Deep Learning Characterization Method of Rock Mass Conditions Based on TBM Rock Breaking Data
-
摘要: 基于TBM施工数据进行围岩感知对保障TBM施工安全、提高施工效率至关重要,其中TBM掘进参数预测的准确率是检验围岩感知效果的重要依据.为此,以吉林引松工程TBM四标段为研究对象,选取TBM上升段破岩数据为输入特征X1,选择两个施工控制参数(刀盘转速和推进速度)为输入特征X2,构建卷积神经网络机器学习模型,对TBM掘进响应参数Y(刀盘扭矩和总推力)进行预测.按照学习对象的不同,分别构建了只学习稳定段掘进响应行为的点预测模型和同时学习上升段和稳定段掘进响应行为的线预测模型,结果表明:点预测模型无法描述控制参数对掘进响应参数的影响;线预测模型虽然可以描述控制参数对掘进响应参数的影响,但是对稳定段的掘进响应预测数值偏低.考虑到上述局限性的原因是稳定段行为样本数量只占总样本数量的9%,提出了一种通过调节损失函数的方法来提高稳定段行为样本的权重,显著提高了线预测模型的预测精度.改进后的结果表明:在TBM掘进参数预测中,应对整个掘进段的行为进行学习,并提高稳定段行为的权重,以便获得高精度的掘进响应参数预测模型.获得的模型能够为进一步的围岩感知和控制参数优化提供基础.Abstract: Surrounding rock perception based on TBM construction data is essential to ensuring the safety of TBM construction and improving its construction efficiency, in which the accuracy of TBM tunnelling parameter prediction is crucial to testing the effect of surrounding rock perception. Therefore, in this paper it takes Jilin Yin-Song's project TBM4 bid section as the research object, selects the characteristic parameters of the surrounding rock from the rock breaking data of the loading phase of the TBM as input feature X1, and selects two construction control parameters (the rotation speed and penetration rate) as input feature X2, and constructs a convolutional neural network machine learning model to predict the TBM tunnelling response parameters Y (cutterhead torque and total thrust). According to the different learning objects, the point prediction model that only learns the response behavior of the stable boring phase and the line prediction model that simultaneously learns the response behavior of the loading phase and the stable boring phase are constructed, respectively. The improved results show that the point prediction model cannot describe the influence of control parameters on tunnelling response parameters. Although the line prediction model can describe the influence of control parameters on tunnelling response parameters, the prediction value of driving response in the stable boring phase is low. Considering that the low predictive value of the line prediction model in the stable boring phase is because the number of behavior samples in the stable boring phase only accounts for 9% of the total number of samples, in this paper, a method of adjusting loss function is proposed to improve the weight of behavior samples in the stable boring phase, which significantly improves the prediction accuracy of the line prediction model. The results show that the behavior of the loading boring phase should be studied, and the weight of the behavior of the stable boring phase should be increased to obtain a high-precision prediction model of tunnelling response parameters. The model obtained in this paper can provide a basis for further surrounding rock perception and control parameter optimization.
-
表 1 TBM破岩关键参数
Table 1. Key parameters of TBM rock breaking
参数名称 符号 单位 参数类型 备注 刀盘转速 n r/min 控制参数 刀盘每分钟旋转圈数,由TBM司机设定 推进速度 v mm/min 控制参数 刀盘每分钟推进距离,由TBM司机设定 贯入度 p mm/r $ p=\frac{v}{n} $ 刀盘每转贯入深度 刀盘扭矩 T kN·m 响应参数 由电机驱动系统提供 总推力 F kN 响应参数 由液压系统提供 表 2 输入特征及输出标签
Table 2. Input features and output labels
输入特征 输出标签
TBM掘进响应参数T、F代表围岩条件的破岩数据 TBM控制参数n、v X1(A×B) X2(1×2) Y(1×2) 注:A为行数;B为列数;T为刀盘扭矩,单位为$ \mathrm{k}\mathrm{N}·\mathrm{m} $;F为总推力,单位为$ \mathrm{k}\mathrm{N} $;n为刀盘转速,单位为$ \mathrm{r}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n} $;v为推进速度,单位为$ \mathrm{m}\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n} $. 表 3 用于提取岩体信息的输入特征X1
Table 3. Input feature X1 for extracting rock mass information
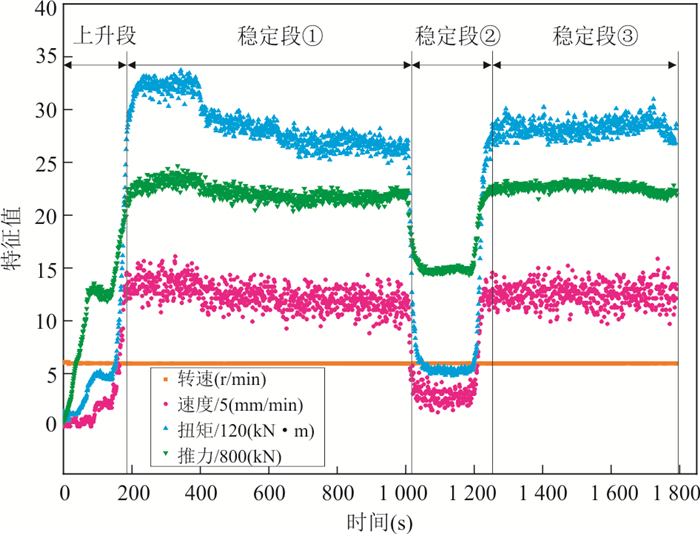
输入特征X1 输入维度 上升段随机30 s的T、F、n、v 30×4 注:在CNN模型训练过程中,关键的训练参数是学习率、批量大小和训练次数.经过一系列交叉验证,最终确定CNN模型的学习率、批量大小和训练次数分别取0.003、45、200. 表 4 输入特征X2和预测对象Y的比选方案
Table 4. Scheme of input feature X2 and prediction object Y
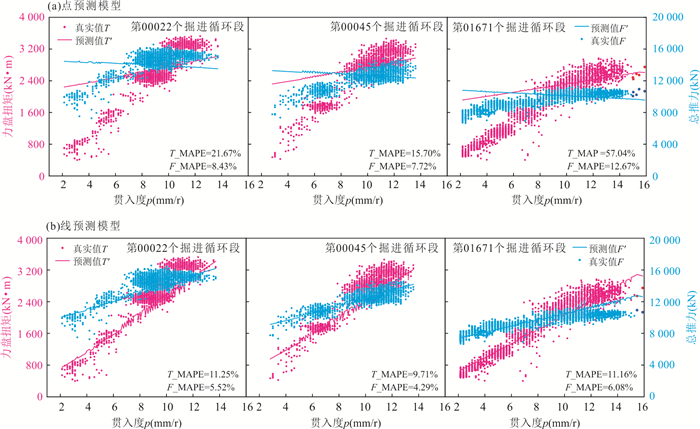
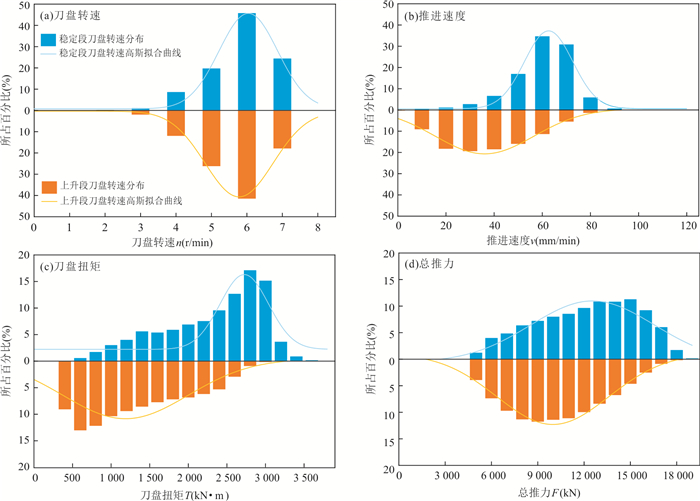
方案 输入特征X2 预测对象Y 数据样本量 ① 稳定段转速和速度的平均值 稳定段刀盘扭矩和总推力的平均值 NI ② 上升段按速度大小划分为10个区间,取每个区间转速和速度的平均值;稳定段转速和速度的平均值 上升段按速度大小划分为10个区间,取每个区间刀盘扭矩和总推力的平均值;稳定段刀盘扭矩和总推力的平均值 11×NI 注:(1)NI为训练集包含的样本数量(即掘进循环段的数量),随机挑选80%的数据作为训练集;(2)方案①仅对1个点进行预测,称之为点预测模型;方案②对11个点构成的线进行预测,称之为线预测模型. 表 5 训练集和验证集的划分
Table 5. Division of training set and verification set
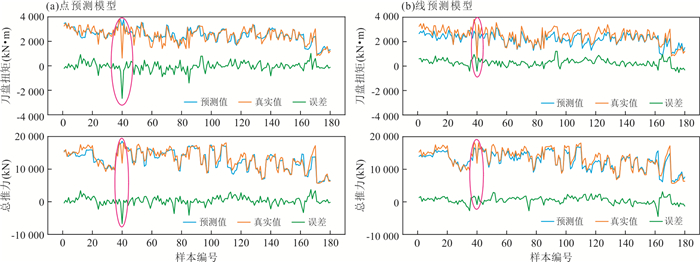
编号 样本数量 说明 验证集A 180 基于人工挑选的75个“台阶状”掘进段构建,用于评估模型预测结果能否反映控制参数的影响 验证集B 1 857 随机挑选20%,用于评估模型预测的效果 训练集C 8 883 随机挑选80%,用于模型的训练 表 6 各模型总体预测结果评估表
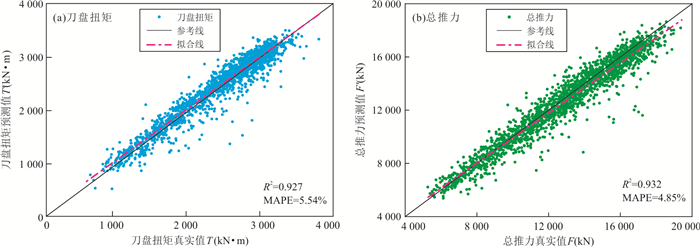
Table 6. Evaluation table of overall prediction results of each model
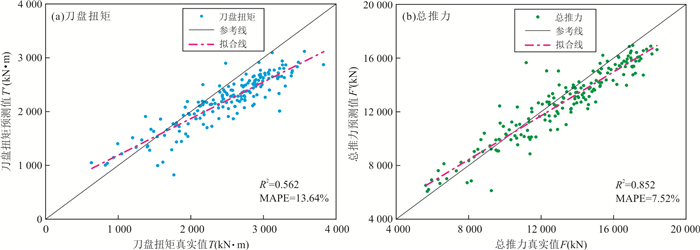
模型 评价指标 T_R2 F_R2 T_MAPE F_MAPE 点预测模型 0.927 0.932 5.54% 4.85% 线预测模型 0.600 0.865 13.34% 7.41% 表 7 考虑控制参数影响的各模型在验证集A上的预测结果
Table 7. Prediction results of models considering control parameters on verification set A
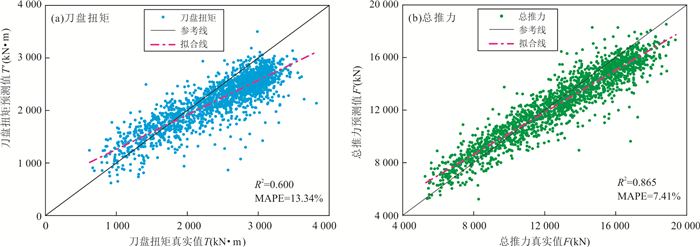
模型 评价指标 T_R2 F_R2 T_MAPE F_MAPE 点预测模型 0.589 0.823 13.48% 7.09% 线预测模型 0.562 0.852 13.64% 7.52% 表 8 稳定段行为样本和上升段行为样本的损失权重分配
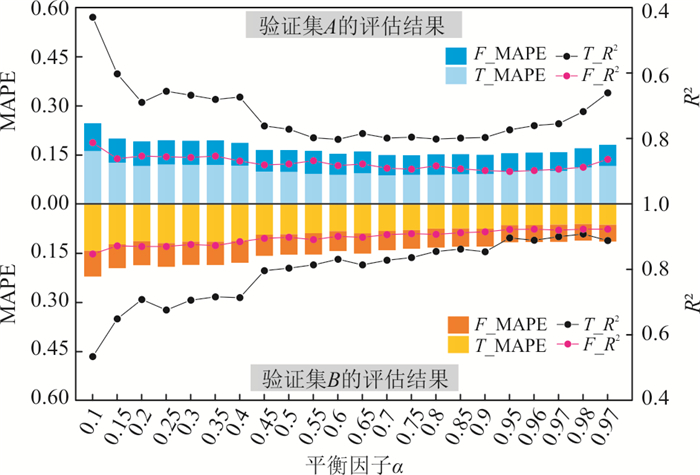
Table 8. Loss weight distribution of behavior samples in stable boring phase and loading phase
样本名称 取值 样本数量 平衡因子 稳定段行为样本 稳定段平均值 NI $ \alpha $ 上升段行为样本 按速度大小划分为十个区间,取每个区间的平均值 10×NI 1$ - $$ \alpha $ 注:NI为8 883,是训练集C所包含的样本数量(即掘进循环段的数量). 表 9 各模型在验证集A、B上的预测结果评估
Table 9. Evaluation of prediction results of each model on verification sets A and B
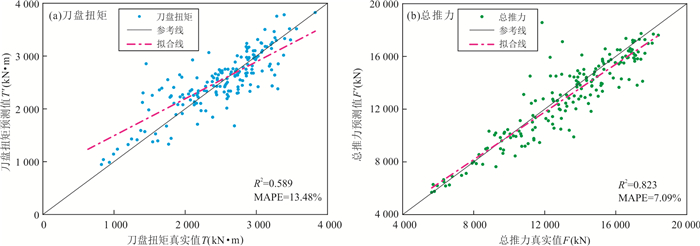
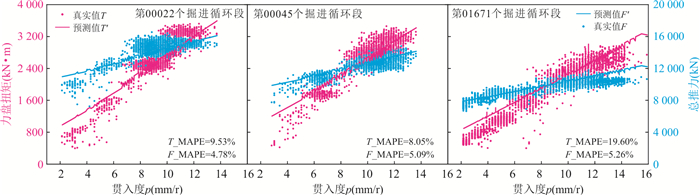
模型 评价指标 T_R2 F_R2 T_MAPE F_MAPE 验证集A 点预测模型 0.589 0.823 13.48% 7.09% 线预测模型 0.562 0.852 13.64% 7.52% 改进线预测模型 0.799 0.893 9.06% 6.14% 验证集B 点预测模型 0.927 0.932 5.54% 4.85% 线预测模型 0.600 0.865 13.34% 7.41% 改进线预测模型 0.862 0.912 7.47% 5.60% -
Chen, C., Qi, F., 2019. Review on Development of Convolutional Neural Network and Its Application in Computer Vision. Computer Science, 46(3): 63-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JSJA201903008.htm Chen, L., Lin, W. B., Chen, P., et al., 2021. Porosity Prediction from Well Logs Using Back Propagation Neural Network Optimized by Genetic Algorithm in One Heterogeneous Oil Reservoirs of Ordos Basin, China. Journal of Earth Science, 32(4): 828-838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1396-5 Chen, Z. Y., Zhang, Y. P., Li, J. B., et al., 2021. Diagnosing Tunnel Collapse Sections Based on TBM Tunneling Big Data and Deep Learning: A Case Study on the Yinsong Project, China. Tunnel and Underground Space Technology, 108: 103700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103700 Chmelina, K., Rabensteiner, K., Krusche, G., 2013. A Tunnel Information System for the Management and Utilization of Geo-Engineering Data in Urban Tunnel Projects. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 31(3): 845-859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9547-9 Gao, J. Y., Yang, X. S., Zhang, T. Z., et al., 2016. Robust Visual Tracking Method via Deep Learning. Chinese Journal of Computers, 39(7): 1419-1434 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/306126889_Robust_visual_tracking_method_via_deep_learning Guo, D., Li, J., Jiang, S. H., et al., 2021. Intelligent Assistant Driving Method for Tunnel Boring Machine Based on Big Data. Acta Geotechnica, 17: 1019-1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11440-021-01327-1 Hao, H. Z., Gu, Q., Hu, X. M., 2021. Research Advances and Prospective in Mineral Intelligent Identification Based on Machine Learning. Earth Science, 46(9): 3091-3106 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hong, K. R., Feng, H. H., 2021. Development and Thinking of Tunnels and Underground Engineering in China in Recent 2 Years (from 2019 to 2020). Tunnel Construction, 41(8): 1259-1280 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, S. K., Liu, Y. R., Zhang, K., 2020. Prediction of TBM Tunnelling Parameters Based on IPSO-BP Hybrid Model. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(8): 1648-1657 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, Z., 2014. Experimental and Munerical Study on Rock Cutting Mechanism of TBM Cutters. Central South University, Changsha (in Chinese with English abstract). Jing, L. J., Zhang, N., Yang, C., 2016. Development of TBM and Its Construction Technologies in China. Tunnel Construction, 36(3): 331-337 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94024X/201603/668453835.html Li, F. Y., Han, W. F., 2018. Building TBM Shield Project, Innovating Big Data Cloud Platform and Leading the Technological Development of the Industry. Construction Machinery & Maintenance, (2): 111-115 (in Chinese). Liu, H., 2021. Analysis of Characteristics of TBM Tunneling Data for Yinsong Project. Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Z. J., 2009. Cutterhead Design Methods of Rock Tunnel Boring Machine. Dalian University of Technology, Dalian (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, H. T., Zhang, Q. C., 2016. Applications of Deep Convolutional Neural Network in Computer Vision. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 31(1): 1-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SJCJ201601001.htm Qian, Q. H., Li, C. F., Fu, D. M., 2002. The Present and Prospect of Application of Tunneler in China's Underground Engineering. Underground Space, 22(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95765X/2002001/6054069.html Sun, W., Shi, M. L., Zhang, C., et al., 2018. Dynamic Load Prediction of Tunnel Boring Machine (TBM) Based on Heterogeneous In-Situ Data. Automation in Construction, 92(AUG. ): 23-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2018.03.030 Wang, D. T., Chen, G. X., 2022. Seismic Wave Impedance Inversion Based on Temporal Convolutional Network. Earth Science, 47(4): 1492-1506 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, S. J., Wang, Y. J., Li, X., et al., 2021. Big Data-Based Boring Indexes and Their Application during TBM Tunneling. Advances in Civil Engineering, (4): 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2621931 Wang, S. J., Wang, Y. J., Li, X., et al., 2022. Study of Standardized Pre-Processing Method of TBM Tunnelling Data. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 59(2): 38-44, 52 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, J. A., Li, J. B., Jing, L. J., et al., 2020. Design and Practice of TBM Intelligent Driving System of Key Parameters. Tunnel Construction, 40(11): 1673-1681 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yan, C. M., Wang, C., 2021. Development and Application of Convolutional Neural Network Model. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science & Technology, 15(1): 27-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, T. Z., Li, J. B., Jing, L. J., et al., 2018. Design and Practice of Cloud Computing Platform for TBM Operation Information. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 55(6): 33-41, 52 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/332867584_Design_and_Practice_of_Cloud_Computing_Platform_for_TBM_Operation_Information Zhang, S., Gong, Y. H., Wang, J. J., 2019. The Development of Deep Convolution Neural Network and Its Applications on Computer Vision. Chinese Journal of Computers, 42(3): 453-482 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8913521/ Zhang, Z. M., Li, X. Y., Ji, J., 2021. TBM Excavation Parameter Prediction Model Based on LS-SVM Method. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 49(4): 373-379 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, G. Z., Wang, Y. X., Li, Y., et al., 2020. Prediction of TBM Performance Based on Optimized BP Neural Network. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 39(5): 139-145 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9421856/ Zhou, H., Ban, S. C., Han, Y., 2009. Research and Application of TBM Optimal Tunneling Parameters. Water Resources Development & Management, 29(4): 86-88, 85 (in Chinese). http://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=0665a9d920c623d683c031ca6d1a76af Zhu, M. Q., Zhu, H. H., Wang, X., et al., 2020. Study on CART-Based Ensemble Learning Algorithms for Predicting TBM Tunneling Parameters and Classing Surrounding Rockmasses. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(9): 1860-1871 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0886779820305496 陈超, 齐峰, 2019. 卷积神经网络的发展及其在计算机视觉领域中的应用综述. 计算机科学, 46(3): 63-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA201903008.htm 高君宇, 杨小汕, 张天柱, 等, 2016. 基于深度学习的鲁棒性视觉跟踪方法. 计算机学报, 39(7): 1419-1434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201607010.htm 郝慧珍, 顾庆, 胡修棉, 2021. 基于机器学习的矿物智能识别方法研究进展与展望. 地球科学, 46(9): 3091-3106. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.360 洪开荣, 冯欢欢, 2021. 近2年我国隧道及地下工程发展与思考(2019—2020年). 隧道建设(中英文), 41(8): 1259-1280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD202108001.htm 侯少康, 刘耀儒, 张凯, 2020. 基于IPSO-BP混合模型的TBM掘进参数预测. 岩石力学与工程学报, 39(8): 1648-1657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202008013.htm 蒋喆, 2014. TBM盘形滚刀破岩机理的试验与模拟研究(硕士学位论文). 长沙: 中南大学. 荆留杰, 张娜, 杨晨, 2016. TBM及其施工技术在中国的发展与趋势. 隧道建设, 36(3): 331-337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201603018.htm 李凤远, 韩伟峰, 2018. 建设盾构TBM工程大数据云平台创新引领行业技术发展. 工程机械与维修, (2): 111-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCJW201802063.htm 刘欢, 2021. 引松工程TBM掘进数据特征分析(硕士学位论文). 北京: 北京交通大学. 刘志杰, 2009. 岩石隧道掘进机刀盘设计方法研究(博士学位论文). 大连: 大连理工大学. 卢宏涛, 张秦川, 2016. 深度卷积神经网络在计算机视觉中的应用研究综述. 数据采集与处理, 31(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJCJ201601001.htm 钱七虎, 李朝甫, 傅德明, 2002. 隧道掘进机在中国地下工程中应用现状及前景展望. 地下空间, 22(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE200201000.htm 王德涛, 陈国雄, 2022. 基于时间卷积网络的地震波阻抗反演. 地球科学, 47(4): 1492-1506. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.070 王双敬, 王玉杰, 李旭, 等, 2022. TBM掘进数据标准化预处理方法研究. 现代隧道技术, 59(2): 38-44, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD202202005.htm 徐剑安, 李建斌, 荆留杰, 等, 2020. TBM关键参数智能掘进系统的设计与实践. 隧道建设(中英文), 40(11): 1673-1681. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD202011018.htm 严春满, 王铖, 2021. 卷积神经网络模型发展及应用. 计算机科学与探索, 15(1): 27-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTS202101002.htm 于太彰, 李建斌, 荆留杰, 等, 2018. TBM施工信息云计算平台的设计与实践. 现代隧道技术, 55(6): 33-41, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD201806006.htm 张顺, 龚怡宏, 王进军, 2019. 深度卷积神经网络的发展及其在计算机视觉领域的应用. 计算机学报, 42(3): 453-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201903001.htm 张哲铭, 李晓瑜, 姬建, 2021. 基于LS-SVM的TBM掘进参数预测模型. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 49(4): 373-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX202104012.htm 赵光祖, 王亚旭, 李尧, 等, 2020. 基于优化BP神经网络的TBM性能预测. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 39(5): 139-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXB202005020.htm 周红, 班树春, 韩颖, 2009. TBM最佳掘进工作参数研究与应用. 水利建设与管理, 29(4): 86-88, 85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLJS200904035.htm 朱梦琦, 朱合华, 王昕, 等, 2020. 基于集成CART算法的TBM掘进参数与围岩等级预测. 岩石力学与工程学报, 39(9): 1860-1871. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202009012.htm -










 下载:
下载: