Simultaneous Quantitative Analysis of Multiple Methylthiolated Arsenates in Geothermal Water
-
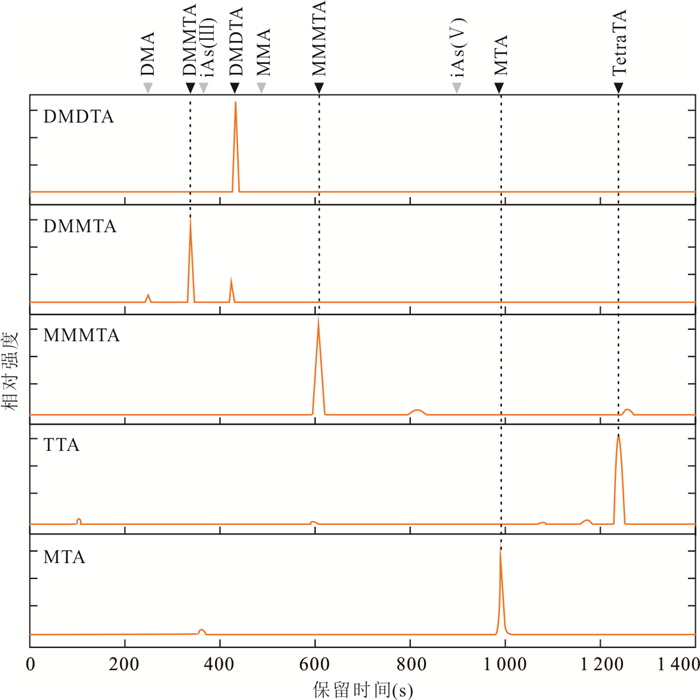
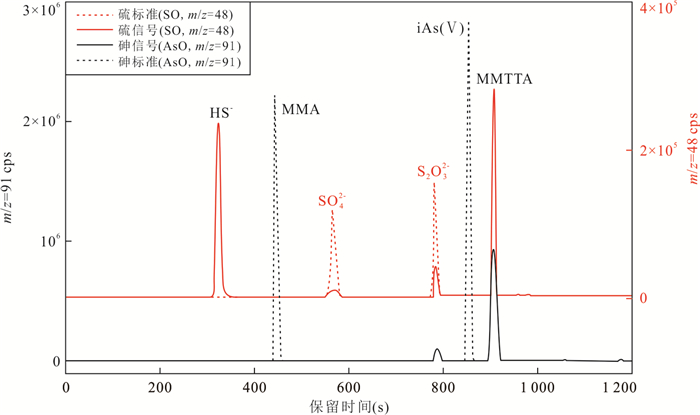
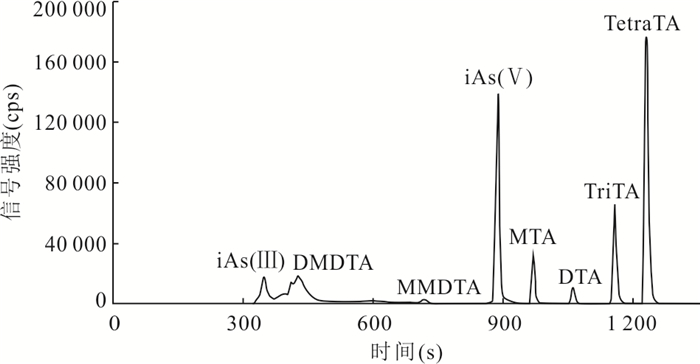
摘要: 地热水中的砷含量常远超过其他类型天然水体,其形态分析具有重要环境地球化学意义;甲基硫代砷酸盐在特定水环境条件下可能成为砷的一种不可忽视的形态,但其环境地球化学研究几为空白.本研究合成了甲基硫代砷酸盐标准,建立了可同时定量测试天然水中多种甲基硫代砷酸盐(包括一甲基一硫代砷酸盐、一甲基二硫代砷酸盐、一甲基三硫代砷酸盐、二甲基一硫代砷酸盐、二甲基二硫代砷酸盐)及砷的其他常见形态的离子色谱‒电感耦合等离子体质谱联用系统(IC-ICP-MS)及其方法,并分析了典型地热水样品中砷的形态分布,可为今后不同类型水环境中甲基硫代砷酸盐的地球化学研究奠定分析方法基础.Abstract: Geothermal waters generally have far higher arsenic concentrations than other types of natural waters, and analysis of arsenic speciation in geothermal waters is of great environmental geochemical significance. Methylthiolated arsenates are non-negligible arsenic species under special aqueous environmental conditions, while little environmental geochemical studies of methylthiolated arsenates have been done so far. In this work, various methylthiolated arsenates standards were synthesized, and an ion chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, capable of determining concentrations of common arsenic species as well as methylthiolated arsenates in natural waters including monomethylmonothioarsenate (MMMTA), monomethyldithioarsenate (MMDTA), monomethyltrithioarsenate (MMTTA), dimethylmonothioarsenate (DMMTA), and dimethyldithioarsenate (DMDTA), was set up. Furthermore, the arsenic speciation in a typical geothermal water sample was analyzed. The efforts made in this study produced an analytical method basis for future geochemical studies of methylthiolated arsenates in aqueous environments.
-
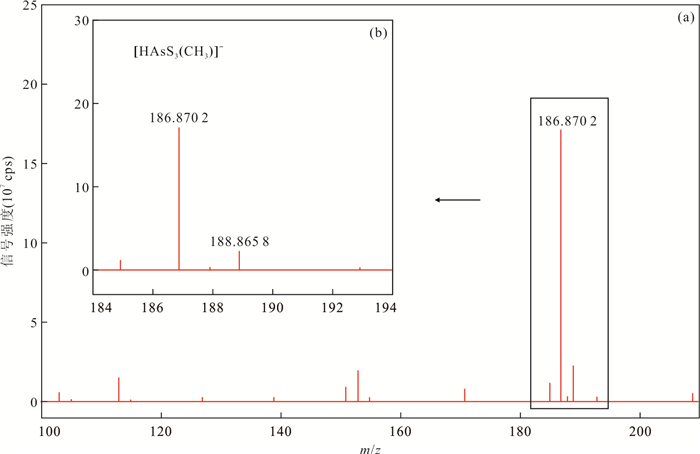
表 1 各种甲基硫代砷酸盐及其脱质子产物的理论质荷比
Table 1. Theoretic mass to charge ratios of various methylthiolated arsenates and their deprotonated products
砷形态 化学结构式 理论m/z 一甲基一硫代砷酸盐(MMMTA) H2AsS(CH3)O2 - HAsS(CH3)O2- 154.915 3 AsS(CH3)O22- 76.954 0 二甲基一硫代砷酸盐(DMMTA) HAsS(CH3)2O - AsS(CH3)2O- 152.936 1 二甲基二硫代砷酸盐(DMDTA) HAsS2(CH3)2 - AsS2(CH3)2- 168.913 2 -
Ackerman, A. H., Creed, P. A., Parks, A. N., et al., 2005. Comparison of a Chemical and Enzymatic Extraction of Arsenic from Rice and an Assessment of the Arsenic Absorption from Contaminated Water by Cooked Rice. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(14): 5241-5246. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048150n Burton, E. D., Johnston, S. G., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2013. Coupling of Arsenic Mobility to Sulfur Transformations during Microbial Sulfate Reduction in the Presence and Absence of Humic Acid. Chemical Geology, 343: 12-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.005 Couture, R. M., Rose, J., Kumar, N., et al., 2013. Sorption of Arsenite, Arsenate, and Thioarsenates to Iron Oxides and Iron Sulfides: A Kinetic and Spectroscopic Investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11): 5652-5659. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3049724 Guo, Q. H., Cao, Y. W., Li, J. X., et al., 2015. Natural Attenuation of Geothermal Arsenic from Yangbajain Power Plant Discharge in the Zangbo River, Tibet, China. Applied Geochemistry, 62: 164-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.01.017 Guo, Q. H., Liu, M. L., Li, J. X., 2017. Thioarsenic Species in the High‐Temperature Hot Springs from the Rehai Geothermal Field (Tengchong) and Their Geochemical Geneses. Earth Science, 42(2): 286-297 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, Q. H., Planer-Friedrich, B., Liu, M. L., et al., 2017. Arsenic and Thioarsenic Species in the Hot Springs of the Rehai Magmatic Geothermal System, Tengchong Volcanic Region, China. Chemical Geology, 453: 12-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.02.010 Guo, Q. H., Planer-Friedrich, B., Liu, M. L., et al., 2019. Magmatic Fluid Input Explaining the Geochemical Anomaly of very High Arsenic in Some Southern Tibetan Geothermal Waters. Chemical Geology, 513: 32-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.008 Hansen, H. R., Raab, A., Jaspars, M., et al., 2004. Sulfur-Containing Arsenical Mistaken for Dimethylarsinous Acid [DMA(Ⅲ)]and Identified as a Natural Metabolite in Urine: Major Implications for Studies on Arsenic Metabolism and Toxicity. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 17(8): 1086-1091. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx049978q Hinrichsen, S., Geist, F., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2015. Inorganic and Methylated Thioarsenates Pass the Gastrointestinal Barrier. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 28(9): 1678-1680. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00268 Naranmandura, H., Suzuki, N., Suzuki, K. T., 2006. Trivalent Arsenicals are Bound to Proteins during Reductive Methylation. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 19(8): 1010-1018. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx060053f Planer-Friedrich, B., London, J., McCleskey, R. B., et al., 2007. Thioarsenates in Geothermal Waters of Yellowstone National Park: Determination, Preservation, and Geochemical Importance. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(15): 5245-5251. https://doi.org/10.1021/es070273v Stauder, S., Raue, B., Sacher, F., 2005. Thioarsenates in Sulfidic Waters. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(16): 5933-5939. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048034k Styblo, M., Del Razo, L. M., Vega, L., et al., 2000. Comparative Toxicity of Trivalent and Pentavalent Inorganic and Methylated Arsenicals in Rat and Human Cells. Archives of Toxicology, 74(6): 289-299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000134 Styblo, M., Serves, S. V., Cullen, W. R., et al., 1997. Comparative Inhibition of Yeast Glutathione Reductase by Arsenicals and Arsenothiols. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 10(1): 27-33. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx960139g Suess, E., Wallschläger, D., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2015. Anoxic, Ethanolic, and Cool-An Improved Method for Thioarsenate Preservation in Iron-Rich Waters. Applied Geochemistry, 62: 224-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.017 Suess, E., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2012. Thioarsenate Formation Upon Dissolution of Orpiment and Arsenopyrite. Chemosphere, 89(11): 1390-1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.109 Suess, E., Wallschläger, D., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2011. Stabilization of Thioarsenates in Iron-Rich Waters. Chemosphere, 83(11): 1524-1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.045 Suzuki, K. T., Iwata, K., Naranmandura, H., Suzuki, N., 2007. Metabolic Differences between Two Dimethylthioarsenicals in Rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 218(2): 166-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.027 Suzuki, K. T., Mandal, B. K., Katagiri, A., et al., 2004. Dimethylthioarsenicals as Arsenic Metabolites and Their Chemical Preparations. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 17(7): 914-921. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx049963s Ullrich, M. K., Pope, J. G., Seward, T. M., et al., 2013. Sulfur Redox Chemistry Governs Diurnal Antimony and Arsenic Cycles at Champagne Pool, Waiotapu, New Zealand. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 262: 164-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2013.07.007 Wallschläger, D., London, J., 2008. Determination of Methylated Arsenic-Sulfur Compounds in Groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(1): 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0707815 Wang, M. D., Guo, Q. H., Guo, W., et al., 2016. Synthesis, Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Aqueous Thioarsenates. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 44(11): 1715-1720 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y., Xu, L. Y., Jia, Y. F., 2015. Study on the Adsorption Behavior of Thioarsenite at the Water-Mineral Interface in an Anaerobic Environment. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 45 (Suppl. 1): 43 (in Chinese). Xiao, F., Jia, Y. F., 2015. Study on the Adsorption Behavior of Thioarsenate at the Water-Mineral Interface in an Anaerobic Environment. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 45 (Suppl. 1): 42 (in Chinese). Zhuang, Y. Q., Guo, Q. H., Liu, M. L., et al., 2016. Geochemical Simulation of Thioarsenic Speciation in High‐Temperature, Sulfide‐Rich Hot Springs: A Case Study in the Rehai Hydrothermal Area, Tengchong, Yunnan. Earth Science, 41(9): 1499-1510 (in Chinese with English abstract). 郭清海, 刘明亮, 李洁祥, 2017. 腾冲热海地热田高温热泉中的硫代砷化物及其地球化学成因. 地球科学, 42(2): 286-297. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.021 王敏黛, 郭清海, 郭伟, 等, 2016. 硫代砷化物的合成、鉴定和定量分析方法研究. 分析化学, 44(11): 1715-1720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201611013.htm 王莹, 许丽英, 贾永锋, 2015. 厌氧环境中硫代亚砷在水‒矿物界面的吸附行为研究. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45(Suppl. 1): 43. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201506002167.htm 肖翻, 贾永锋, 2015. 厌氧环境中硫代As (Ⅴ) 在水‒矿物界面的吸附研究. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45 (Suppl. 1): 42. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201506002166.htm 庄亚芹, 郭清海, 刘明亮, 等, 2016. 高温富硫化物热泉中硫代砷化物存在形态的地球化学模拟: 以云南腾冲热海水热区为例. 地球科学, 41(9): 1499-1510. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2016.513 -










 下载:
下载: