Slope Reliability Analysis Incorporating Observation of Stability Performance under A Past Rainfall Event
-
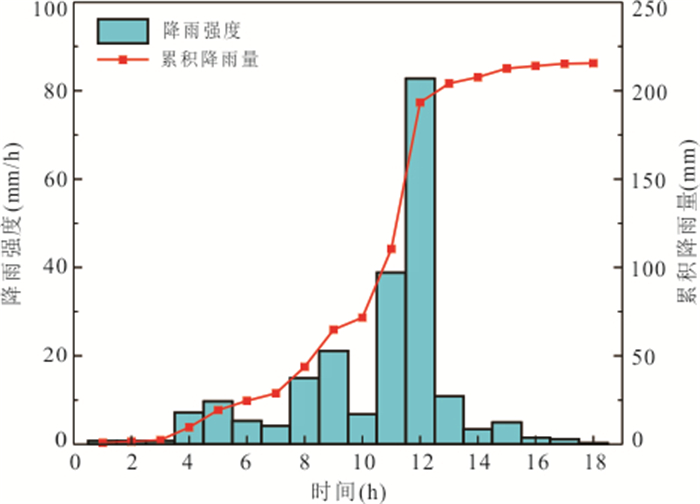
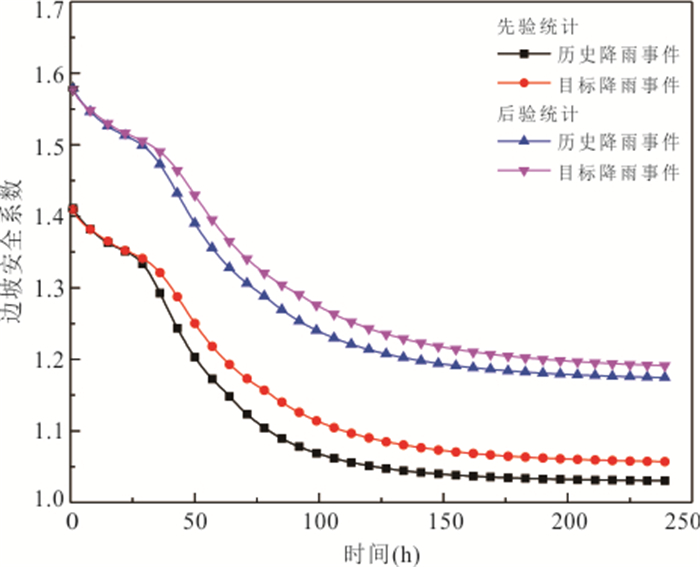
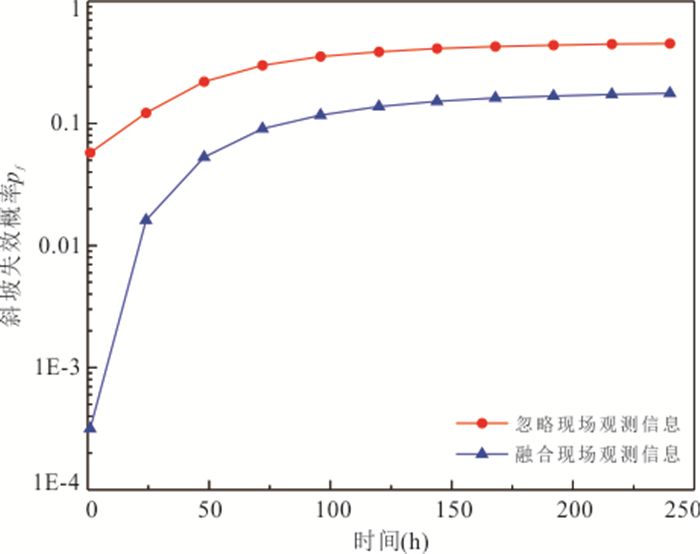
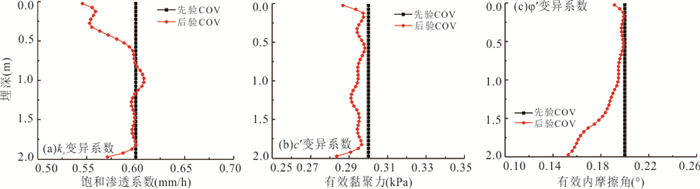
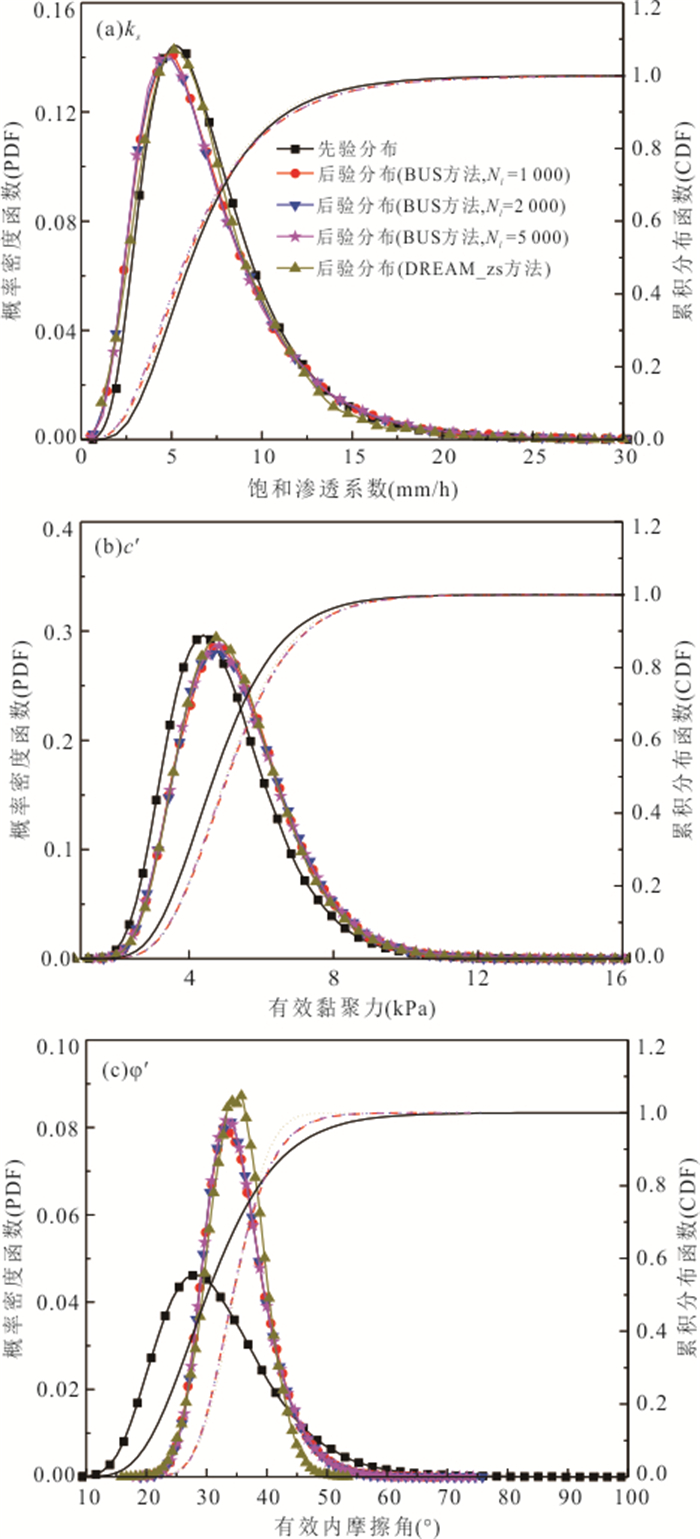
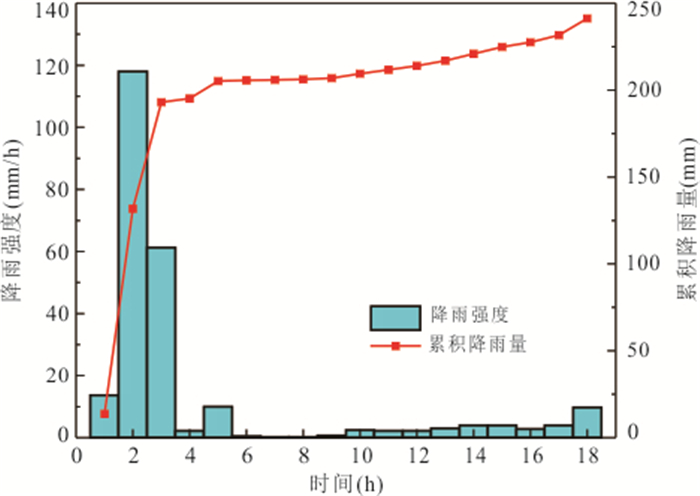
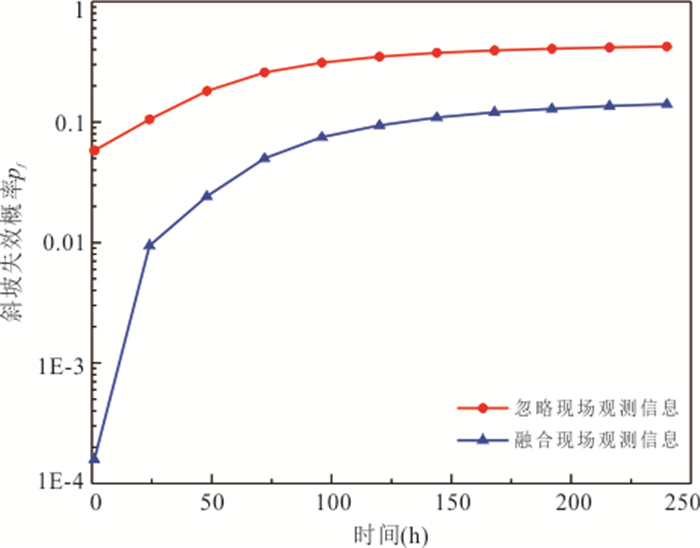
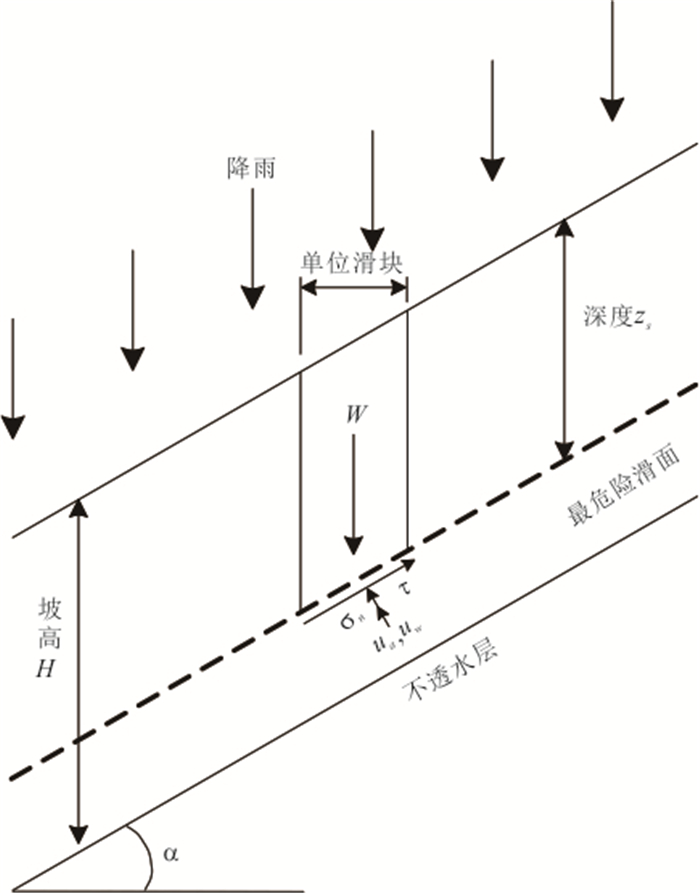
摘要: 降雨诱发斜坡失稳机理及可靠度分析通常忽略了现场观测信息的影响,包括斜坡在天然条件下保持稳定或经历历史降雨后保持稳定等观测信息.以无限长斜坡模型为例,采用贝叶斯更新方法基于“斜坡经历某次历史降雨后仍保持稳定”这一现场观测信息概率反分析空间变异水力和抗剪强度参数,基于蒙特卡洛模拟方法计算不同降雨历时下斜坡失效概率,对比分析忽略观测信息对斜坡失效概率估计所造成的影响.结果表明:概率反分析通过融合历史降雨下斜坡稳定性观测信息,可有效排除因抗剪强度参数空间变异性导致斜坡沿软弱层发生失稳的可能性,为客观评价降雨诱发的空间变异斜坡失效概率奠定了基础.如果忽略“斜坡经历某次历史降雨后仍保持稳定”这一观测信息会明显高估斜坡失效概率,尤其在降雨初期.本研究成果为揭示降雨诱发斜坡失稳机制提供新的视角.Abstract: Failure mechanism and reliability analysis of rainfall-induced slopes generally ignore the effects of field observation information, such as the observation that the slope keeps stable in natural conditions or after a historical rainfall event. In this paper, with an infinite slope model as an example, the BUS (Bayesian Updating with Subset simulation) method is adopted for the probabilistic back analysis of spatially variable hydraulic and shear strength parameters based on the field observation that the slope survived from a previous extreme rainfall event. The probabilities of slope failure under different rainfall durations are evaluated within the framework of Monte-Carlo simulation. The influence of ignoring/incorporating the field observation on the estimate of probability of slope failure is also investigated. The results indicate that the possibility of slope failing along the weak zones caused by the spatial variability of soil parameters can be effectively excluded through the probabilistic back analysis incorporating the field observation. Based on this, more realistic probability of slope failure induced by the rainfall can be produced. If the field observation that the slope survived from a previous extreme rainfall event is ignored, the probability of slope failure will be significantly overestimated, especially in the early stage of rainfall. The research outcomes provide a new perspective for interpreting the rainfall-induced slope failure mechanisms in the spatially variable soils.
-
Key words:
- slope /
- landslide /
- rainfall infiltration /
- spatial variability /
- probabilistic back analysis /
- reliability analysis /
- hazard geology
-
表 1 土体参数取值
Table 1. Values of soil parameters
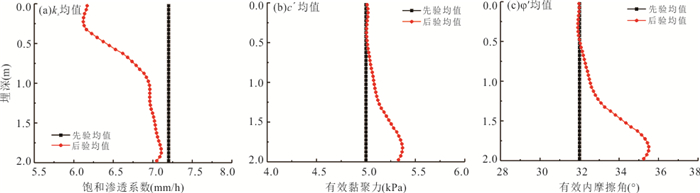
计算参数 取值 计算参数 取值 饱和渗透系数ks 7.2 mm/h 初始基质吸力 10 kPa 饱和含水率$ {\theta }_{s} $ 46.9% 残余含水率$ {\theta }_{r} $ 10.6% 水力参数a 0.943 m 水力参数n 1.395 有效内摩擦角$ {\varphi }^{{'}} $ 32° 有效黏聚力$ {c}^{{'}} $ 5 kPa 土体干重度$ {\gamma }_{d} $ 16 kN/m3 水的重度$ {\gamma }_{w} $ 9.8 kN/m3 -
Bahsan, E., Liao, H. J., Ching, J., et al., 2014. Statistics for the Calculated Safety Factors of Undrained Failure Slopes. Engineering Geology, 172: 85-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.01.005 Chen, Z. H., Huang, J. H., Qin, W. T., et al., 2017. Effects of the Spatial Variability of Saturated Permeability on the Slope Stability. Journal of Chongqing University (Natural Science Edition), 40(3): 59-69 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=FIVE201703007&dbcode=CJFD&year=2017&dflag=pdfdown Cho, S. E., 2014. Probabilistic Stability Analysis of Rainfall-Induced Landslides Considering Spatial Variability of Permeability. Engineering Geology, 171: 11-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.12.015 Christian, J. T., Baecher, G. B., 2011. Unresolved Problems in Geotechnical Risk and Reliability. Geotechnical Risk Assessment and Management, Geotechnical Special Publication, 224: 50-63. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gregory_Baecher/publication/269082290_Unresolved_Problems_in_Geotechnical_Risk_and_Reliability/links/58a313d345851513c5fdde74/Unresolved-Problems-in-Geotechnical-Risk-and-Reliability.pdf Depina, I., Oguz, E. A., Thakur, V., 2020. Novel Bayesian Framework for Calibration of Spatially Distributed Physical-Based Landslide Prediction Models. Computers and Geotechnics, 125: 103660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103660 Guardiani, C., Soranzo, E., Wu, W., 2022. Time- Dependent Reliability Analysis of Unsaturated Slopes under Rapid Drawdown with Intelligent Surrogate Models. Acta Geotechnica, 17(4): 1071-1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01364-w Guo, Z. Z., Yin, K. L., Liu, W. L., et al., 2020. Rainfall Warning of Creeping Landslide in Yunyang County of Three Gorges Reservoir Region Based on Displacement Ratio Model. Earth Science, 45(2): 672-684 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, J. Z., Zhang, J., Huang, H. W., et al., 2023. Value of Information Assessment and Optimization of Slope Boreholes. Earth Science, 48(5): 1977-1988 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, S., Liu, X., Huang, J., 2022. Non-Intrusive Reliability Analysis of Unsaturated Embankment Slopes Accounting for Spatial Variabilities of Soil Hydraulic and Shear Strength Parameters. Engineering with Computers, 38: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01108-6 Jiang, S. H., Huang, J., Qi, X. H., et al., 2020. Efficient Probabilistic back Analysis of Spatially Varying Soil Parameters for Slope Reliability Assessment. Engineering Geology, 271: 105597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105597 Jiang, S. H., Liu, X., Huang, F. M., et al., 2020. Failure Mechanism and Reliability Analysis of Soil Slopes under Rainfall Infiltration Considering Spatial Variability of Multiple Soil Parameters. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 42(5): 900-907 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, D. Q., Qi, X. H., Phoon, K. K., et al., 2014. Effect of Spatially Variable Shear Strength Parameters with Linearly Increasing Mean Trend on Reliability of Infinite Slopes. Structural Safety, 49: 45-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2013.08.005 Liu, X., Wang, Y., 2021. Reliability Analysis of an Existing Slope at a Specific Site Considering Rainfall Triggering Mechanism and Its Past Performance Records. Engineering Geology, 288: 106144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106144 Luo, Y., He, S. M., He, J. C., 2014. Effect of Rainfall Patterns on Stability of Shallow Landslide. Earth Science, 39(9): 1357-1363 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201409012.htm Ray, R. L., Jacobs, J. M., de Alba, P., 2010. Impacts of Unsaturated Zone Soil Moisture and Groundwater Table on Slope Instability. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 136(10): 1448-1458. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000357 Simunek, J., van Genuchten, M. T., Sejna, M., 2013. The Hydrus-1D Software Package for Simulating the Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably Saturated Media, Version 4.16, HYDRUS Software Series 3. Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside, Riverside, California. Straub, D., Papaioannou, I., 2015. Bayesian Updating with Structural Reliability Methods. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 141(3): 04014134. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000839 Tang, Y., Yin, K. L., Wang, Y., et al., 2017. The Landslide Rain Infiltration Based on the Improved Mein- Larson Model. Earth Science, 42(4): 634-640 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201701004.htm van Genuchten, M. T., 1980. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44(5): 892-898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x Wai, R. C. T., Lee, R. W. H., Law, R. H. C., 2016. Review of Landslides in 2016. GEO Report No. 341, Hong Kong. Wang, L., Wu, C., Gu, X., et al., 2020. Probabilistic Stability Analysis of Earth Dam Slope under Transient Seepage Using Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 79(6): 2763-2775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01730-0 Xiao, J. H., Wang, M., Wang, C., et al., 2021. Reliability Analysis of Slope with Dominant Seepage Interlayer under Rainfall Infiltration. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(6): 193-204 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, H. Q., Zhang, L., Li, D. Q., 2018. Efficient Method for Probabilistic Estimation of Spatially Varied Hydraulic Properties in a Soil Slope Based on Field Responses: A Bayesian Approach. Computers and Geotechnics, 102: 262-272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.11.012 Yang, H. Q., Zhang, L., Xue, J., et al., 2019. Unsaturated Soil Slope Characterization with Karhunen-Loève and Polynomial Chaos via Bayesian Approach. Engineering with Computers, 35(1): 337-350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0610-x Yuan, J., Papaioannou, I., Straub, D., 2019. Probabilistic Failure Analysis of Infinite Slopes under Random Rainfall Processes and Spatially Variable Soil. Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards, 13(1): 20-33. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2018.1489059 Zhang, L. L., Wu, F., Zheng, Y. F., et al., 2018. Probabilistic Calibration of a Coupled Hydro-Mechanical Slope Stability Model with Integration of Multiple Observations. Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards, 12(3): 169-182. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2018.1440317 Zhang, L. L., Zhang, J., Zhang, L. M., et al., 2010. Back Analysis of Slope Failure with Markov Chain Monte Carlo Simulation. Computers and Geotechnics, 37(7/8): 905-912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2010.07.009 Zhang, W. G., Gu, X., Liu, H. L., et al., 2022. Probabilistic back Analysis of Soil Parameters and Displacement Prediction of Unsaturated Slopes Using Bayesian Updating. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 43(4): 1112-1122 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, H., Griffiths, D. V., Fenton, G. A., et al., 2015. Undrained Failure Mechanisms of Slopes in Random Soil. Engineering Geology, 191: 31-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.03.009 Zhu, H., Zhang, Z. L., Zhang, L. L., et al., 2013. Two- Dimensional Probabilistic Infiltration Analysis with a Spatially Varying Permeability Function. Computers and Geotechnics, 48: 249-259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.07.010 陈朝晖, 黄景华, 秦文涛, 等, 2017. 饱和渗透系数空间变异性对边坡稳定性的影响. 重庆大学学报, 40(3): 59-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FIVE201703007.htm 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 刘庆丽, 等, 2020. 基于位移比模型的三峡库区云阳县域内蠕变型滑坡降雨预警. 地球科学, 45(2): 672-684. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.005 胡金政, 张洁, 黄宏伟, 等, 2023. 边坡勘察钻孔信息价值评价及优化布置方法. 地球科学, 48(5): 1977-1988. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.216 蒋水华, 刘贤, 黄发明, 等, 2020. 考虑多参数空间变异性的降雨入渗边坡失稳机理及可靠度分析. 岩土工程学报, 42(5): 900-907. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202005017.htm 罗渝, 何思明, 何尽川, 2014. 降雨类型对浅层滑坡稳定性的影响. 地球科学, 39(9): 1357-1363. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.118 唐扬, 殷坤龙, 汪洋, 等, 2017. 斜坡降雨入渗的改进Mein-Larson模型. 地球科学, 42(4): 634-640. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.050 肖景红, 王敏, 王川, 等, 2021. 含优势渗流层边坡降雨入渗下的可靠度分析. 地质科技通报, 40(6): 193-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106021.htm 仉文岗, 顾鑫, 刘汉龙, 等, 2022. 基于贝叶斯更新的非饱和土坡参数概率反演及变形预测. 岩土力学, 43(4): 1112-1122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202204024.htm -









 下载:
下载: