Temporal and Spatial Variation of Wet Deposition of Nitrogen in the Source Region of the Yangtze River
-
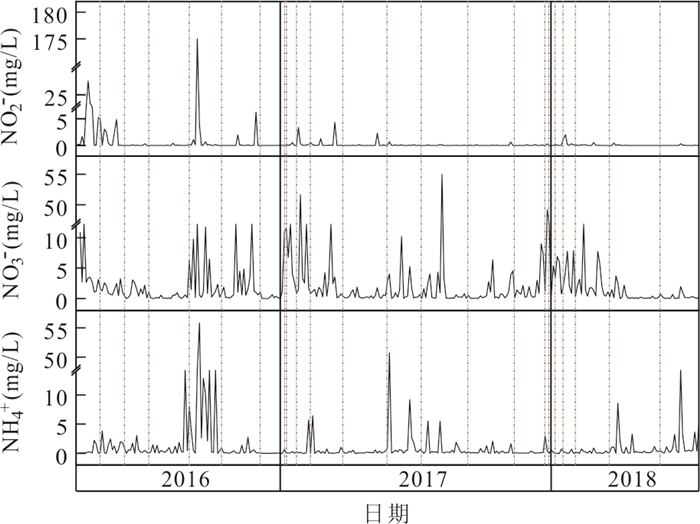
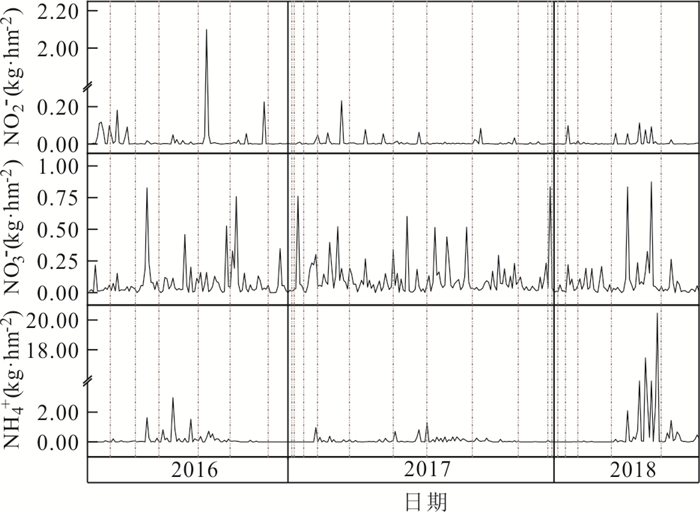
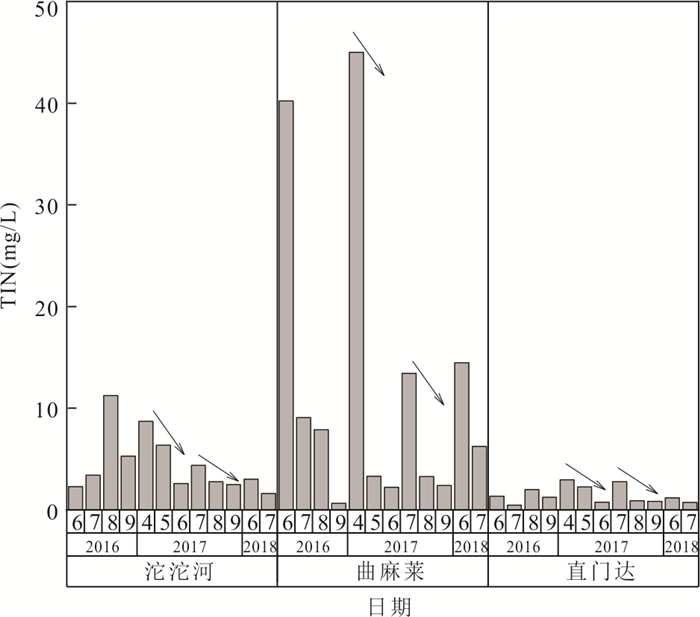
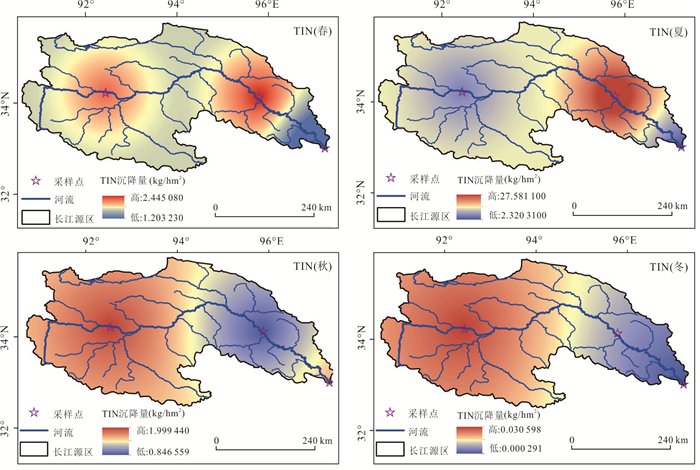
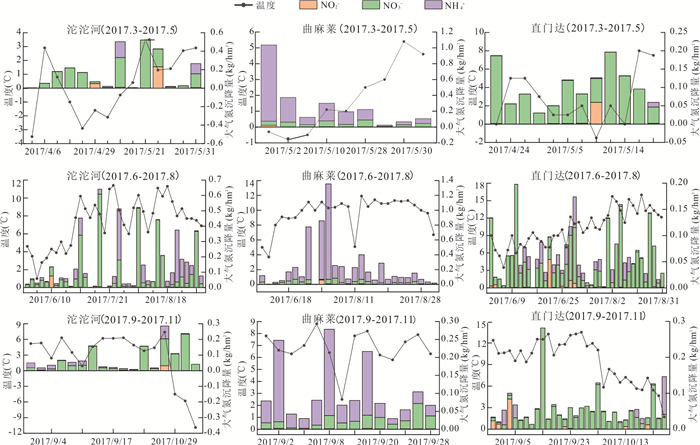
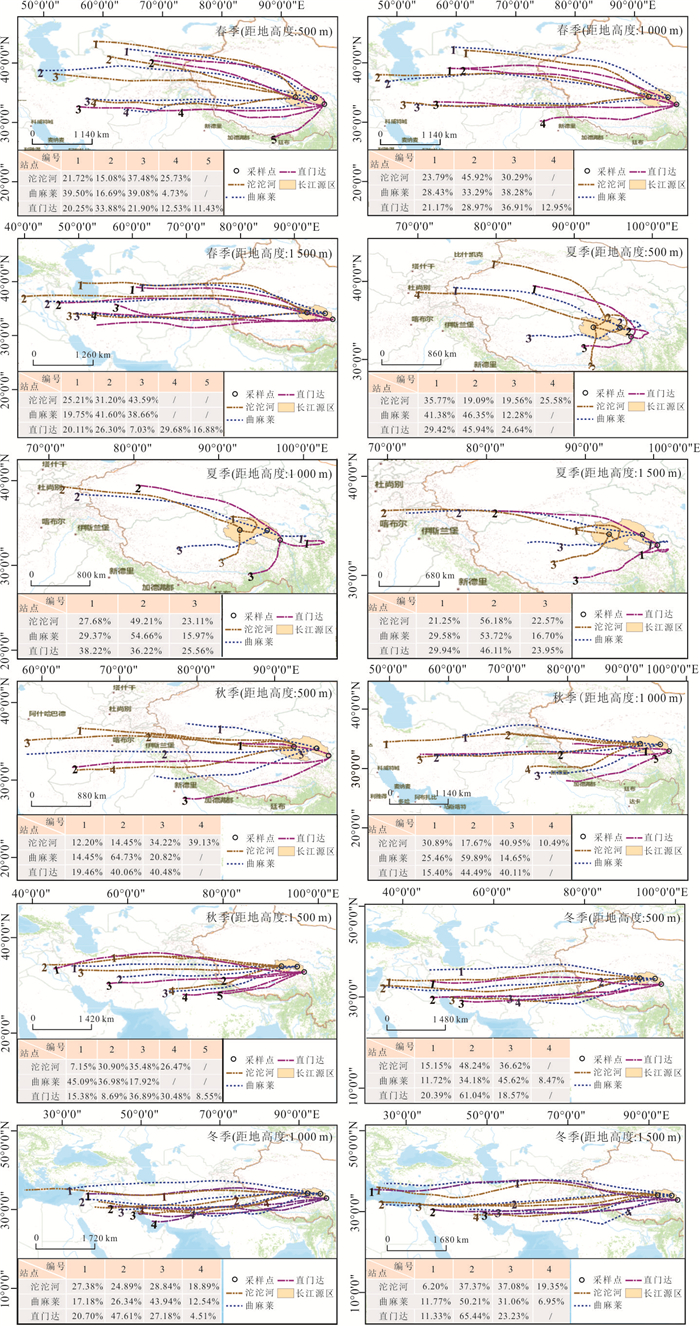
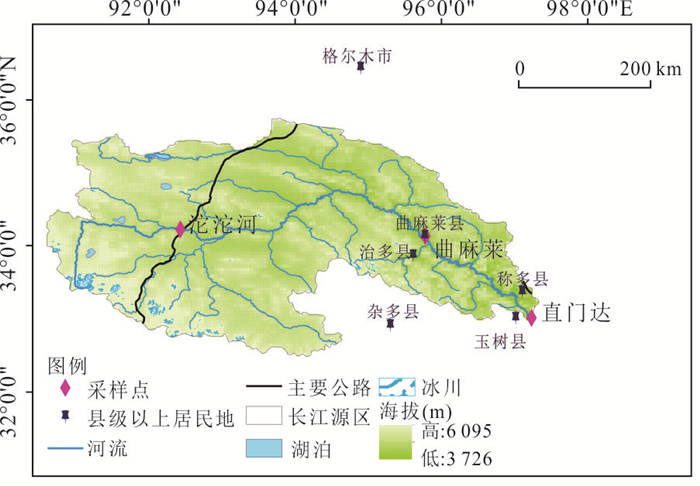
摘要: 长江源区作为亚洲第一长河的发源地,探究其氮沉降特征,对于保护我国水源地安全具有十分重要的意义.本文在野外采样、数理分析的基础上,利用氮源分析及后向轨迹模型判断氮沉降的环境意义.结果表明:(1)2016年4月-2018年7月,NO2--N、NO3--N、NH4+-N的平均浓度分别为1.01 mg/L、2.45 mg/L、1.30 mg/L;NO2--N、NO3--N、NH4+-N的平均沉降量分别为0.02 kg/hm2、0.09 kg/hm2、0.30 kg/hm2.曲麻莱氮浓度占源区比重最高,沱沱河次之,直门达最小,且春、夏季氮沉降量高于秋、冬季.(2)氮沉降浓度与降水量之间呈对数函数关系,沉降量与降水量之间呈正向幂函数关系;NO2--N、NO3--N沉降量与温度呈负相关性,NH4+-N与温度呈正相关性.(3)长江源区夏季NH4+-N沉降增加主要源于牧民放牧,冬季NOx--N沉降增加主要源于煤炭燃烧,且污染物传递还受到西风环流及局地环流影响,境外来源更多集中在西亚地区.Abstract: As the source of the longest river in Asia, the source region of the Yangtze River is great significance to explore its nitrogen deposition characteristics for protecting the safety of water sources in China. The result shows: (1) From April 2016 to July 2018, the average concentrations of NO2--N、NO3--N and NH4+-N were 1.01 mg/L, 2.45 mg/L and 1.30 mg/L respectively, the average deposition of NO2--N、NO3--N and NH4+-N were 0.02 kg/hm2、0.09 kg/hm2、0.30 kg/hm2. Qumalai had the highest proportion to the overall nitrogen deposition concentration in the source region of the Yangtze River, followed by the Tuotuo River, Zhimenda was the smallest, and the nitrogen deposition in spring and summer was higher than that in autumn and winter. (2) There was a logarithmic function relationship between nitrogen concentration and precipitation, and a positive power function relationship between deposition and precipitation; NO2--N and NO3--N deposition were negatively correlated with temperature, and NH4+-N was positively correlated with temperature. (3) The increase in NH4+-N deposition in the source region of the Yangtze River in summer is mainly due to grazing by herdsmen, and the increase in NOx--N deposition in winter is mainly due to coal combustion, and the transmission of pollutants is also affected by westerly circulation and local circulation, and overseas sources are more concentrated in West Asia.
-
表 1 长江源区采样点NH4+-N/NOx--N
Table 1. NH4+-N/NOx--N of the source region of the Yangtze River
春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 直门达 0.10 0.48 0.12 0.12 曲麻莱 4.42 3.35 2.77 0.26 沱沱河 0.17 0.90 0.13 0.01 表 2 大气氮沉降浓度与温度的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis between N concentration and temperature
NO2‒-N浓度 NO3‒-N浓度 NH4+-N浓度 TIN浓度 温度 ‒0.178** ‒0.192** 0.147** ‒0.079 注:显著性(双尾):**在0.01水平上显著. 表 3 大气氮沉降量与温度的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis between N deposition and temperature
NO2‒-N沉降量 NO3‒-N沉降量 NH4+-N沉降量 TIN沉降量 温度 ‒0.008 ‒0.042 0.085 0.080 注:显著性(双尾):**在0.01水平上显著. -
Adams, P. J., Seinfeld, J. H., Koch, D. M., 1999. Global Concentrations of Tropospheric Sulfate, Nitrate, and Ammonium Aerosol Simulated in a General Circulation Model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 104(D11): 13791-13823. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999jd900083 Barile, P. J., Lapointe, B. E., 2005. Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition from a Remote Source Enriches Macroalgae in Coral Reef Ecosystems near Green Turtle Cay, Abacos, Bahamas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(11): 1262-1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.04.031 Cai, Y. Q., Li, W. H., Yu, Z. X., et al., 2022. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Precipitation in the Headwaters of the Yangtze River. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 39(5): 28-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, Z. L., Huang, T., Huang, X. H., et al., 2019. Characteristics, Sources and Environmental Implications of Atmospheric Wet Nitrogen and Sulfur Deposition in Yangtze River Delta. Atmospheric Environment, 219: 116904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.116904 Cong, Z. Y., Kawamura, K., Kang, S. C., et al., 2015. Penetration of Biomass-Burning Emissions from South Asia through the Himalayas: New Insights from Atmospheric Organic Acids. Scientific Reports, 5: 9580. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09580 Cui, L. K., Song, X. Q., Zhong, G. Q., 2021. Comparative Analysis of Three Methods for HYSPLIT Atmospheric Trajectories Clustering. Atmosphere, 12(6): 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060698 Galloway, J. N., Dentener, F. J., Capone, D. G., et al., 2004. Nitrogen Cycles: Past, Present, and Future. Biogeochemistry, 70(2): 153-226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-0370-0 Galloway, J. N., Townsend, A. R., Erisman, J. W., et al., 2008. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science, 320(5878): 889-892. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136674 Gao, S. Y., Fan, Q. S., Cao, X., et al., 2014. Glacial Fluctuation in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 17: 012135. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/17/1/012135 Gou, Y. J., 2021. Research on the Ecological Product Value Realization of the Sanjiangyuan (Dissertation). Qinghai Normal University, Qinghai, 81-93 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gruber, N., Galloway, J. N., 2008. An Earth-System Perspective of the Global Nitrogen Cycle. Nature, 451(7176): 293-296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06592 Jia, J. Y., Zhang, Y., Cai, X. B., et al., 2009. A Dynamic Changes of Wet Deposition of Nitrogen in Southeast Tibet: Taking Linzhi Experiment Station as an Example. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(4): 1907-1913 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.04.034 Li, Y., Cao, M. D., Jin, M. G., et al., 2020. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Tracing of Nitrate Sources in Quanshui River Catchment, Hubei Province. Earth Science, 45(3): 1061-1070 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Su, F. G., Tang, Q. H., et al., 2022. Contributions of Moisture Sources to Precipitation in the Major Drainage Basins in the Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 65(6): 1088-1103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-021-9890-6 Li, Z. J., Duan, R., Ke, H. C., et al., 2022. Research Progress of Ecological Hydrology Based on Hydrochemical Characteristics in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 44(1): 288-298 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Z. J., Li, Z. X., Song, L. L., et al., 2020. Precipitation Chemistry in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. Atmospheric Research, 245: 105073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105073 Liu, C. M., Wan, X. J., Zeng, W. K., et al., 2018. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Bulk Nitrogen Deposition in the Dongting Lake Region. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(3): 1137-1146 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, X. J., Zhang, Y., Han, W. X., et al., 2013. Enhanced Nitrogen Deposition over China. Nature, 494(7438): 459-462. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11917 Liu, Y. W., Xu, R., Wang, Y. S., et al., 2015. Wet Deposition of Atmospheric Inorganic Nitrogen at Five Remote Sites in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(20): 11683-11700 doi: 10.5194/acp-15-11683-2015 Lu, J. P., Zhang, X. J., Liu, Y. X., et al., 2021. Variation Characteristics and Source Analysis of Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition Flux on a Reservoir in Sand Source Areas of Beijing-Inner Mongolia. China Environmental Science, 41(3): 1034-1044 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.03.005 Pan, Y. P., Wang, Y. S., Tang, G. Q., et al., 2012. Wet and Dry Deposition of Atmospheric Nitrogen at Ten Sites in Northern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(14): 6515-6535. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-6515-2012 Paulot, F., Jacob, D. J., Henze, D. K., 2013. Sources and Processes Contributing to Nitrogen Deposition: An Adjoint Model Analysis Applied to Biodiversity Hotspots Worldwide. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(7): 3226-3233. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3027727 Qiu, J., 2015. Pollutants Waft over the Himalayas. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2015.17312 Schumann, U., Huntrieser, H., 2007. The Global Lightning-Induced Nitrogen Oxides Source. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7(14): 3823-3907. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-3823-2007 Wang, G. Z., Liu, S. J., Yu, X. N., 2021. Characteristics of Precipitation Chemistry and Wet Deposition in Zhuhai, China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 34(7): 1612-1620 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, L. F., Song, L. L., Cai, Y. Q., et al., 2017. Study on the Characteristics and Sources of Acid Rain in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. Plateau Meteorology, 36(5): 1386-1393 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, R., Ding, J. L., Ma, W., et al., 2021. Analysis of Atmospheric Particulates Source in Urumqi Based on PSCF and CWT Models. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(8): 3033-3042 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, S. Y., He, X. B., Wu, J. K., et al., 2019. Chemical Characteristics and Ionic Sources of Precipitation in the Source Region of the Yangtze River. Environmental Science, 40(10): 4431-4439 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiao, T., Qi, Y. Q., Wang, J. B., 2010. Nitrogen Budget Estimation Based on Precipitation and Runoff in the Source of Yangtze River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(19): 5404-5412 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, W., Luo, X. S., Pan, Y. P., et al., 2015. Quantifying Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition through a Nationwide Monitoring Network across China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(21): 12345-12360. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-12345-2015 Xu, W., Zhao, Y. H., Liu, X. J., et al., 2018. Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition in the Yangtze River Basin: Spatial Pattern and Source Attribution. Environmental Pollution, 232: 546-555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.086 Yu, C. X., Deng, X. L., Shi, C. E., et al., 2018. The Scavenging Effect of Precipitation and Wind on PM2.5 and PM10. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(12): 4620-4629 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, W. T., Jiang, C. M., Ma, Q., et al., 2011. Observation of the Nitrogen Deposition in the Lower Liaohe River Plain, Northeast China and Assessing Its Ecological Risk. Atmospheric Research, 101(1-2): 460-468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.04.011 Zhang, X. J., Lu, J. P., Ma, T. L., et al., 2017. Wet Deposition of Atmospheric Nitrogen and Phosphorus and Its Impact on Water Environment of Reservoir in Sand Source Area. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(12): 2093-2101 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X. Y., Edwards, R., 2011. Anthropogenic Sulfate and Nitrate Signals in Snow from Bogda Glacier, Eastern Tianshan. Journal of Earth Science, 22(4): 490-502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-011-0196-3 Zhang, X., Lin, C. Y., Zhou, X. L., et al., 2019. Concentrations, Fluxes, and Potential Sources of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Species in Atmospheric Wet Deposition of the Lake Qinghai Watershed, China. Science of the Total Environment, 682: 523-531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.224 Zhao, X., Yan, X. Y., Xiong, Z. Q., et al., 2009. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Inorganic Nitrogen Wet Deposition to the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 203(1): 277-289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0011-2 Zhao, Z. Z., 2015. Characterization and Source Analysis of Atmopheric Aerosol over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (Dissertation). Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi'an, 31-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, X. H., Fu, C. B., Xu, X. K., et al., 2002. The Asian Nitrogen Cycle Case Study. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 31(2): 79-87. https://doi.org/10.1579/0044-7447-31.2.79 Zhu, J. X., He, N. P., Wang, Q. F., et al., 2015. The Composition, Spatial Patterns, and Influencing Factors of Atmospheric Wet Nitrogen Deposition in Chinese Terrestrial Ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 511: 777-785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.038 蔡宜晴, 李文辉, 于泽兴, 等, 2022. 长江源区降水时空演变规律. 长江科学院院报, 39(5): 28-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202205005.htm 苟廷佳, 2021. 三江源生态产品价值实现研究(博士学位论文). 青海: 青海师范大学, 81-93. 贾钧彦, 张颖, 蔡晓布, 等, 2009. 藏东南大气氮湿沉降动态变化: 以林芝观测点为例. 生态学报, 29(4): 1907-1913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB200904036.htm 李严, 曹明达, 靳孟贵, 等, 2020. 湖北泉水河流域水化学特征和硝酸盐来源示踪. 地球科学, 45(3): 1061-1070. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.060 李宗杰, 段然, 柯浩成, 等, 2022. 基于水化学特征的长江源区生态水文学研究进展. 冰川冻土, 44(1): 288-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202201025.htm 刘超明, 万献军, 曾伟坤, 等, 2018. 洞庭湖大气氮湿沉降的时空变异. 环境科学学报, 38(3): 1137-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201803037.htm 卢俊平, 张晓晶, 刘廷玺, 等, 2021. 京蒙沙源区水库大气氮沉降变化特征及源解析. 中国环境科学, 41(3): 1034-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ202103007.htm 王国祯, 刘偲嘉, 于兴娜, 2021. 珠海市降水化学与沉降特征. 环境科学研究, 34(7): 1612-1620. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202107012.htm 王烈福, 宋玲玲, 蔡玉琴, 等, 2017. 长江源酸雨变化特征及来源分析. 高原气象, 36(5): 1386-1393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYQX201705021.htm 汪蕊, 丁建丽, 马雯, 等, 2021. 基于PSCF与CWT模型的乌鲁木齐市大气颗粒物源区分析. 环境科学学报, 41(8): 3033-3042. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202108008.htm 汪少勇, 何晓波, 吴锦奎, 等, 2019. 长江源区大气降水化学特征及离子来源. 环境科学, 40(10): 4431-4439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201910015.htm 肖桐, 齐永青, 王军邦, 2010. 基于降水和径流的长江源头氮素收支研究. 生态学报, 30(19): 5404-5412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201019033.htm 于彩霞, 邓学良, 石春娥, 等, 2018. 降水和风对大气PM2.5、PM10的清除作用分析. 环境科学学报, 38(12): 4620-4629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201812008.htm 张晓晶, 卢俊平, 马太玲, 等, 2017. 大气氮磷湿沉降特征及对沙源区水库水环境的影响. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2093-2101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201712013.htm 赵竹子, 2015. 青藏高原大气气溶胶的理化组成及其来源解析(博士学位论文). 西安: 中国科学院地球环境研究所, 31-35. -









 下载:
下载: