Comparison of InSAR Technology for Identification of Hidden Dangers of Geological Hazards in Alpine and Canyon Areas
-
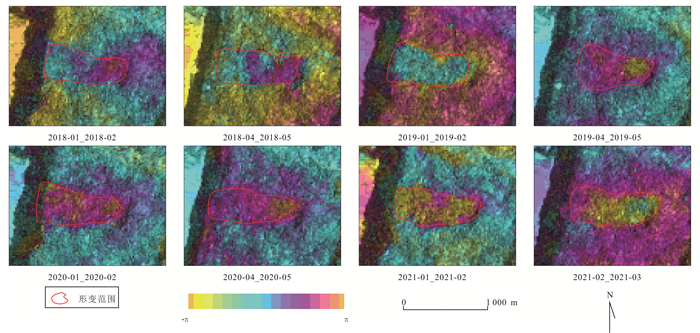
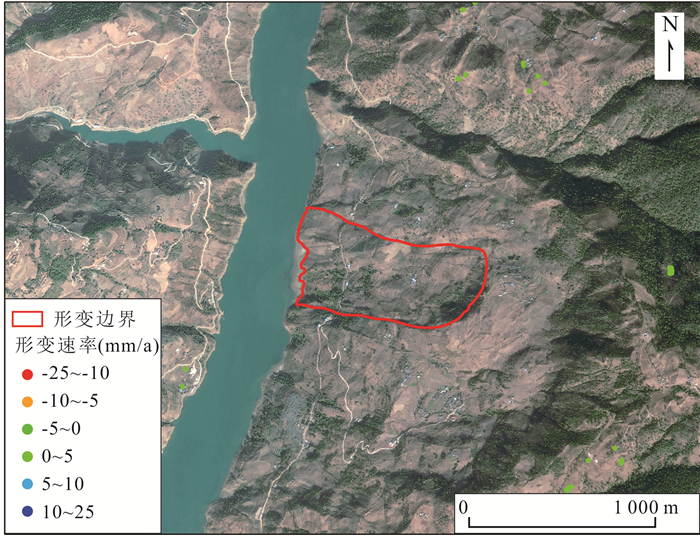
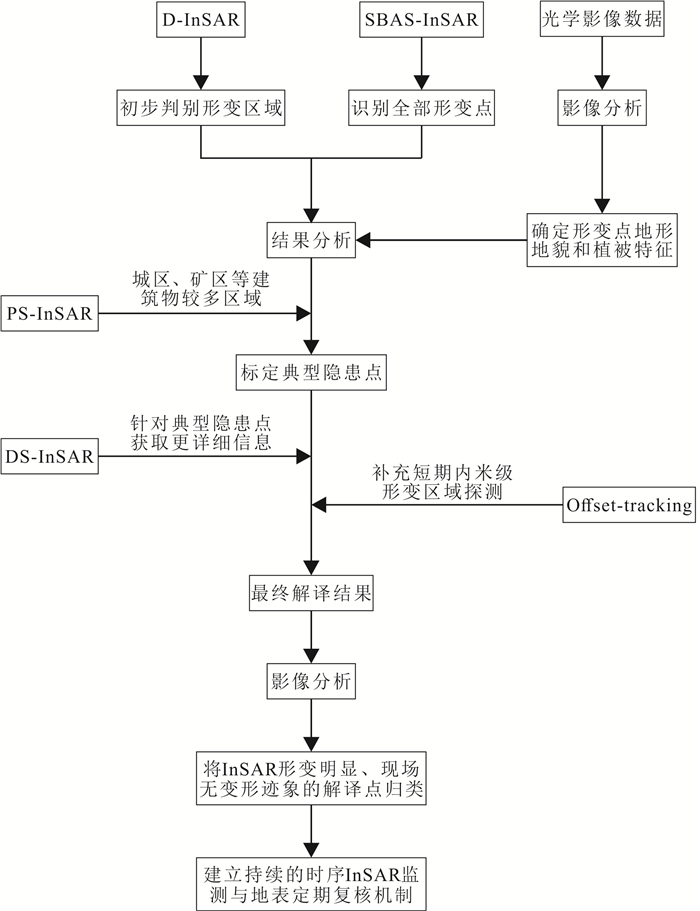
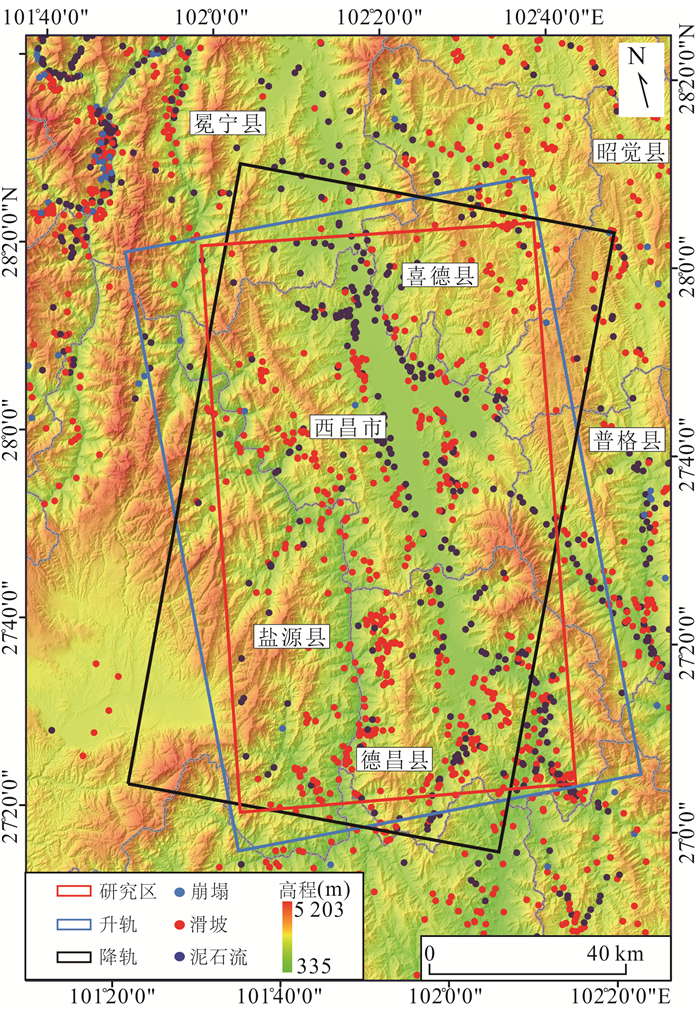
摘要: InSAR技术广泛应用于地质灾害隐患识别,不同InSAR方法具有一定的应用条件和限制因素,而高山峡谷地区地质灾害成灾机制复杂,灾害模式多样,采用一种技术方法往往难以有效识别.采用差分干涉测量(D-InSAR)、永久散射体测量(PS-InSAR)、小基线集测量(SBAS-InSAR)、分布式目标测量(DS-InSAR)和偏移量追踪(Offset-tracking)共5种InSAR技术,以雅砻江沿线西昌区域为研究区开展地质灾害隐患识别,应用不同InSAR技术方法比对分析.共识别28处形变点,其中D-InSAR识别到16处,SBAS-InSAR识别到27处,PS-InSAR识别到3处,DS-InSAR识别到21处,Offset-tracking识别到0处.在高山峡谷地区,SBAS-InSAR技术应用范围最广,识别隐患点数最多,兼顾精确度和效率,能有效识别高山峡谷地区地质灾害隐患.分析在高山峡谷地区使用InSAR技术识别地质灾害隐患的特殊性,针对不同方法技术特点,提出一种在高山峡谷地区使用InSAR技术进行地质灾害隐患识别的技术路线,使得更高效、准确地识别地质灾害隐患.Abstract: InSAR technology is widely used in the identification of hidden dangers of geological disasters. Different InSAR methods have certain application conditions and limiting factors. However, the disaster-causing mechanism of geological disasters in alpine and canyon areas is complex and the disaster patterns are diverse, which is often difficult to effectively identify using one technical method. In this paper, differential interferometry (D-InSAR), permanent scatterer measurement (PS-InSAR), small baseline set measurement (SBAS-InSAR), distributed target measurement (DS-InSAR) and offset tracking (Offset-tracking) a total of 5 InSAR technologies, taking the Xichang area along the Yalong River as the research area to identify potential geological hazards, and to carry out comparison and analysis of different InSAR technology methods. The results show that a total of 28 deformation points were identified, of which 16 were identified by D-InSAR, 27 by SBAS-InSAR, 3 by PS-InSAR, 21 by DS-InSAR, and 21 by Offset-tracking 0.In the alpine and canyon areas, SBAS-InSAR technology has the widest application range and the largest number of hidden danger points. Taking into account the accuracy and efficiency, it can effectively identify the hidden dangers of geological disasters in the alpine and canyon areas. Based on the analysis of the particularity of using InSAR technology to identify hidden dangers of geological disasters in high mountains and valleys, a technical route of using InSAR technology to identify hidden dangers of geological disasters in high mountains and valleys is proposed according to the characteristics of different methods and technologies, so as to identify hidden dangers of geological disasters more efficiently and accurately.
-
Key words:
- InSAR /
- alpine canyon area /
- hazards /
- identification of hidden danger /
- technical comparison /
- environmental geology
-
表 1 Sentinenl-1数据参数
Table 1. Sentinenl-1 data parameters
卫星 轨道方向 雷达波长(cm) 空间分辨率(m) 入射角(°) 影像时间 影像期数 极化方式 Sentinel-1A 升轨 5.6 5×20 39.87 2018/1/7‒2021/3/28; 97 VV Sentinel-1A 降轨 5.6 5×20 39.95 2018/1/9‒2021/3/30 96 VV Sentinel-1B 降轨 5.6 5×20 39.95 2018/12/17;2020/9/1‒2021/3/24. 18 VV 表 2 多种监测手段识别结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of identification results of multiple monitoring methods
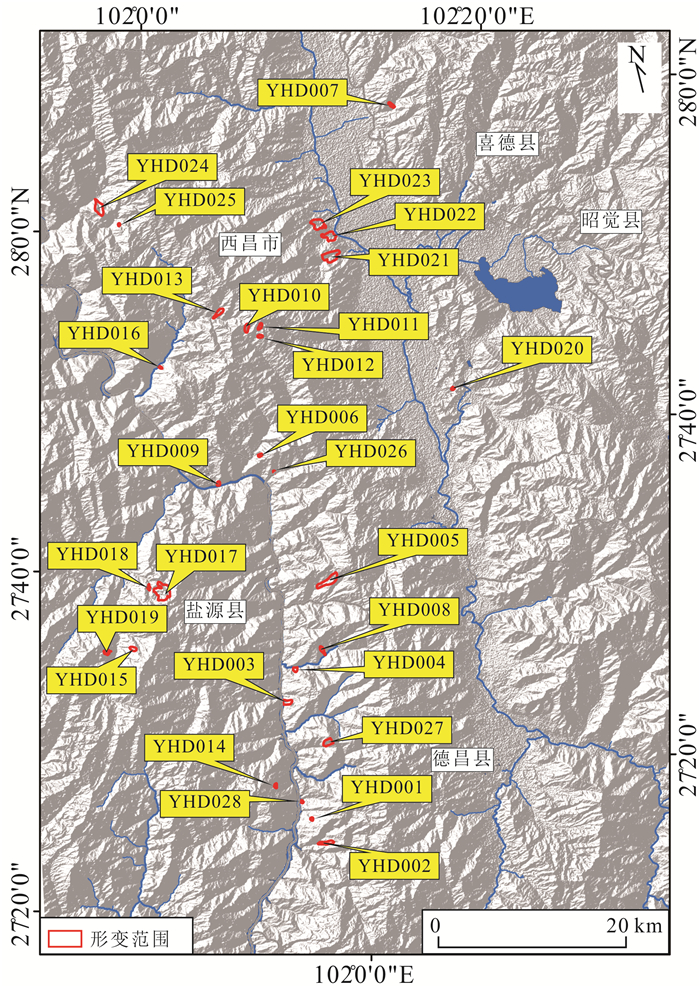
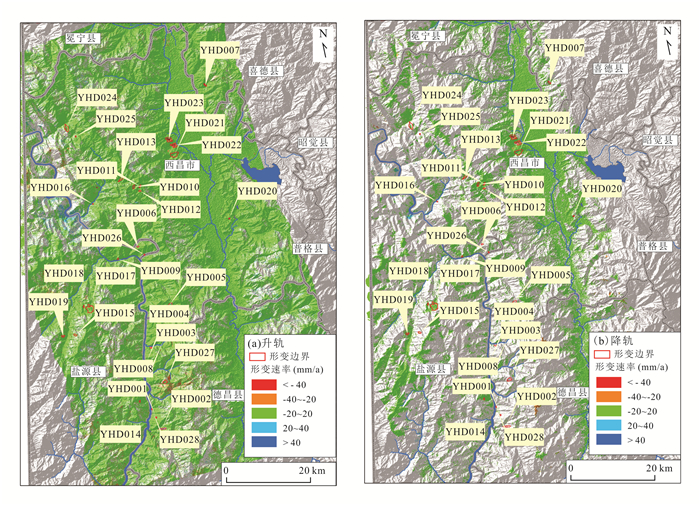
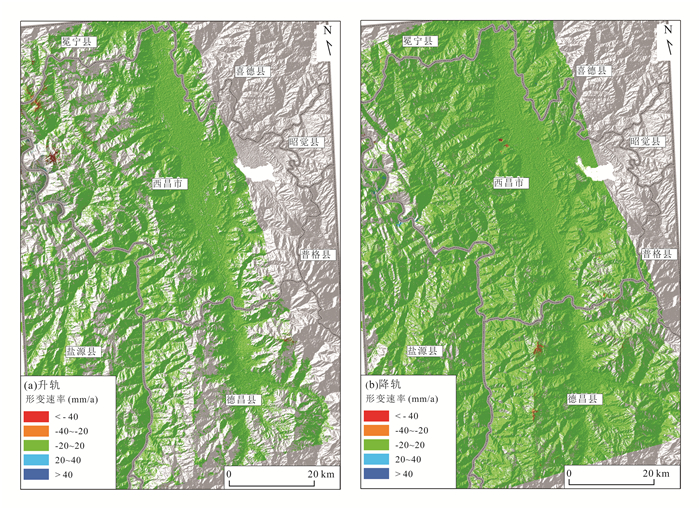
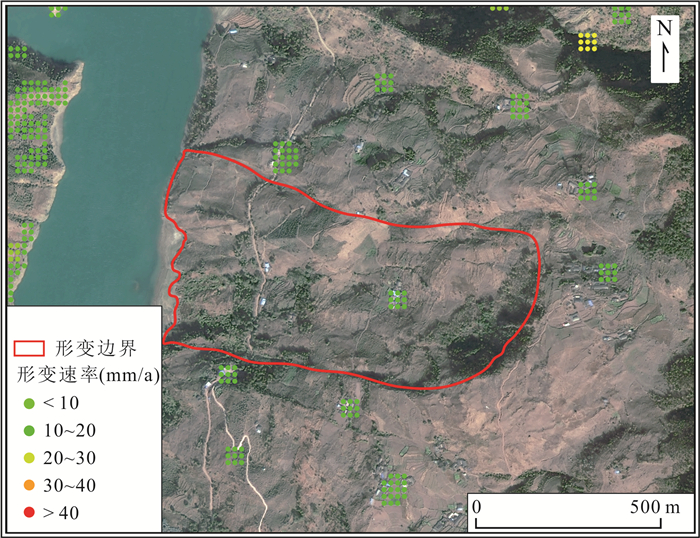
技术方法 成像模式 形变点 点数 总计 D-InSAR 升轨 YHD001、YHD002、YHD004、YHD005、YHD017、YHD018、YHD020、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD025 12处 16处 降轨 YHD001、YHD002、YHD003、YHD005、YHD013、YHD014、YHD017、YHD018、YHD020、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD027、YHD028 15处 PS-InSAR 升轨 YHD021、YHD022、YHD023 3处 3处 降轨 YHD021、YHD022、YHD023 3处 SBAS-InSAR 升轨 YHD001、YHD002、YHD003、YHD004、YHD005、YHD006、YHD007、YHD008、YHD009、YHD010、YHD014、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD025、YHD026 17处 27处 降轨 YHD002、YHD003、YHD005、YHD011、YHD012、YHD013、YHD015、YHD016、YHD017、YHD018、YHD019、YHD020、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD025、YHD026、YHD027 19处 DS-InSAR 升轨 YHD001、YHD002、YHD003、YHD008、YHD009、YHD010、YHD014、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD026 12处 21处 降轨 YHD002、YHD003、YHD012、YHD015、YHD016、YHD017、YHD018、YHD019、YHD020、YHD021、YHD022、YHD023、YHD024、YHD025、YHD028 15处 Offset-tracking 升轨 无 0处 0处 降轨 表 3 监测点形变量和形变速率
Table 3. Monitoring point deformation and deformation rates
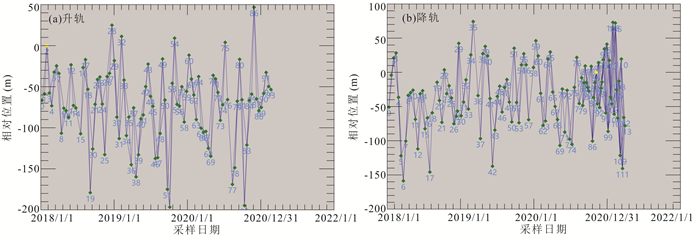
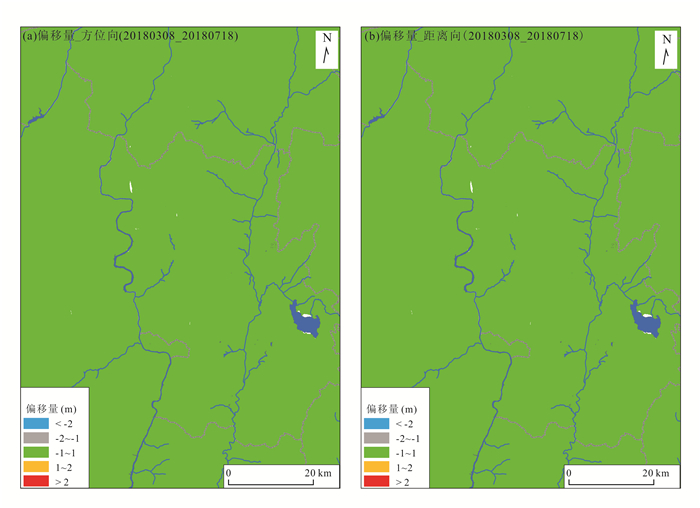
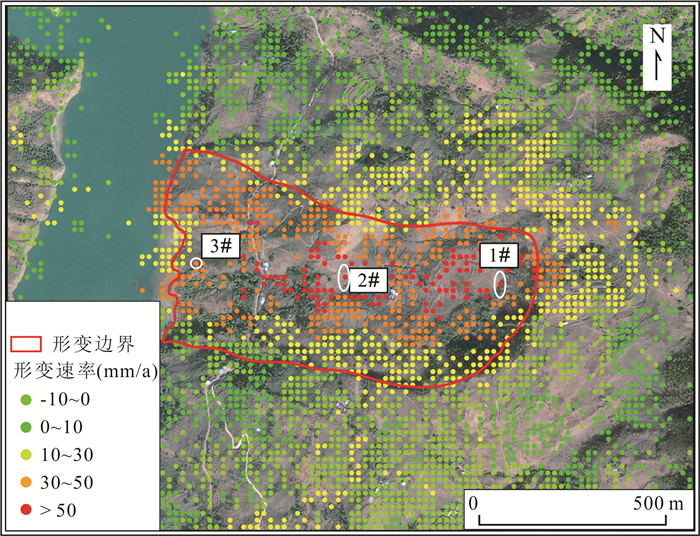
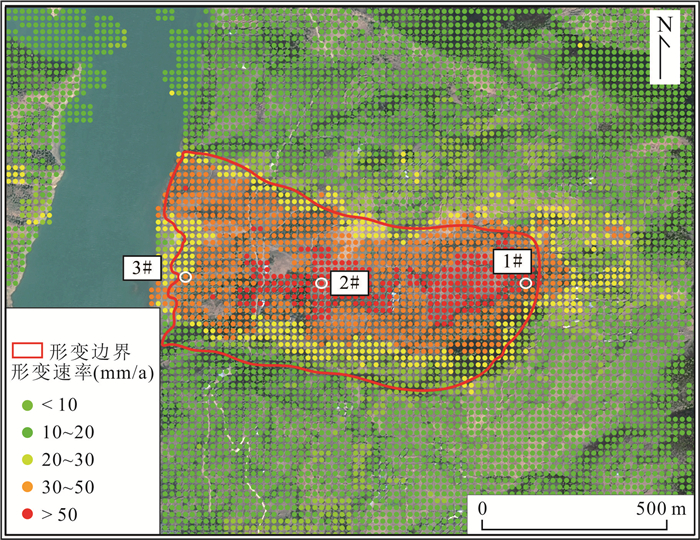
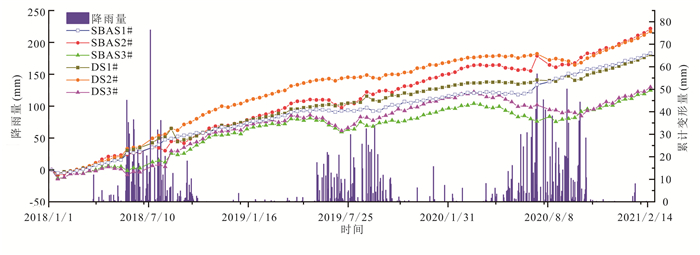
技术方法 监测点位 累计形变量(mm) 形变速率(mm/a) SBAS-InSAR(升轨) 1# 182.78 53.02 2# 221.49 67.20 3# 124.81 36.28 DS-InSAR(升轨) 1# 180.54 52.37 2# 216.99 65.83 3# 129.69 37.70 表 4 多种InSAR监测手段差异性对比
Table 4. Difference comparison of various InSAR monitoring methods
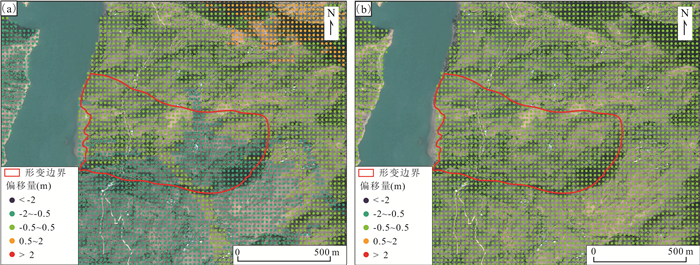
监测手段 适用区域 精度 速度 优点 缺点 D-InSAR 短期内厘米级形变区域 厘米级 快 覆盖范围广、需要数量少、成本低、应用广泛 易受干涉失相关、大气延迟等误差影响,结果依赖于DEM精度 PS-InSAR 植被较少、干涉条件较稳定的区域 毫米级 中 精度高、可以得到时序数据 需要数据多、效率低、结果依赖于PS点密度 SBAS-InSAR 长期缓慢毫米级形变区域 毫米级 中 数据利用率高、精度高、可提取非线性形变、应用广泛 成本高、高相干点获取较难 DS-InSAR 小范围形变区域 毫米级 慢 数据利用率高、结果精度高、形变点密度高 计算效率低,不适用于大范围区域监测 Offset-tracking 短期内米级形变区域 米级 快 不受相干性限制,速度快 精度不及其他InSAR技术,形变监测受影像空间分辨率影响 -
Berardino, P., Fornaro, G., Lanari, R., et al., 2002. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 40(11): 2375-2383. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792 Chen, F. L, Hui, L., Zhen, L., et al., 2012. Interaction between Permafrost and Infrastructure along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway Detected via Jointly Analysis of C- and L-band Small Baseline SAR Interferometry. Remote Sensing of Environment, 123: 532-540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.04.020 Costantini, M., Ferretti, A., Minati, F., et al., 2017. Analysis of Surface Deformations over the Whole Italian Territory by Interferometric Processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-Sky Med Radar Data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 202: 250-275. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.017 Dai, K., Chen, G., Xu, Q., et al., 2018. Potential Landslide Early Detection near Wenchuan by a Qualitatively Multi-baseline D InSAR Method. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-3: 253-256. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-253-2018 Ferretti, A., Prati, C., Rocca, F., 2001. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 39(1): 8-20. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.898661 Gabriel, A. K., Goldstein, R. M., Zebker, H. A., 1989. Mapping Small Elevation Changes over Large Areas: Differental Radar Interferometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 94(B7): 9183-9191. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB07p09183 Gong, W., Thiele, A., Hinz, S., et al., 2016. Comparsion of Small Baseline Interferometric SAR Processors for Estimating Ground Deformation. Remote Sensing, 8(4): 330. doi: 10.3390/rs8040330 Grandin, R., Klein, E., Métois, M., et al., 2016. Three-Dimensional Displacement Field of the 2015 Mw 8.3 Illapel Earthquake (Chile) from Across- and Along-Track Sentinel-1 TOPS Interferometry. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(6): 2552-2561. Hooper, A., Bekaert, D., Spaans, K., et al., 2012. Recent Advances in SAR Interferometry Time Series Analysis for Measuring Crustal Deformation. Tectonophysics, 514: 1-13. Hu, X., Wang, T., Liao, M. S., 2014. Meassring Coseismic Displacements with Point-Like Targets Offset Tracking. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11(1): 283-287. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2256104 Huang, R., Han, J. Q., Li, J. T., et al., 2021. Research on Application of PS-InSAR Technology in Subsidence Monitoring of Sino-Myanmar Oil and Gas Pipelines. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 59(16): 1628006 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, J. X., Du, Y. L., Chen, Y., et al., 2021. Monitoring and Analysis of Surface Deformation in Peibei Mining Region Based on DS-InSAR Technique. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (2): 117-121 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, K. G., Wang, L., Teng, C. Q., et al., 2021. Research on Dynamic Monitoring Method of Surface Three-Dimensional Deformation of Coal Mine Based on Fusion of Single Sight D-InSAR and BK Model. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University (in Chinese with English abstract). Lanari, R., Mora, O., Manunta, M., et al., 2004. A Small-Baseline Approach for Investigating Deformations on Full-Resolution Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42(7): 1377-1386. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.828196 Li, S., Wen, J. S., Hu, H. F., 2021. Research on Large Gradient Deformation of Mining Area Based on InSAR Technology. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 46(11): 56-62, 97 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X. E., Zhou, L., Su, F. Z., et al., 2021. Application of InSAR Technology in Landslide Hazard: Progress and Prospects. Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(2): 614-629(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Z. H., Song, C., Yu, C., et al., 2019. Application of Satellite Radar Remote Sensing to Landslide Detection and Monitoring: Challenges and Solutions. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 967-979 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lin, H., Ma, P. F., Wang, W. X., 2017. Urban Infrastructure Health Monitoring with Spaceborne Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 46(10): 1421-1433 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, G. X., Chen, Q., Luo, X. J., et al., 2019. Principle and Application of InSAR. Science Press, Beijing, 9 (in Chinese). Liu, P. Y., Chang, M., Wu, B. B., et al., 2022. Route Selection of Landslide Prone Area in Wenchuan Section of Chengdu-Wenchuan Expressway Based on SBAS-InSAR. Earth Science, 47(6): 2048-2057 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mohammed, O. I., Saeidi, V., Pradhan, B., et al., 2014. Advanced Differential Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar Techniques for Deformation Monitoring: A Review on Sensors and Recent Research Development. Geocarto International, 29(5): 536-553. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.807305 Raucoules, D., de Michele, M., Malet, J. P., et al., 2013. Time-Variable 3D Ground Displacements from High-Resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): Application to La Valette Landslide (South French Alps). Remote Sensing of Environment, 139: 198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.006 Wang, X. L., Du, Y. L., Jiang, J. X., et al., 2021. Monitoring of Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Surface Deformation in Yuncheng Mining Area with DS-InSAR. Safety in Coal Mines, 52(5): 120-125 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, X. M., Yin, J., Luo, M. H., et al., 2021. Active High-Locality Landslides in Mao County: Early Identification and Deformational Rules. Journal of Earth Science: 1-39. Wang, X. W., Liu, G. X., Yu, B., et al., 2014.3D Coseismic Deformations and Source Parameters of the 2010 Yushu Earthquake (China) Inferred from D InSAR and Multiple-Aperture InSAR Measurements. Remote Sensing of Environment, 152: 174-189. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.06.014 Wang, Z. D., Wen, X. H., Tang, W., et al., 2020. Early Detection of Geological Hazards in Longmenshan‐Dadu River Area Using Various InSAR Techniques. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 45(3): 451-459 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, H., Fan, H. D., Zhen, C. L, et al., 2022. Deformation Monitoring and Analysis of Tailings Dam Based on DS-InSAR: A Case Study of Brumadinho Mine in Brazil. Metal Mine (in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, M. L., Zhao, J. J., Ju, N. P., et al., 2020. Research on Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Landslide Based on Multisource Data: A Case Study of Huangnibazi Landslide. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 45(6): 923-932 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Q., Dong, X. J., Li, W. L., 2019. Integrated Space-Air-Ground Early Detection, Monitoring and Warning System for Potential Catastrophic Geohazards. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 957-966 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, X. B., Ma, C., Shan, X. J., et al., 2020. Monitoring Ground Subsidence in High-Intensity Mining Area by Integrating D InSAR and Offset-Tracking Technology. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 22(12): 2425-2435 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, C. S., Zhang, Q., Zhao, C. Y., et al., 2014. Small Baseline Bubset InSAR Technology Used in Datong Basin Ground Subsidence, Fissure and Fault Zone Monitoring. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 39(8): 945-950 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, L., Liao, M. S., Dong, J., et al., 2018. Early Detection of Landslide Hazards in Mountainous Areas of West China Using Time Series SAR Interferometry—A Case Study of Danba, Sichuan. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 43(12): 2039-2049 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, G. P., 2016. Structure Character Research of the Daliang Mountain in the Southern Margin of Sichuan Basin (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, 7-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, D. Y., Zuo, X. Q., Xi, W. F., et al., 2022. Early Identification of Landslide Hazards in Deep Cut Alpine Canyon Using SBAS-InSAR Technology. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 33(2): 16-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhuo, G. C., Dai, K. R., Zhou, F. J., et al., 2021. Monitoring Typical Construction Sites of Sichuan-Tibet Railway by InSAR and Intensive Distortion Analysis. Earth Science (in Chinese with English abstract). 黄锐, 韩建强, 李进田, 等, 2021. PS-InSAR技术在中缅油气管道沉降监测中的应用研究. 激光与光电子学进展, 59(16): 1628006. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ202216053.htm 蒋金雄, 杜玉玲, 陈宇, 等, 2021. 利用DS-InSAR技术监测沛北矿区地表形变. 测绘通报, (2): 117-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB202102024.htm 江克贵, 王磊, 滕超群, 2021. 融合单视线D-InSAR和BK模型的煤矿地表三维变形动态监测方法研究. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH202304015.htm 李帅, 温建生, 胡海峰, 2021. 融合InSAR技术的矿区大梯度形变研究. 测绘科学, 46(11): 56-62, 97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD202111009.htm 李晓恩, 周亮, 苏奋振, 等, 2021. InSAR技术在滑坡灾害中的应用研究进展. 遥感学报, 25(2): 614-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB202102008.htm 李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等, 2019. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(7): 967-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907003.htm 林珲, 马培峰, 王伟玺, 2017. 监测城市基础设施健康的星载MT-InSAR方法介绍. 测绘学报, 46(10): 1421-1433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201710026.htm 刘国祥, 陈强, 罗小军, 等, 2019. InSAR原理与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXYY201520027.htm 刘沛源, 常鸣, 武彬彬, 等, 2022. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的成汶高速汶川段滑坡易发区选线研究. 地球科学, 47(6): 2048-2057. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.069 王新玲, 杜玉玲, 蒋金雄, 等, 2021. 郓城矿区地表形变时空演变DS-InSAR监测. 煤矿安全, 52(5): 120-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ202105020.htm 王之栋, 文学虎, 唐伟, 等, 2020. 联合多种InSAR技术的龙门山‒大渡河区域地灾隐患早期探测. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 45(3): 451-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH202003017.htm 吴昊, 范洪冬, 郑春柳, 等, 2022. 基于DS-InSAR的尾矿库变形监测与分析——以巴西Brumadinho矿为例. 金属矿山. 解明礼, 赵建军, 巨能攀, 等, 2020. 多源数据滑坡时空演化规律研究: 以黄泥坝子滑坡为例. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 45(6): 923-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH202006016.htm 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐, 2019. 基于天‒空‒地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(7): 957-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907002.htm 徐小波, 马超, 单新建, 等, 2020. 联合D InSAR与Offset-tracking技术监测高强度采区开采沉陷的方法. 地球信息科学学报, 22(12): 2425-2435. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX202012014.htm 杨成生, 张勤, 赵超英, 等, 2014. 短基线集InSAR技术用于大同盆地地面沉降、地裂缝及断裂活动监测. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 39(8): 945-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201408012.htm 张路, 廖明生, 董杰, 等, 2018. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别: 以四川丹巴为例. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 43(12): 2039-2049. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201812031.htm 赵高平, 2016. 四川盆地南缘大凉山地区构造特征研究(硕士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学, 7-8. 周定义, 左小清, 喜文飞, 等, 2022. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的深切割高山峡谷区滑坡灾害早期识别. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 33(2): 16-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202202003.htm 卓冠晨, 戴可人, 周福军, 等, 2021. 川藏铁路典型工点InSAR监测及几何畸变精细判识. 地球科学. -









 下载:
下载: