Genesis of Delong Granite in East Kunlun Orogen and Its Implication on the Evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean
-
摘要: 东昆仑造山带为古特提斯域重要组成部分,该区古特提斯洋的闭合时间和古特提斯演化相关岩浆岩广泛存在的Nd-Hf解耦原因仍然不清.选取该造山带德龙花岗岩开展锆石年代学和全岩元素-同位素地球化学研究.结果表明德龙花岗岩侵位于中三叠世;岩体属准铝质-弱过铝质高硅I型花岗岩,岩石总体Sr/Y和La/Yb比值较低,与正常岛弧岩浆岩类似;岩体具有富集的Sr-Nd和富集至亏损的锆石Hf同位素特征.综合岩相学、同位素-元素特征表明德龙花岗岩来源于新老地壳混合熔融或者富集地幔和板片(玄武质洋壳和沉积物的混合物)等混合源区来源岩石的重熔作用,这些混合过程导致德龙及同时代中酸性岩浆岩出现Nd-Hf解耦.综合区域地质地球化学特征表明古特提斯洋在240 Ma左右闭合.Abstract: The East Kunlun Orogen is an important part of the Paleo-Tethys domain. The closure time of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean and the reason for decoupling Nd-Hf isotopes of Permian-Triassic magmatic rocks are still controversial. Zircon chronology and whole rock elemental and isotopic analyses have been carried out on the Delong granite in the East Kunlun Orogen. The results show that the Delong granite was emplaced in the Middle Triassic and belong to metaluminous to weakly peraluminous high silica I-type granite, with low Sr/Y and La/Yb ratios, similar to normal island arc magmatic rocks. Isotopic data show enriched Sr-Nd and enriched to depleted zircon Hf isotopic signatures for the Delong granite. These data, together with petrography, indicate that the Delong granite comes from the mixed melting of new and old crust or the remelting of rocks from mixed source areas such as enriched mantle and oceanic plate (mixture of basalt crust and sediments). These special sources contribute to widespread decoupling of εNd(t) and εHf(t) of the Delong granite and even regional contemporaneous intermediate-acid magmatic rocks. Based on the above conclusions and the geological and geochemical characteristics of the rocks regionally, it is inferred that the Paleo-Tethys Ocean was closed at about 240 Ma.
-
Key words:
- granite /
- crust remelting /
- Nd-Hf decoupling /
- Paleo-Tethys Ocean /
- ocean-continental conversion /
- East Kunlun Orogen /
- geochemistry
-
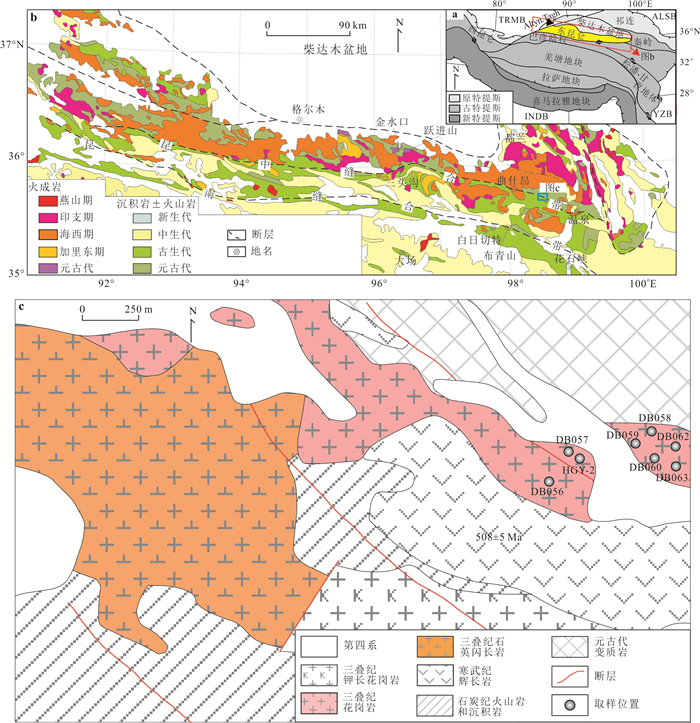
图 1 (a) 青藏高原主要块体分布图(据Chen et al., 2017); (b)东昆仑造山带地质图(据Chen et al., 2017); (c)德龙地区地质图
Fig. 1. (a) Geological map showing the main blocks in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau(after Chen et al., 2017); (b) Geological map of the East Kunlun Orogen(after Chen et al., 2017); (c) Geological map of the Delong area
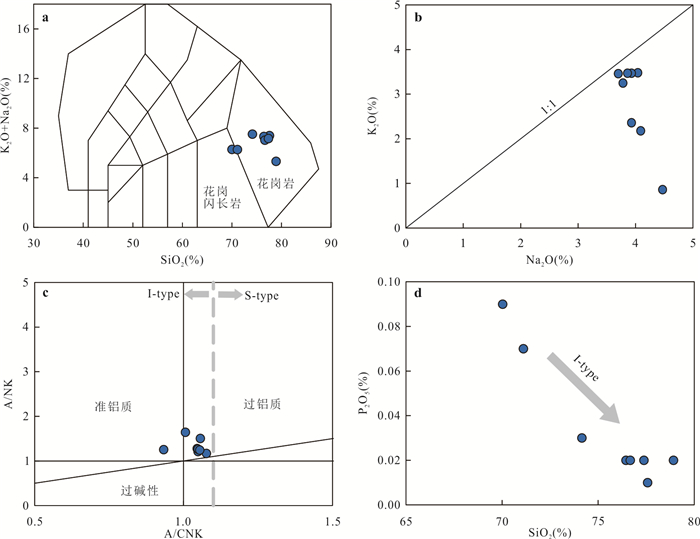
图 4 德龙花岗岩主量元素图解
a. K2O+Na2O(%)vs. SiO2(%)图解(据Middlemost,1994);b. K2O(%)vs. Na2O(%)图解;c. A/NK vs. A/CNK图解;d. P2O5(%)vs. SiO2(%)图解
Fig. 4. Diagrams for major elements of the Delong granite
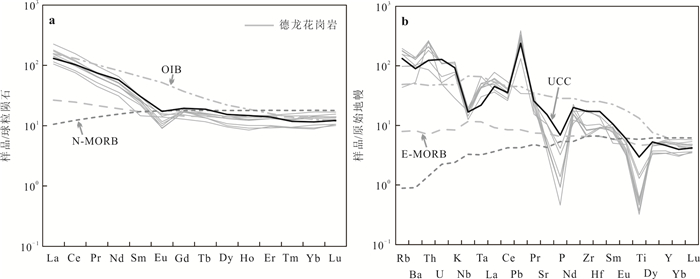
图 5 德龙花岗岩(a)稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解和(b)微量元素原始地幔标准化图解
UCC. 大陆上地壳;OIB. 洋岛玄武岩;E-MORB. 富集洋中脊玄武岩;N-MORB. 正常洋中脊玄武岩;球粒标准化数据、原始地幔标准化数据、OIB、E-MORB和N-MORB据Sun and McDonough(1989),UCC数据据Rudnick and Gao(2003)
Fig. 5. (a) Chondrite normalized rare-earth element diagram and (b) primitive mantle normalized trace element diagram for the Delong granite
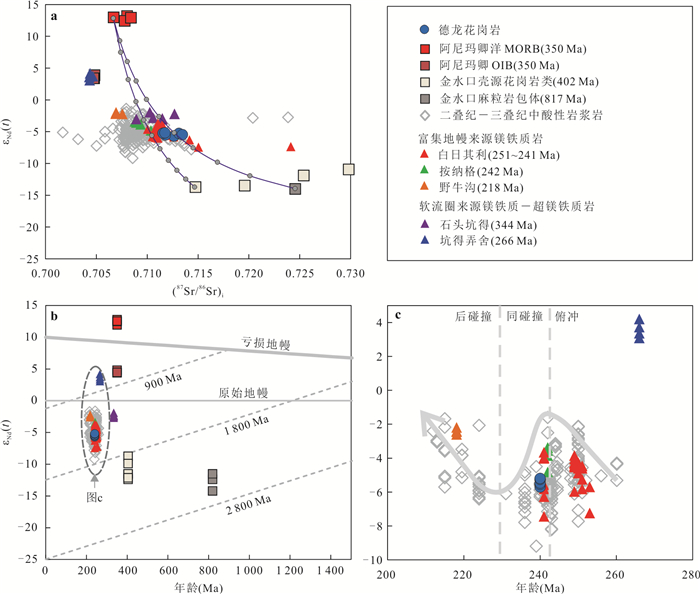
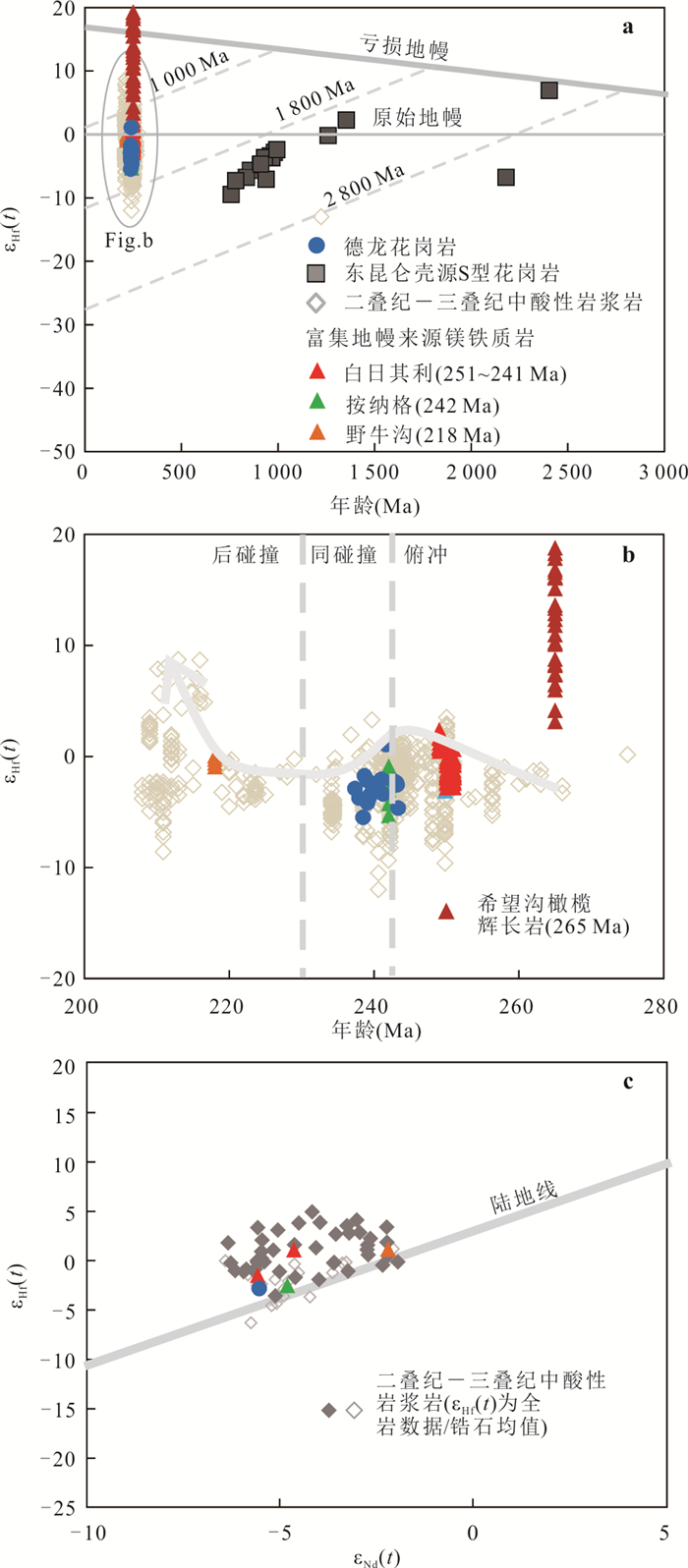
图 7 德龙花岗岩εHf(t) vs. 年龄图解(a, b)和εHf(t) vs. εNd(t)图解(c)
Nd-Hf同位素数据来源见附件1;图c中陆地线据Vervoort et al.(1999)
Fig. 7. εHf(t) vs. age diagrams (a, b) and εHf(t) vs. εNd(t) diagram (c)
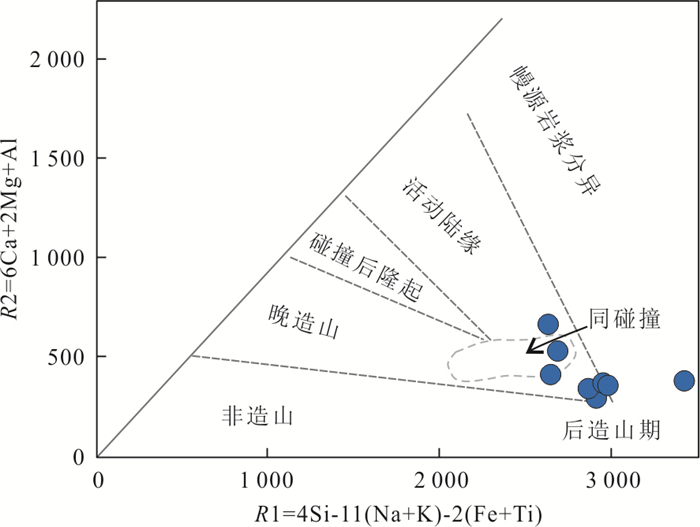
图 11 德龙花岗岩构造判别图解(据Batchelor and Bowde, 1985)
Fig. 11. Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Delong granite (after Batchelor and Bowden, 1985)
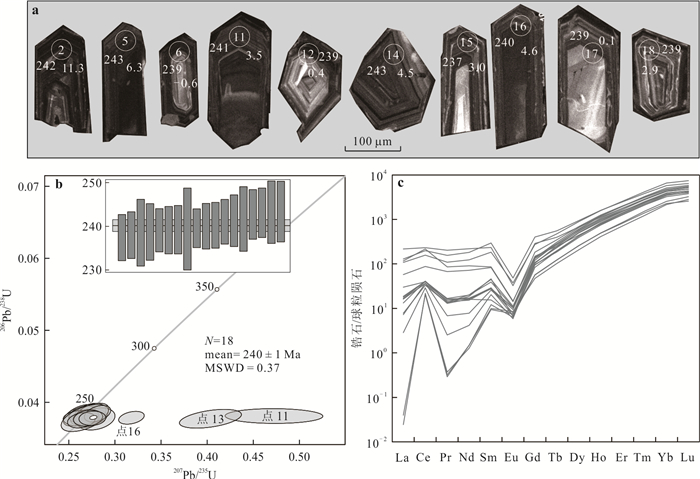
表 1 东昆仑德龙花岗岩(DB057)锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb data of the Delong granite (DB057) from the East Kunlun Orogen
点号 232Th 238U Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) μg/g μg/g 207Pb/206Pb ±σ 207Pb/235U ±σ 206Pb/238U ±σ 208Pb/232Th ±σ 207Pb/235U ±σ 206Pb/238U ±σ 1 265 377 0.70 0.051 7 0.001 8 0.270 2 0.008 7 0.038 1 0.000 5 0.011 4 0.000 2 243 7 241 3 2 451 1 017 0.44 0.049 4 0.001 2 0.261 6 0.007 1 0.038 2 0.000 6 0.011 6 0.000 2 236 6 242 4 3 403 1 031 0.39 0.051 0 0.001 1 0.268 2 0.006 6 0.037 9 0.000 4 0.011 8 0.000 2 241 5 240 3 4 453 1 054 0.43 0.051 3 0.001 3 0.273 0 0.007 0 0.038 5 0.000 6 0.012 5 0.000 3 245 6 243 4 5 373 1 095 0.34 0.049 9 0.001 0 0.264 7 0.005 9 0.038 4 0.000 5 0.011 8 0.000 2 238 5 243 3 6 339 636 0.53 0.053 9 0.001 7 0.279 4 0.008 5 0.037 7 0.000 6 0.011 4 0.000 3 250 7 239 4 7 564 1 323 0.43 0.052 1 0.001 1 0.269 6 0.005 5 0.037 6 0.000 4 0.011 8 0.000 2 242 4 238 3 8 302 733 0.41 0.051 7 0.001 3 0.275 0 0.007 5 0.038 4 0.000 6 0.012 1 0.000 2 247 6 243 4 9 202 377 0.54 0.050 6 0.001 6 0.263 2 0.007 9 0.037 8 0.000 4 0.011 6 0.000 3 237 6 239 3 10 378 956 0.40 0.051 2 0.001 0 0.268 5 0.005 7 0.038 0 0.000 4 0.012 0 0.000 2 242 5 240 3 11 336 775 0.43 0.090 0 0.004 3 0.472 4 0.021 7 0.038 1 0.000 4 0.020 8 0.000 9 393 15 241 3 12 236 549 0.43 0.051 0 0.001 8 0.267 3 0.010 5 0.037 8 0.000 8 0.012 7 0.000 4 241 8 239 5 13 541 1 210 0.45 0.076 9 0.002 4 0.403 5 0.013 8 0.037 7 0.000 5 0.016 5 0.000 4 344 10 239 3 14 472 1 163 0.41 0.053 0 0.001 1 0.281 1 0.005 8 0.038 4 0.000 5 0.012 6 0.000 2 252 5 243 3 15 422 840 0.50 0.050 9 0.001 2 0.263 7 0.006 2 0.037 5 0.000 4 0.012 5 0.000 3 238 5 237 3 16 674 1 300 0.52 0.060 7 0.001 1 0.317 9 0.005 7 0.037 9 0.000 4 0.012 1 0.000 2 280 4 240 2 17 285 752 0.38 0.051 9 0.001 3 0.270 9 0.006 4 0.037 8 0.000 5 0.012 1 0.000 2 243 5 239 3 18 266 598 0.44 0.052 9 0.001 2 0.275 5 0.005 9 0.037 8 0.000 4 0.012 0 0.000 2 247 5 239 3 表 2 东昆仑德龙花岗岩锆石微量元素(μg/g)分析结果
Table 2. Trace elements (μg/g) data of zircons extracted from the Delong granite from the East Kunlun Orogen
点号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y Ti Nb Ta TTi(℃) 1 0.0 12.6 0.0 0.7 1.5 0.5 10 4 53 23 119 32 371 72 745 2.4 1.8 1.2 629 2 0.7 17.8 0.2 2.0 3.1 0.3 21 10 141 57 278 71 732 122 1 713 3.2 8.8 5.1 650 3 3.2 24.9 1.3 9.5 6.9 0.7 30 11 150 61 298 74 755 132 1 854 2.0 9.9 5.7 617 4 1.7 22.5 0.6 3.7 3.9 0.5 25 11 155 67 328 84 876 149 2 007 3.3 13.1 5.7 652 5 1.9 20.5 1.3 8.7 7.1 0.4 28 12 167 68 327 80 803 138 2 006 1.2 11.6 6.6 584 6 4.5 25.2 1.5 8.1 4.2 0.6 20 7 100 42 213 54 595 105 1 312 6.0 6.7 3.5 698 7 13.7 53.7 6.4 34.0 12.7 0.8 38 13 176 71 337 81 819 141 2 125 1.5 11.1 7.0 599 8 0.0 13.2 0.0 0.7 1.9 0.4 17 7 107 45 226 57 618 102 1 388 1.4 7.7 4.1 593 9 0.0 13.4 0.0 0.6 1.5 0.4 12 5 66 28 143 39 436 83 882 3.1 3.6 1.9 648 10 3.8 22.6 1.5 7.9 4.5 0.5 22 9 129 54 255 64 668 111 1 581 2.0 8.9 5.0 616 11 27.8 133.4 8.2 42.5 13.1 0.9 31 9 113 45 211 54 554 96 1 346 13.7 7.1 3.6 769 12 7.1 24.2 1.5 7.6 2.4 0.4 12 5 66 28 137 36 392 66 849 2.1 4.1 2.4 619 13 25.9 97.3 10.4 58.3 28.3 2.2 56 18 227 90 429 107 1 124 191 2 692 8.5 14.3 6.2 727 14 51.5 141.7 19.4 103.1 36.1 1.9 60 15 173 64 297 71 728 122 1 877 1.4 10.4 6.1 591 15 4.0 25.2 1.4 7.2 4.3 0.6 22 9 127 51 251 63 652 110 1 554 1.7 8.0 3.9 607 16 30.7 122.4 14.8 86.0 45.6 2.8 83 21 240 91 415 99 988 165 2 637 9.7 14.5 6.1 738 17 3.9 22.1 1.2 7.6 4.2 0.4 20 7 109 47 236 61 666 112 1 429 0.4 8.1 4.3 524 18 4.2 24.7 1.6 9.4 6.0 0.6 27 10 139 57 261 62 622 104 1 615 2.5 8.4 3.6 633 表 3 东昆仑德龙花岗岩主量(%)和微量(μg/g)元素数据分析结果
Table 3. Major (%) and trace elements (μg/g) data of the Delong granite from the East Kunlun Orogen
样号 DB056 DB057 DB058 DB059 DB060 DB062 DB063 HGY2 SiO2 74.2 70.0 77.6 76.5 76.7 78.9 77.4 71.1 Al2O3 13.3 14.8 12.0 12.3 12.3 10.4 12.3 13.7 Fe2O3T 1.52 2.93 1.66 1.58 1.86 1.48 1.79 3.02 MgO 0.28 0.74 0.10 0.13 0.17 0.14 0.18 0.65 CaO 1.26 3.13 0.48 0.86 1.10 1.56 0.98 2.12 Na2O 4.04 3.93 3.93 3.86 3.78 4.47 3.70 4.09 K2O 3.48 2.36 3.47 3.47 3.25 0.86 3.46 2.18 MnO 0.05 0.07 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.07 P2O5 0.03 0.09 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.07 TiO2 0.12 0.32 0.07 0.08 0.11 0.13 0.10 0.28 Total 99.35 99.45 100.26 99.36 99.81 99.72 100.34 99.64 LOI 0.96 0.84 0.81 0.47 0.31 1.65 0.26 2.20 A/CNK 1.05 1.01 1.08 1.05 1.05 0.93 1.05 1.06 Li 3.93 9.38 3.28 4.41 7.23 2.57 5.01 4.68 Be 2.91 2.39 3.07 2.06 2.63 1.94 2.84 2.99 Sc 6.88 9.72 6.82 7.30 7.69 6.24 7.07 7.92 V 9.72 29.50 3.10 3.57 5.06 3.99 6.11 23.40 Cr 24.2 11.7 13.1 16.3 5.8 10.5 6.6 20.2 Co 198.0 166.0 138.0 108.0 101.0 99.9 89.4 82.2 Ni 95.7 76.7 66.8 52.4 46.0 47.5 40.1 41.1 Cu 2.46 1.56 2.00 2.30 0.51 0.72 0.47 1.33 Zn 22.7 39.4 10.3 16.9 21.2 5.6 21.0 29.0 Ga 13.1 15.6 12.3 13.6 13.5 10.0 13.1 14.5 Rb 100.0 62.0 98.2 112.0 115.0 27.7 124.0 62.4 Sr 123.0 223.0 77.3 96.8 104.0 103.0 95.8 220.0 Zr 112.0 191.0 77.8 72.7 91.8 92.2 94.5 204.0 Nb 12.30 10.20 12.10 11.80 14.10 12.30 13.10 8.95 Cs 1.00 0.74 0.76 1.08 1.88 0.27 1.70 0.65 Ba 702 714 956 891 894 368 966 685 La 27.1 42.4 33.2 36.2 40.7 53.4 33.8 24.9 Ce 49.9 74.1 59.9 64.0 70.8 95.4 59.6 46.3 Pr 4.93 6.98 6.16 6.25 7.28 9.35 6.11 4.27 Nd 16.7 23.6 20.7 21.1 24.3 30.6 21.0 14.6 Sm 3.37 3.92 4.05 3.84 4.21 4.65 3.56 2.23 Eu 0.53 0.91 0.52 0.62 0.67 0.83 0.58 0.81 Gd 3.46 3.10 3.50 3.43 3.57 3.54 3.90 2.62 Tb 0.60 0.50 0.57 0.54 0.59 0.51 0.60 0.43 Dy 3.56 2.74 3.33 3.35 3.61 2.53 3.61 2.41 Ho 0.83 0.57 0.69 0.72 0.71 0.52 0.77 0.48 Er 2.47 1.66 2.16 2.17 2.17 1.52 2.45 1.61 Tm 0.40 0.24 0.31 0.33 0.32 0.24 0.37 0.23 Yb 2.88 1.56 2.44 2.37 2.25 1.74 2.49 1.50 Lu 0.43 0.26 0.35 0.34 0.32 0.27 0.40 0.27 Y 26.0 17.1 21.8 23.4 23.8 15.6 24.5 15.4 Hf 3.24 4.44 2.88 2.76 2.83 2.75 2.80 4.23 Ta 2.71 1.81 2.05 1.74 2.08 1.75 1.84 1.24 Pb 27.60 15.50 19.40 23.60 21.10 2.43 22.90 9.43 Th 15.50 10.50 22.30 20.90 17.90 22.60 17.70 7.33 U 2.32 1.38 2.26 2.31 2.33 1.04 2.30 1.10 REE 117.16 162.53 137.89 145.26 161.50 205.09 139.23 102.66 δEu 0.48 0.80 0.42 0.52 0.53 0.63 0.47 1.02 TZr (℃) 710 747 685 674 695 685 699 767 注:LOI=烧失量; A/CNK=molar[Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O)]; Fe2O3T为总铁含量, δEu=Eu/Eu*=EuN/(SmN×GdN)1/2;球粒陨石标准化值取自(Sun and Mcdonough, 1989); TZr=10 108/(0.32+1.16M+lnDZr, zircon/melt)-273; M=(Na+K+2×Ca)/(Al×Si); Boehnke et al.(2013) .表 4 东昆仑德龙花岗岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果
Table 4. Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the Delong granite fromthe East Kunlun Orogen
样品号 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr ±2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd ±2σ εNd(t) T2DM (Nd) (Ma) fSm/Nd DB056 2.355 214 0.720 662 0.000 007 0.712 622 0.121 986 0.512 229 0.000 003 -5.7 1 475 -0.38 DB057 0.804 937 0.714 525 0.000 007 0.711 777 0.100 408 0.512 203 0.000 004 -5.5 1 462 -0.49 DB059 3.353 077 0.724 557 0.000 009 0.713 110 0.110 014 0.512 232 0.000 004 -5.3 1 440 -0.44 DB062 0.778 727 0.716 119 0.000 010 0.713 461 0.091 860 0.512 193 0.000 004 -5.5 1 456 -0.53 DB063 3.751 015 0.724 364 0.000 006 0.711 559 0.102 477 0.512 221 0.000 004 -5.2 1 438 -0.48 DB063r 3.751 083 0.724 551 0.000 012 0.711 745 0.102 477 0.512 224 0.000 004 -5.2 1 434 -0.48 注:(87Sr/86Sr)i和εNd(t)回算至240 Ma; 计算采用的参数(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR=0.196 7, (143Nd/144Nd)CHUR=0.512 638, 现今(147Sm/144Nd)DM=0.213 7, (143Nd/144Nd)DM=0.513 15, 衰变常数λRb=1.42×10-11 a-1, λSm=6.54×10-12 a-1.参数来源同 Chen et al. (2017) .表 5 东昆仑德龙花岗岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 5. Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of the Delong granite from the East Kunlun Orogen
点号 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 1σ εHf(t) TDM(Hf)(Ma) T2DM(Hf) (Ma) fLu/Hf 1 0.026 808 0.000 922 0.282 542 0.000 010 -3.4 1 002 1 305 -0.97 2 0.080 351 0.002 459 0.282 675 0.000 026 1.1 850 1 059 -0.93 3 0.041 008 0.001 326 0.282 552 0.000 017 -3.1 999 1 289 -0.96 4 0.037 468 0.001 244 0.282 507 0.000 027 -4.7 1 060 1 377 -0.96 5 0.065 850 0.002 007 0.282 580 0.000 014 -2.2 977 1 241 -0.94 6 0.039 955 0.001 301 0.282 485 0.000 019 -5.5 1 094 1 422 -0.96 7 0.074 427 0.002 216 0.282 538 0.000 032 -3.8 1 044 1 326 -0.93 8 0.058 700 0.001 875 0.282 570 0.000 016 -2.6 988 1 259 -0.94 9 0.036 191 0.001 207 0.282 521 0.000 013 -4.2 1 040 1 350 -0.96 10 0.060 590 0.001 784 0.282 573 0.000 015 -2.4 981 1 253 -0.95 11 0.048 923 0.001 512 0.282 582 0.000 017 -2.1 961 1 232 -0.95 12 0.035 816 0.001 192 0.282 536 0.000 015 -3.7 1 019 1 321 -0.96 13 0.079 778 0.002 600 0.282 596 0.000 021 -1.8 969 1 215 -0.92 14 0.058 097 0.001 984 0.282 576 0.000 015 -2.4 982 1 249 -0.94 15 0.050 350 0.001 772 0.282 560 0.000 016 -2.9 1 000 1 279 -0.95 16 0.063 608 0.002 191 0.282 548 0.000 021 -3.4 1 028 1 305 -0.93 17 0.043 116 0.001 587 0.282 532 0.000 012 -3.9 1 034 1 331 -0.95 18 0.051 711 0.001 688 0.282 579 0.000 013 -2.2 970 1 240 -0.95 注:计算过程中所用参数(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR=0.033 2, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR=0.282 772; (176Lu/177Hf)DM=0.038 4, (176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.283 25; λ(176Lu)=1.867×10-11 a-1; 176Lu/177Hf(Crust)=0.015; 参数来源同 Chen et al. (2017) . -
Batchelor, R. A., Bowden, P., 1985. Petrogenetic Interpretation of Granitoid Rock Series Using Multicationic Parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1/2/3/4): 43-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(85)90034-8 Boehnke, P., Watson, E. B., Trail, D., et al., 2013. Zircon Saturation Re-Revisited. Chemical Geology, 351(7): 324-334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.028 Chappell, B. W., White, A. J. R., 1992. I- and S-Type Granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 83: 1-26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263593 300007720 doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007720 Chen, J. J., Wei, J. H., Fu, L. B., et al., 2017. Multiple Sources of the Early Mesozoic Gouli Batholith, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Linking Continental Crustal Growth with Oceanic Subduction. Lithos, 292-293: 161-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2017.09.006 Chen, J. J., Fu, L. B., Wei, J. H., et al., 2020. Proto-Tethys Magmatic Evolution along Northern Gondwana: Insights from Late Silurian-Middle Devonian A-Type Magmatism, East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Lithos, 356-357(6529): 105304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105304 Chen, L., Sun, Y., Pei, X. Z., et al., 2001. Northernmost Paleo-Tethyan Oceanic Basin in Tibet: Geochronological Evidence from 40Ar/39Ar Age Dating of Dur'ngoi Ophiolite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(14): 1203-1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02900603 Cope, T., 2017. Phanerozoic Magmatic Tempos of North China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 468(B11): 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.03.022 Ding, Q. F., Jiang, S. Y., Sun, F. Y., 2014. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic Compositions of the Triassic Granite and Diorite Dikes from the Wulonggou Mining Area in the Eastern Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Lithos, 205: 266-283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.07.015 Dong, Y. P., He, D. F., Sun, S. S., et al., 2018. Subduction and Accretionary Tectonics of the East Kunlun Orogen, Western Segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth-Science Reviews, 186(B1): 231-261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.006 Feng, K., Li, R. B., Pei, X. Z., et al., 2022. Zircon U-Pb Chronology, Geochemistry and Geological Significance of Late Triassic Intermediate-Acid Volcanic Rocks in Boluositai Area, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Earth Science, 47 (4): 1194-1216 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, A. L., Zhang, G. W., Sun, Y. G., et al., 2007. Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Geochemistry of Late-Paleozoic Mafic Volcanic Rocks in the Surrounding Areas of Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province and Geological Implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23 (4): 747-754 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, D. F., Dong, Y. P., Zhang, F. F., et al., 2016. The 1.0Ga S-Type Granite in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Meso- to Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 130(5): 46-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.07.019 Hoffmann, J. E., Münker, C., Polat, A., et al., 2011. The Origin of Decoupled Hf-Nd Isotope Compositions in Eoarchean Rocks from Southern West Greenland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(21): 6610-6628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.08.018 Hu, N., Pei, X., Li, R., et al., 2013. Provenance and Tectonic Setting Study of the Maerzheng Formation at the Delistan of Buqingshan Area in the Southern Margin of East Kunlun. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87: 1731-1747 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, Z. C., Liu, Y. S., Gao, S., et al., 2012. Improved in Situ Hf Isotope Ratio Analysis of Zircon Using Newly Designed X Skimmer Cone and Jet Sample Cone in Combination with the Addition of Nitrogen by Laser Ablation Multiple Collector ICP-MS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27(9): 1391. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ja30078h Huang, H., Niu, Y. L., Mo, X. X., 2017. Garnet Effect on Nd-Hf Isotope Decoupling: Evidence from the Jinfosi Batholith, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Lithos, 274-275(1): 31-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2016.12.025 Huang, H., Niu, Y. L., Nowell, G., et al., 2014. Geochemical Constraints on the Petrogenesis of Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Continental Crust Growth through Syn-Collisional Felsic Magmatism. Chemical Geology, 370(1594): 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.01.010 Kong, J. J., Niu, Y. L., Hu, Y., et al., 2020. Petrogenesis of the Triassic Granitoids from the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Implications for Continental Crust Growth from Syn-Collisional to Post-Collisional Setting. Lithos, 364-365(6): 105513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105513 Li, R. B., Pei, X. X., Li, Z. C., et al., 2012. Geological Characteristics of Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic Unconformities and their Response to some Significant Tectonic Events in Eastern Part of Eastern Kunlun. Earth Science Frontier, 19 (5): 244-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y. S., Zong, K. Q., Kelemen, P. B., et al., 2008. Geochemistry and Magmatic History of Eclogites and Ultramafic Rocks from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drill Hole: Subduction and Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism of Lower Crustal Cumulates. Chemical Geology, 247(1/2): 133-153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.016 Long, X. P., 2004. The Research of Zircon Chronology in Orogenic Belts: a Case Study in Jinshuikou Zone(Dissertation). Jilin University, Changchun, 129 (in Chinese with English abstract). Luais, B., Le Carlier de Veslud, C., Géraud, Y., et al., 2009. Comparative Behavior of Sr, Nd and Hf Isotopic Systems during Fluid-Related Deformation at Middle Crust Levels. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(10): 2961-2977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.12.026 Middlemost, E. A. K., 1994. Naming Materials in the Magma/igneous Rock System. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3/4): 215-224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 Rudnick, R. L., Gao, S., 2003. Composition of the Continental Crust. Elsevier-Pergamon, Oxford, 3: 1-64. Schiano, P., Monzier, M., Eissen, J. P., et al., 2010. Simple Mixing as the Major Control of the Evolution of Volcanic Suites in the Ecuadorian Andes. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 160(2): 297-312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0478-2 Shannon, W. M., Barens, C. G., Bickford, M. E., 1997. Grenville Magmatism in West Texas: Petrology and Geochemistry of the Red Bluff Granitic Suite. Journal of Petrology, 38(10): 1279-1305. https://doi.org/10.1093/petroj/38.10.1279 Shao, F. L., Niu, Y. L., Liu, Y., et al., 2017. Petrogenesis of Triassic Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau and their Tectonic Implications. Lithos, 282-283(251): 33-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2017.03.002 Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19 Vermeesch, P., 2018. Isoplot R: A Free and Open Toolbox for Geochronology. Geoscience Frontiers, 9: 1479-1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2018.04.001 Vervoort, J. D., Patchett, P. J., Blichert-Toft, J., et al., 1999. Relationships between Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd Isotopic Systems in the Global Sedimentary System. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 168(1/2): 79-99. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(99)00047-3 Wang, B. Z., Li, J. Q., Fu, C. L., et al., 2022. Research on Formation and Evolution of Early Paleozoic Bulhanbuda Arc in East Kunlun Orogen. Earth Science, 47 (4): 1253-1270 (in Chinese with English abstract). Watson, E. B., Wark, D. A., Thomas, J. B., 2006. Crystallization Thermometers for Zircon and Rutile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 151(4): 413-433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5 Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., Chappell, B. W., 1987. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00402202 Wu, Y. B., Zheng, Y. F., 2004. Genesis of Zircon and Uts Constraints on Interpretation of U-Pb Age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49 (16): 1589-1604 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589 Xia, R., Wang, C. M., Qing, M., et al., 2015. Zircon U-Pb Dating, Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O Isotopes for the Nan'getan Granodiorites and Mafic Microgranular Enclaves in the East Kunlun Orogen: Record of Closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos, 234-235: 47-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.018 Xiong, F. H., Ma, C. Q., Wu, L., et al., 2015. Geochemistry, Zircon U-Pb Ages and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes of an Ordovician Appinitic Pluton in the East Kunlun Orogen: New Evidence for Proto-Tethyan Subduction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111: 681-697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.025 Xiong, F., Ma, C., Zhang, J., et al., 2014. Reworking of Old Continental Lithosphere: An Important Crustal Evolution Mechanism in Orogenic Belts, as Evidenced by Triassic I-Type Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of the Geological Society, 171(6): 847-863. https://doi.org/10.1144/jgs2013-038 Yang, J. S., Robinson, P. T., Jiang, C. F., et al., 1996. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their Tectonic Implications. Tectonophysics, 258(1/2/3/4): 215-231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(95)00199-9 Yang, Y. Q., Li, B. Y., Xu, Q. L., et al., 2013. Zircon U-Pb Ages and its Geological Significance of the Monzonitic Granite in the Aikengdelesite, Eastern Kunlun. Northwestern Geology, 46: 56-62 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.01.006 Yu, N., Jin, W., Ge, W. C., et al., 2005. Geochemical Study On Peraluminous Granite From Jinshuikou in East Kunlun. Global Geology, 24: 123-128 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, X., Fu, L. B., Wei, J. H., et al., 2019. Late Permian Back-Arc Extension of the Eastern Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Evidence from the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Lithos, 340-341(4): 34-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.05.006 Zhu, Y. X., Wang, L. X., Ma, C. Q., et al., 2022. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implication of the Late Triassic A1-Type Alkaline Volcanics from the Xiangride Area, Eastern Segment of the East Kunlun Orogen (China). Lithos, 412-413: 106595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2022.106595 封铿, 李瑞保, 裴先治, 等, 2022. 东昆仑造山带波洛斯太地区晚三叠世中酸性火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及地质意义. 地球科学, 47(4): 1194-1216. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.116 郭安林, 张国伟, 孙延贵, 等, 2007. 青海省共和盆地周缘晚古生代镁铁质火山岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 23: 747-754. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200704007.htm 胡楠, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等, 2013. 东昆仑南缘布青山得力斯坦地区马尔争组物源分析及其构造背景研究. 地质学报, 87: 1731-1747. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201311008.htm 李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等, 2012. 东昆仑东段晚古生代—中生代若干不整合面特征及其对重大构造事件的响应. 地学前缘, 19: 244-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205025.htm 龙晓平, 2004. 造山带锆石年代学研究——以金水口地区为例(硕士毕业论文). 长春: 吉林大学, 129. 王秉璋, 李积清, 付长垒, 等, 2022. 东昆仑布尔汗布达早古生代岩浆弧的形成与演化初探. 地球科学, 47(4): 1253-1270. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.094 吴元保, 郑永飞, 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49: 1589-1604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm 杨延乾, 李碧乐, 许庆林, 等, 2013. 东昆仑埃坑德勒斯特二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义. 西北地质, 46: 56-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201301010.htm 余能, 金巍, 葛文春, 等, 2005. 东昆仑金水口过铝花岗岩的地球化学研究. 世界地质, 24: 123-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200502004.htm -
 dqkxzx-49-2-560-附录.docx
dqkxzx-49-2-560-附录.docx

-









 下载:
下载: