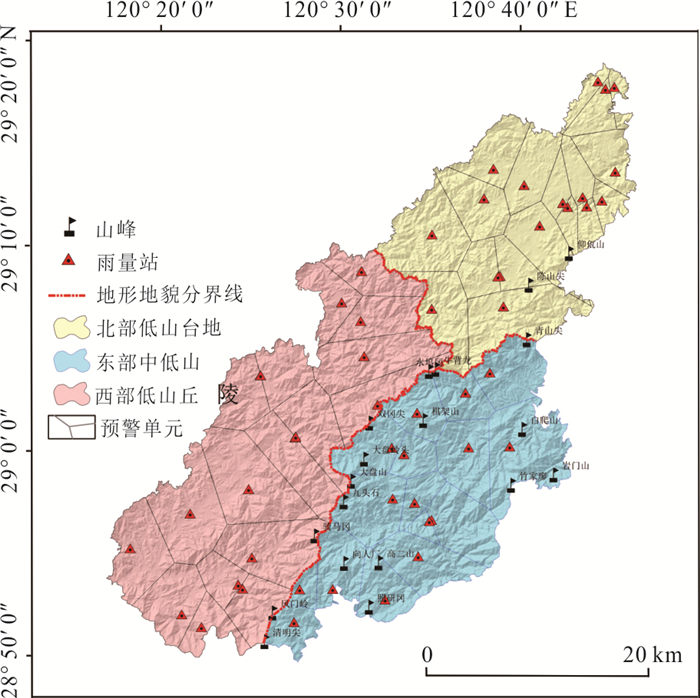
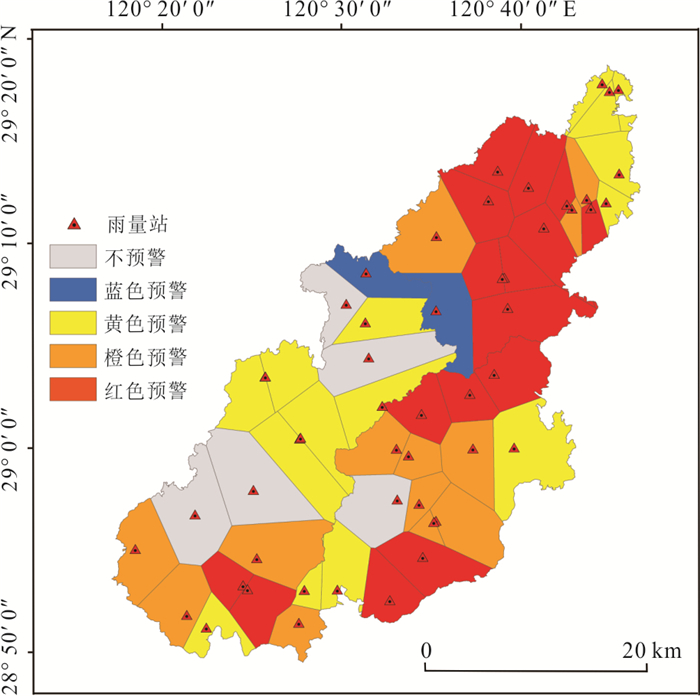
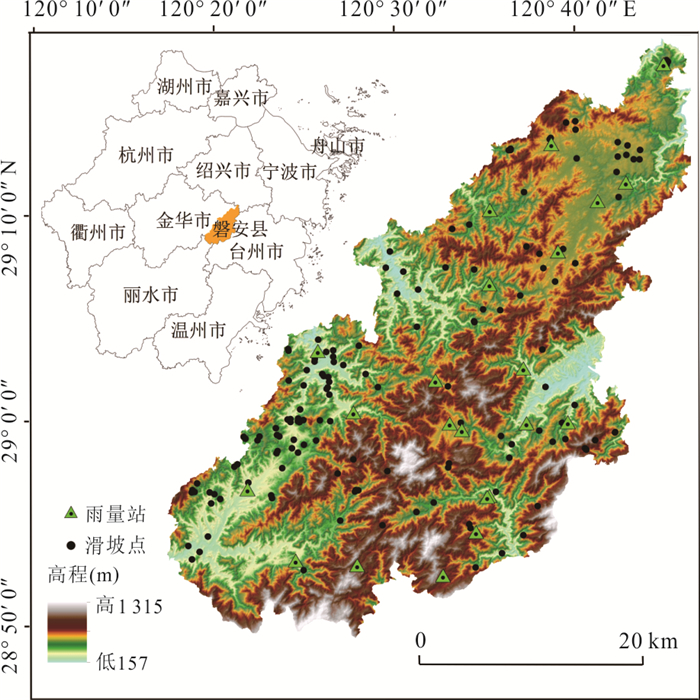
摘要: 建立滑坡灾害多维度气象预警判据和划分“网格化”预警单元能够为滑坡灾害气象预警提供科学依据.本文以浙江省金华市磐安县205个降雨型滑坡为研究对象,首先,基于平均有效降雨强度‒降雨历时(I⁃D)阈值模型,采用普通最小二乘回归(OLSQ)和分位数回归(QR)划分临界阈值曲线;其次,引入当日降雨量(R),进一步优化I⁃D阈值模型,建立I⁃D⁃R阈值模型,采用不同参数估计方法对比不同阈值模型精度,选择最优阈值模型作为磐安县滑坡灾害气象预警判据;最后,基于降雨分布的差异性,在划分地形单元的基础上利用泰森多边形(VD)建立了乡镇级别的“网格化”预警单元.结果显示:(1)I⁃D⁃R阈值模型相比于I⁃D阈值模型具有更好的预警精度,且基于QR的I⁃D⁃R阈值模型效果更好,警告及以上阈值等级精度提升到50%,特别注意及以上阈值等级精度提升到88.9%;(2)采用基于QR的I⁃D⁃R降雨阈值作为磐安县51个预警单元四级气象预警(红、橙、黄、蓝)的判据,并提出相应的应急响应措施.研究成果提供了一种新的阈值模型,能够为磐安县区域气象预警提供借鉴与参考.Abstract: The establishment of the multi-dimensional meteorological early warning criterion of landslide and the division of the "grid" early warning unit can provide a scientific basis for the landslide early warning, for the purpose of which 205 rainfall-induced landslides in Panan County, Zhejiang Province were studied in this paper. Firstly, based on the average effective rainfall intensity-diachronic (I-D) threshold model, the critical threshold curves were divided by ordinary least squares regression (OLSQ) and quantile regression (QR). Secondly, the I-D-R threshold model was established by the I-D threshold model optimized by considering the daily rainfall (R), and different parameter estimation methods were used to compare the accuracy of different threshold models. The optimal threshold model was considered as the meteorological early warning criterion for landslide disasters in Pan'an County. Finally, considering the difference of rainfall distribution, the township level grid early warning unit was established by the terrain zoning and Voronoi diagram (VD) of Pan'an. The results show that: (1) The I⁃D⁃R threshold model has better early warning accuracy than the I⁃D model. The I⁃D⁃R threshold model based on QR has a better warning ability, and the accuracy of the threshold degree of warning and above is increased to 50%, and the accuracy of the threshold level of special attention and above is increased to 88.9%; (2) the rainfall conditions with I⁃D⁃R based on QR rainfall threshold are proposed as the early warning criteria (red, orange, yellow and blue) of 51 early warning units in Pan'an County, and the emergency response measures are put forward. A new threshold model is established on the basis of the research results, which can provide reference for regional meteorological early warning in Pan'an County.
-
表 1 基于OLSR和QR方法划分的临界降雨阈值方程
Table 1. critical rainfall threshold equation based on OLSR and QR methods
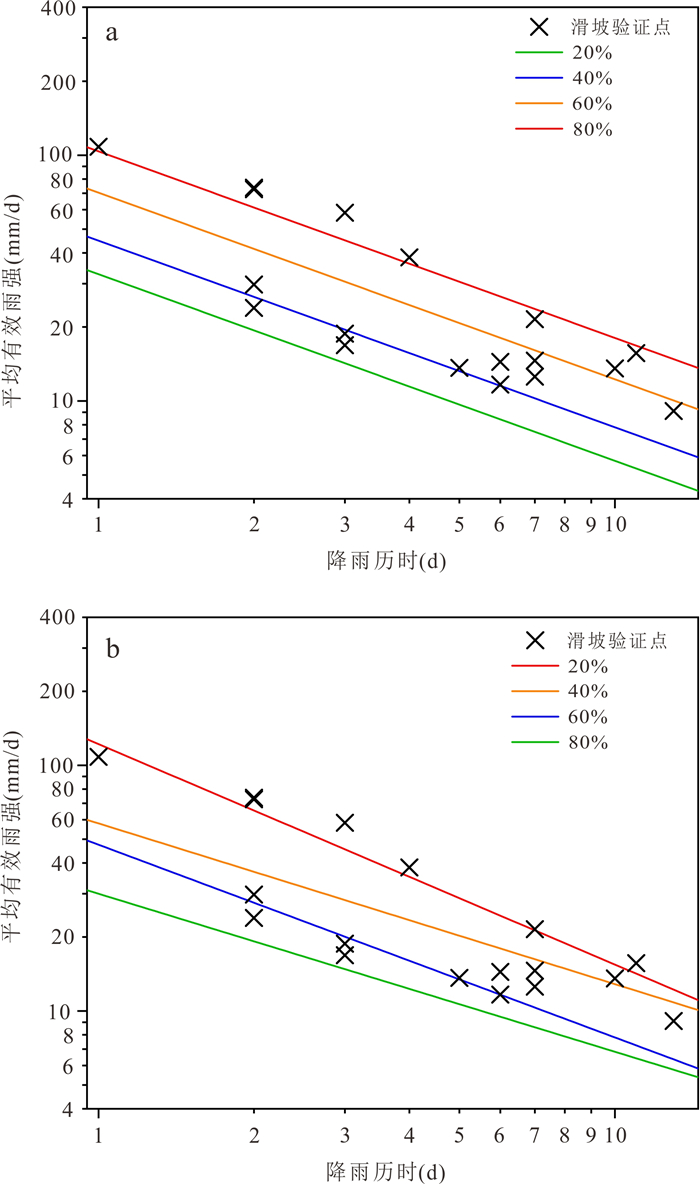
阈值划分方法 OLSR QR 20%阈值方程 I=32.8D‒0.759 2 I=30.0D‒0.643 0 40%阈值方程 I=44.9D‒0.759 2 I=47.5D‒0.784 3 60%阈值方程 I=70.4D‒0.759 2 I=58.0D‒0.654 1 80%阈值方程 I=103.7D‒0.759 2 I=121.9D‒0.89 7 表 2 阈值等级重现期
Table 2. Threshold degrees return periods
气象站点 安文站 大盘站 方前站 严重警告天数(≥121.9 mm/d) 745 678 791 警告及以上天数(≥58.0 mm/d) 138 118 163 特别注意及以上天数(≥47.5 mm/d) 93 85 103 注意及以上天数(≥30.0 mm/d) 33 31 35 表 3 磐安县四级阈值对应的降雨阈值
Table 3. Rainfall threshold of IV threshold degrees in Pan'an
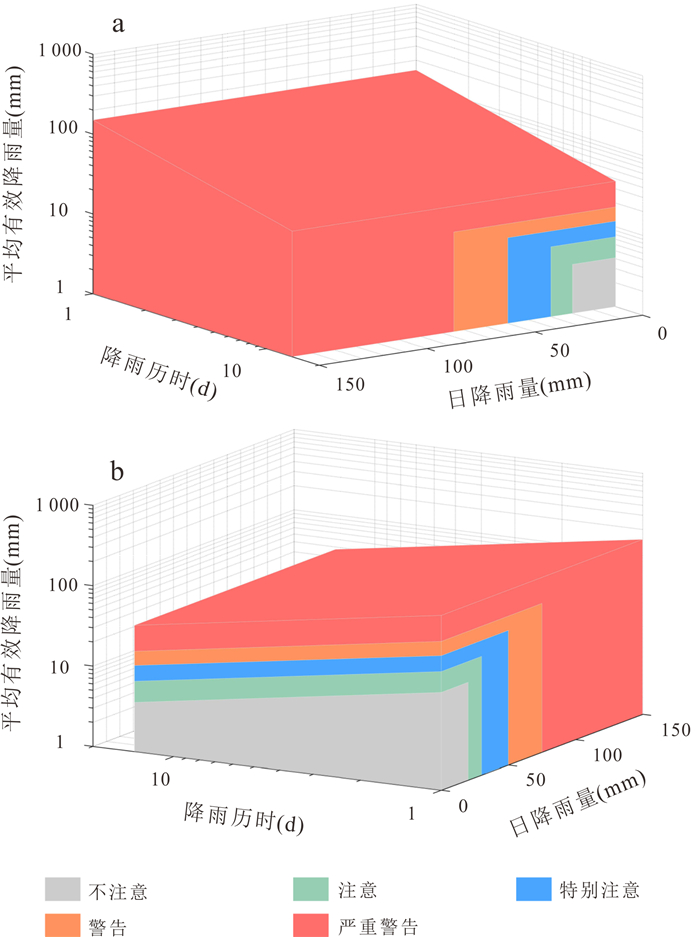
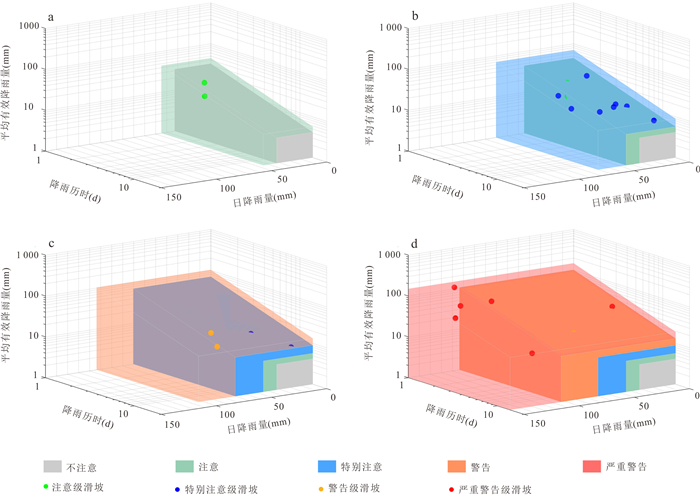
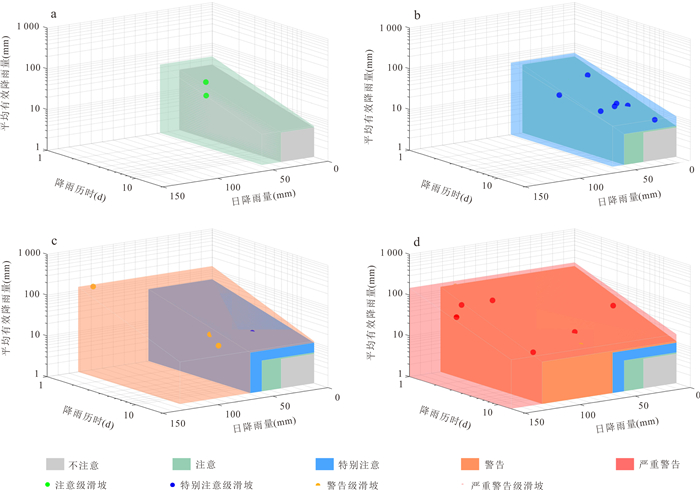
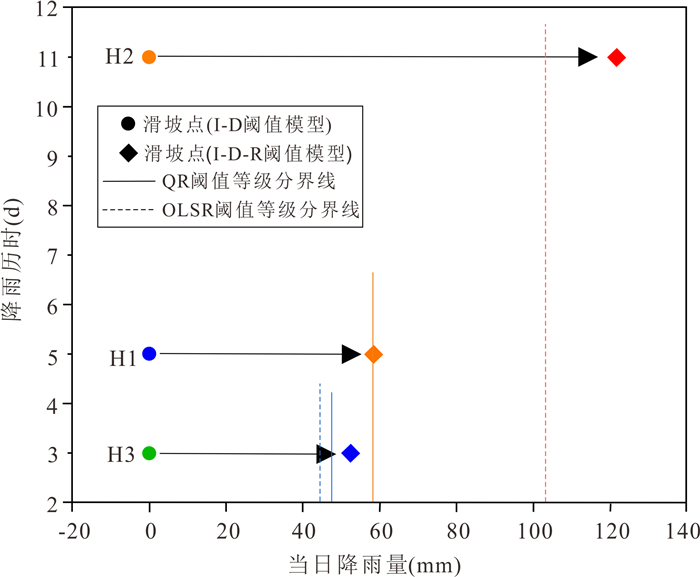
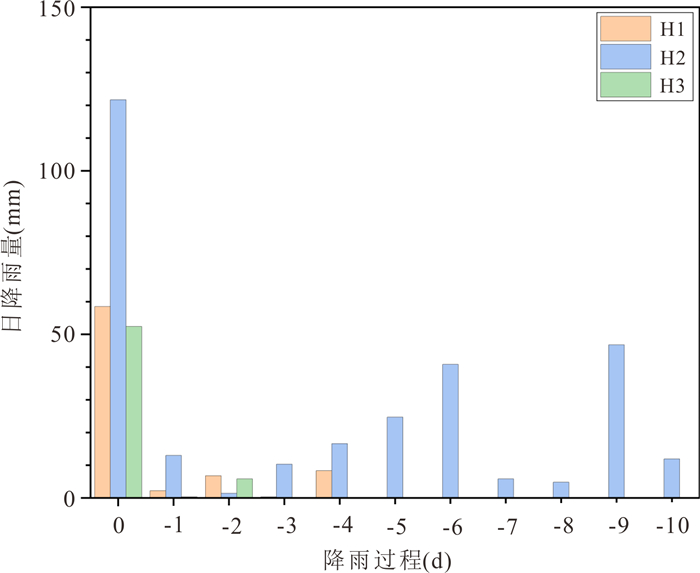
阈值等级 降雨阈值 注意 ①30.0D‒0.643 0≤I < 47.5D‒0.784 3且R < 47.5 ②I < 30.0D‒0.643 0且30.0≤R < 47.5 特别注意 ①47.5D‒0.784 3≤I < 58.0D‒0.654 1且R < 58.0 ②I < 47.5D‒0.784 3且47.5≤R < 58.0 警告 ①58.0D‒0.654 1≤I < 121.9D‒0.897且R < 121.9 ②I < 58.0D‒0.654 1且58.0≤R < 121.9 严重警告 ①I≥121.9D‒0.897 ②I < 121.9D‒0.897且R≥121.9 表 4 磐安县四级阈值对应的实际降雨总量
Table 4. Actual total rainfall of IV threshold degrees in Pan'an
阈值等级 宏观累计降雨总量(mm) 注意 [54.6, 74.0) 特别注意 [74.0, 104.3) 警告 [104.3, 167.8) 严重警告 [167.8, ∞) 表 5 磐安县四级预警管控响应
Table 5. Early warning control response in Pan'an County
预警等级 等级预警管控响应 蓝色预警 发布蓝色预警,预警区域根据滑坡灾害风险情况做好防范. 黄色预警 发布黄色预警,群防群策员开展预报预警区域地质灾害隐患点、风险防范区的巡查与监测;做好地质灾害预防工作情况的每日统计、分析和报告. 橙色预警 发布橙色预警,在黄色预警响应基础上,群防群策员加强巡查与监测,职能部门加大地质灾害气象预警的密度,注意研判地质灾害发展趋势,做好地质灾害隐患点、风险防范区的人员转移等应急工作. 红色预警 发布红色预警,在橙色预警响应基础上,各职能部门24 h应急值守,加强短时预报预警,派驻专业人员驻扎一线指导工作,对地质灾害隐患点、风险防范区等受灾害威胁区域的人员要安置在避灾场所,应急办公室视灾情派遣省级应急专家队伍与应急抢险救援队伍进驻预警区域. 注:风险防范区指各预警单元内有承灾体分布的斜坡单元. -
Bai, S. B., Wang, J., Thiebes, B., et al., 2014. Analysis of the Relationship of Landslide Occurrence with Rainfall: A Case Study of Wudu County, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(4): 1277-1285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517⁃013⁃0939⁃9 Caine, N., 1980. The Rainfall Intensity: Duration Control of Shallow Landslides and Debris Flows. Geografiska Annaler Series A, Physical Geography, 62(1-2): 23-27. https://doi.org/10.2307/520449 Campbell, R. H., 1975. Soil Slips, Debris Flows, and Rainstorms in the Santa Monica Mountains and Vicinity, Southern California. U. S. Geological Survey, Reston. Croley, T. E., Hartmann, H. C., 1985. Resolving Thiessen Polygons. Journal of Hydrology, 76(3-4): 363-379. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022⁃1694(85)90143⁃X Crozier, M. J., 1986. Landslides: Causes, Consequences and Environment. Croom Helm, London. Feng, H. J., Zhou, A. G., Tang, X. M., et al., 2016. Development and Distribution Characteristics of Debris Flow in Zhejiang Province and Its Regional Forecast. Earth Science, 41(12): 2088-2099 (in Chinese with English abstract). Glade, T., Crozier, M., Smith, P., 2000. Applying Probability Determination to Refine Landslide⁃Triggering Rainfall Thresholds Using an Empirical "Antecedent Daily Rainfall Model". Pure and Applied Geophysics, 157(6): 1059-1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000240050017 Guo, Z. Z., Yin, K. L., Liu, Q. L., et al., 2020. Rainfall Warning of Creeping Landslide in Yunyang County of Three Gorges Reservoir Region Based on Displacement Ratio Model. Earth Science, 45(2): 672-684 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guzzetti, F., Peruccacci, S., Rossi, M., et al., 2007. Rainfall Thresholds for the Initiation of Landslides in Central and Southern Europe. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 98(3): 239-267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703⁃007⁃0262⁃7 Guzzetti, F., Peruccacci, S., Rossi, M., et al., 2008. The Rainfall Intensity⁃Duration Control of Shallow Landslides and Debris Flows: An Update. Landslides, 5(1): 3-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346⁃007⁃0112⁃1 Hong, Y., Hiura, H., Shino, K., et al., 2005. The Influence of Intense Rainfall on the Activity of Large⁃Scale Crystalline Schist Landslides in Shikoku Island, Japan. Landslides, 2(2): 97-105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346⁃004⁃0043⁃z Hu, L., Hu, Y. Q., Sun, P., et al., 2021. A Quantitative Analysis of Disaster Threshold and Landslide Risk of Rainfall⁃Type Landslide in Southeast Tibet. Journal of Catastrophology, 36(4): 194-199 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, F. M., Cao, Z. S., Yao, C., et al., 2021. Landslides Hazard Warning Based on Decision Tree and Effective Rainfall Intensity. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 55(3): 472-482 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, F. M., Chen, J. W., Fan, X. M., et al., 2022. Logistic Regression Fitting of Rainfall⁃Induced Landslide Occurrence Probability and Continuous Landslide Hazard Prediction Modelling. Earth Science, 47(12): 4609-4628 (in Chinese with English abstract). Irawan, A. M., Virgianto, R. H., Safril, A., et al., 2019. Rainfall Threshold and Soil Moisture Indexes for the Initiation of Landslide in Banjarmangu Sub⁃District, Central Java, Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 243: 012028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755⁃1315/243/1/012028 Kim, S. W., Chun, K. W., Kim, M., et al., 2021. Effect of Antecedent Rainfall Conditions and Their Variations on Shallow Landslide⁃Triggering Rainfall Thresholds in South Korea. Landslides, 18(2): 569-582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346⁃020⁃01505⁃4 Koenker, R., Hallock, K. F., 2001. Quantile Regression. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 15(4): 143-156. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.15.4.143 Lagomarsino, D., Segoni, S., Rosi, A., et al., 2015. Quantitative Comparison between Two Different Methodologies to Define Rainfall Thresholds for Landslide Forecasting. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 15(10): 2413-2423. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess⁃15⁃2413⁃201510.5194/nhessd⁃3⁃891⁃2015 Lee, D. H., Lai, M. H., Wu, J. H., et al., 2013. Slope Management Criteria for Alishan Highway Based on Database of Heavy Rainfall⁃Induced Slope Failures. Engineering Geology, 162: 97-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.04.012 Li, C. J., Ma, T. H., Li, W., et al., 2010. Fractal Relation of Landslide Frequency and Rainfall. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 21(1): 87-93 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.018 Lin, W., Li, Y. Y., Xu, Y., et al., 2020. Rainfall Thresholds of Rainfall⁃Triggered Landslides in Cili County, Hunan Province. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 37(2): 48-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lumb, P., 1975. Slope Failures in Hong Kong. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 8(1): 31-65. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.qjeg.1975.008.01.02 Luo, Y., He, S. M., He, J. C., 2014. Effect of Rainfall Patterns on Stability of Shallow Landslide. Earth Science, 39(9): 1357-1363 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, T. H., Li, C. J., Lu, Z. M., et al., 2014. An Effective Antecedent Precipitation Model Derived from the Power⁃Law Relationship between Landslide Occurrence and Rainfall Level. Geomorphology, 216: 187-192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.03.033 Martinović, K., Gavin, K., Reale, C., et al., 2018. Rainfall Thresholds as a Landslide Indicator for Engineered Slopes on the Irish Rail Network. Geomorphology, 306: 40-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.01.006 Melillo, M., Brunetti, M. T., Peruccacci, S., et al., 2015. An Algorithm for the Objective Reconstruction of Rainfall Events Responsible for Landslides. Landslides, 12(2): 311-320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346⁃014⁃0471⁃3 Peng, J. B., Fan, Z. J., Wu, D., et al., 2015. Heavy Rainfall Triggered Loess⁃Mudstone Landslide and Subsequent Debris Flow in Tianshui, China. Engineering Geology, 186: 79-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.015 Peng, Q. Y., 2020. Evaluation and Data Analysis of Gansu Landslide and Debris Flow Monitoring System (Dissertation). Lanzhou University, Lanzhou (in Chinese with English abstract). Rosi, A., Segoni, S., Catani, F., et al., 2012. Statistical and Environmental Analyses for the Definition of a Regional Rainfall Threshold System for Landslide Triggering in Tuscany (Italy). Journal of Geographical Sciences, 22(4): 617-629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442⁃012⁃0951⁃0 Wang, S. W., Sun, L. S., Rong, J., et al., 2014. Transit Traffic Analysis Zone Delineating Method Based on Thiessen Polygon. Sustainability, 6(4): 1821-1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6041821 Wu, Y. P., Yin, K. L., Jiang, W., 2009. Early Warning of Landslide Risk in Yongjia County, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Natural Disasters, 18(2): 124-130 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, Y. P., Zhang, Q. X., Tang, H. M., et al., 2014. Landslide Hazard Warning Based on Effective Rainfall Intensity. Earth Science, 39(7): 889-895 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xia, M. X., Li, Y. Y., Wu, J. M., et al., 2021. Research on Rainfall Early Warning Threshold of Landslide Disaster in Zhangjiajie City Based on I⁃D Statistical Model. Journal of Natural Disasters, 30(4): 203-212 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, L. H., Zhou, Z. C., 2014. Comparison of Ordinary Least Square Regression and Quantile Regression in the Study of Hydrological Elements of Yanhe River Basin. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 12(5): 45-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G. R., Yin, K. L., Liu, L. L., et al., 2005. Warning System for Rain⁃Induced Landslides Based on Internet in Zhejiang Province, China. Earth Science, 30(2): 250-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y., Wen, Z., Cheng, Y. J., 2020. A Discussion of the Relationship between Landslide Disaster and Rainfall Types in Bazhong of Sichuan. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(2): 178-182 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, B. R., Dai, Q., Han, D. W., et al., 2019. Probabilistic Thresholds for Landslides Warning by Integrating Soil Moisture Conditions with Rainfall Thresholds. Journal of Hydrology, 574: 276-287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.062 冯杭建, 周爱国, 唐小明, 等, 2016. 浙江省泥石流灾害发育分布规律及区域预报. 地球科学, 41(12): 2088-2099. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2016.514 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 刘庆丽, 等, 2020. 基于位移比模型的三峡库区云阳县域内蠕变型滑坡降雨预警. 地球科学, 45(2): 672-684. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.005 胡磊, 胡玉乾, 孙鹏, 等, 2021. 藏东南地区降雨型滑坡致灾阈值及滑坡危险性量化分析. 灾害学, 36(4): 194-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU202104032.htm 黄发明, 曹中山, 姚池, 等, 2021. 基于决策树和有效降雨强度的滑坡危险性预警. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 55(3): 472-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC202103007.htm 黄发明, 陈佳武, 范宣梅, 等, 2022. 降雨型滑坡时间概率的逻辑回归拟合及连续概率滑坡危险性建模. 地球科学, 47(12): 4609-4628. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.164 李长江, 麻土华, 李炜, 等, 2010. 滑坡频度‒降雨量的分形关系. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 21(1): 87-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201001023.htm 林巍, 李远耀, 徐勇, 等, 2020. 湖南慈利县滑坡灾害的临界降雨量阈值研究. 长江科学院院报, 37(2): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202002011.htm 罗渝, 何思明, 何尽川, 2014. 降雨类型对浅层滑坡稳定性的影响. 地球科学, 39(9): 1357-1363. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.118 彭启园, 2020. 甘肃滑坡与泥石流监测体系评价与数据分析研究(硕士学位论文). 兰州: 兰州大学. 吴益平, 殷坤龙, 姜玮, 2009. 浙江省永嘉县滑坡灾害风险预警研究. 自然灾害学报, 18(2): 124-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH200902019.htm 吴益平, 张秋霞, 唐辉明, 等, 2014. 基于有效降雨强度的滑坡灾害危险性预警. 地球科学, 39(7): 889-895. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.083 夏梦想, 李远耀, 吴吉民, 等, 2021. 基于I⁃D统计模型的张家界市滑坡灾害降雨预警阀值研究. 自然灾害学报, 30(4): 203-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH202104022.htm 杨丽红, 周正朝, 2014. 最小二乘与分位数回归方法在河流水沙研究中的应用: 以陕北延河流域为例. 中国水土保持科学, 12(5): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBC201405008.htm 张桂荣, 殷坤龙, 刘礼领, 等, 2005. 基于WEB的浙江省降雨型滑坡预警预报系统. 地球科学, 30(2): 250-254. http://www.earth-science.net/article/id/1446 张勇, 温智, 程英建, 2020. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨. 水文地质工程地质, 47(2): 178-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202002024.htm -









 下载:
下载: