Tide Current-Reworked Sandy Submarine Fan Deposits in Miocene Zhujiang Formation, Baiyun Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
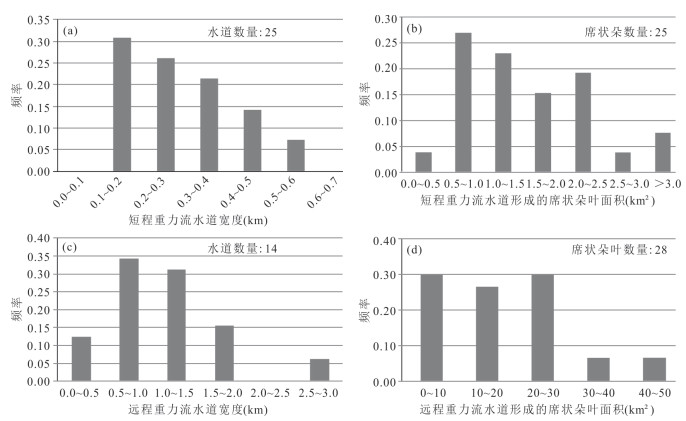
摘要: 近年来,浅海扇和底流改造作用的较多发现对深水扇术语、鲍马序列等传统认识带来了挑战,有待进一步研究. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷是我国海底扇油气勘探的重要场所之一,中新统珠江组SQ21层序(层序底界年龄21 Ma)是该凹陷砂质海底扇发育和油气发现的主力层位. 采取岩心观察与测井相、地震反射结构、地震地貌分析相结合,揭示了该层序下降期体系域和低位体系域发育为数众多的海底扇,由重力流水道、天然堤和席状朵叶体构成,在地震属性图上分别表现为均方根振幅高值条带和朵状形态. 上陆坡带重力流水道由块状‒递变层理中‒细砂岩、波状层理粉‒细砂岩组成,具有正旋回、箱型‒钟型测井相、水道充填地震相等识别标志. 其中,波状层理粉‒细砂岩夹较多泥岩纹层,局部表现为单粘土层和双粘土层构造,且富含潜穴、生物扰动构造和菱铁质结核,指示该时期海平面大幅下降直至陆架坡折以下,上陆坡带逐渐演化为浅海环境,导致研究区砂质海底扇发育及其重力流水道沉积在上陆坡带遭受明显的潮流改造. 地震地貌分析方法的应用,保证了潮流改造型海底扇沉积相的准确识别. 此外,本文的研究还表明,鲍马序列可以是底流改造成因;“深水扇”术语并非广泛适用.Abstract: Recently increasingly-identified shallow marine fans and bottom current-reworking processes, which bought challenge on traditional knowledge such as the item of deep-water fan and Bouma Sequence, are needed for further research. The Baiyun Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin is an important area for oil and gas exploration of submarine fans. The Miocene sequence SQ21 in this sag, whose base was dated as 21 Ma, is the main stratum hosting sandy submarine fans and petroleum discoveries, so was taken as the object in this study. Integrating core observation with analyses of well logging motifs, seismic reflection configurations and seismic geomorphology, this study revealed a large number of submarine fans in the falling stage and lowstand systems tracts of SQ21. The fans are constructed by gravity flow channels, levees and sheet lobes, corresponding to high-amplitude strips and lobate shapes, respectively, in seismic root mean square amplitude attribute maps. At the upper continental slope, the channels were deposited with mainly massive medium- to fine-grained sandstone and ripple-laminated fine-grained sandstone to siltstone, presenting upward-fining successions. They are characterized by cylindrical- to bell-shaped logging motifs, channel-infilling seismic reflections. Further, ripple-laminated sandstone to siltstone is intercalated with a lot of mudstone laminae partly illustrating single-clay and double-clay structures. This, together with abundant biological burrows, disturbance structure and siderite nodule, indicates that sea level greatly fell below shelf break. Consequently, the sandy submarine fan deposits, which were generated with their gravity flow channels at the upper continental slope, had been severely reworked by tide current, while shallow sea environment gradually occurred at the upper continental slope along with sea level greatly falling till below the shelf break. In this study, the application of seismic geomorphological analyses guarantees correct identification of the tidal current-reworked submarine fans. Moreover, it is suggested that the Bouma Sequence can be resulted from bottom current-reworking processes, and term of deep-water fan should not be overused.
-
Key words:
- Miocene /
- submarine fan /
- bottom current-reworking process /
- gravity flow /
- Bouma Sequence /
- Pearl River Mouth Basin /
- Baiyun Sag /
- sedimentology
-
图 1 珠江口盆地构造单元区划(据施和生等(2014)简化)及研究区位置
Fig. 1. Tectonic unit divisions in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (simplified after Shi et al., 2014) and the study area
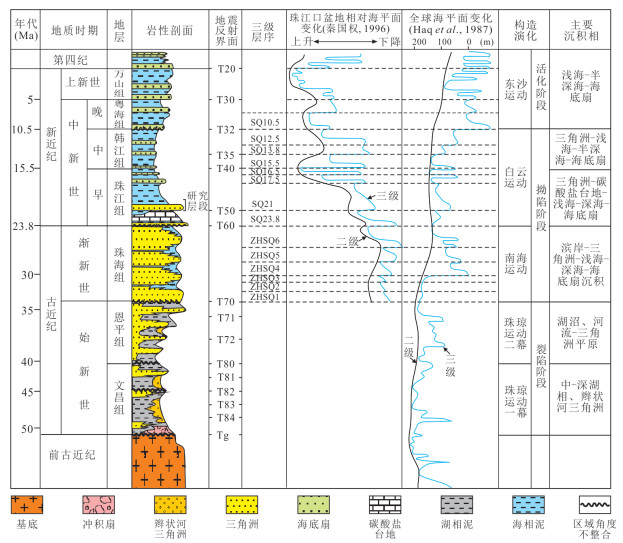
图 2 珠江口盆地东部地层综合柱状图(据施和生等(2014)修改)及研究层段
Fig. 2. Stratigraphic column in the eastern Pearl River Mouth basin (modified after Shi et al., 2014) and the targeted strata in this study
图 3 白云凹陷东部SQ21地震层序界面(a,剖面位置见图 1)、反射结构及体系域划分(b)
Fig. 3. Seismic sequence boundaries (a), reflection configurations and division of system tracts (b) in sequence SQ21, the eastern Baiyun Sag
图 4 SQ21层序下降期‒低位体系域海底扇地震地貌解释(位置见图 1)
Fig. 4. Seismic geomorphological interpretation of submarine fans in the falling stage and lowstand systems tracts of sequence SQ21
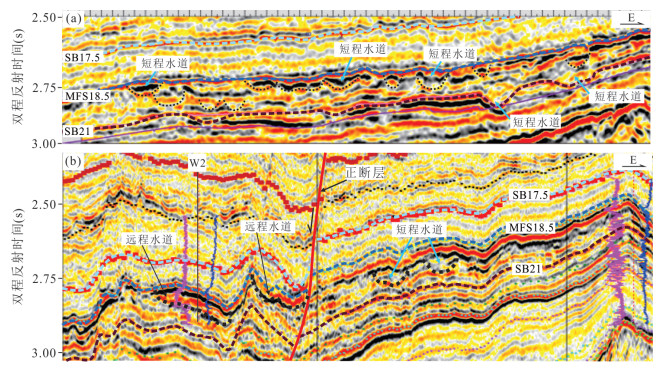
图 5 重力流水道的地震相特征(剖面位置见图 4)
Fig. 5. Features of seismic facies representing gravity flow channels
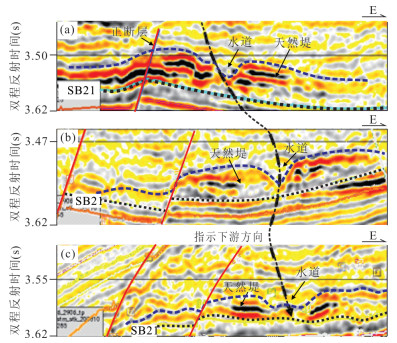
图 7 远程重力流水道的地震反射特征(剖面位置见图 4)
Fig. 7. Seismic reflection characteristics of long-extending gravity-flow channels
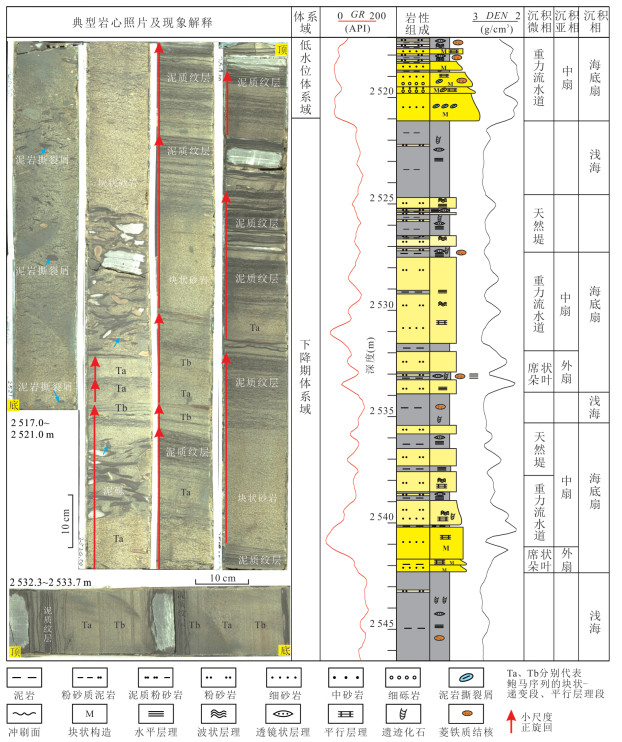
图 8 W1井2 515.0~2 546.5 m岩心海底扇沉积特征(井位见图 4)
Fig. 8. Sedimentary characteristic of submarine fans in the cores from 2 515.0-2 546.5 m in depth, Well W1
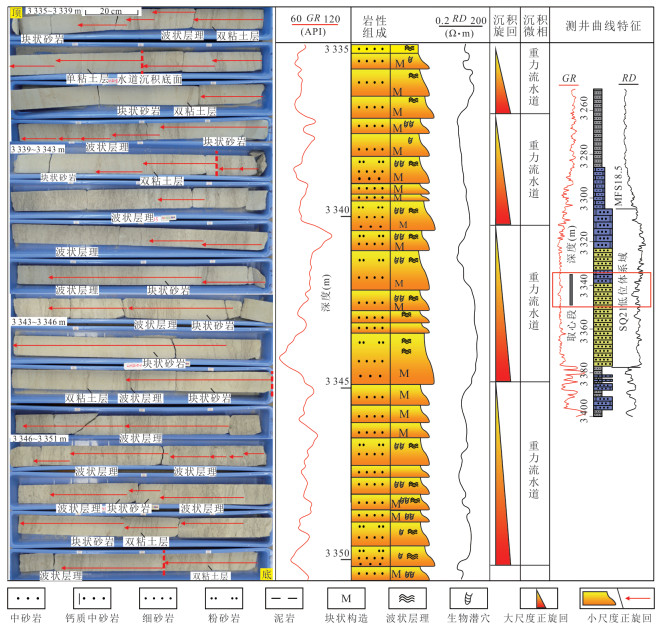
图 9 W2井3 335~3 351 m重力流水道沉积的岩性组成及测井响应特征(井位见图 4)
Fig. 9. Lithological composition and logging responses of gravity flow channel deposits in the cores from 3 335 m to 3 351 m in depth, Well W2
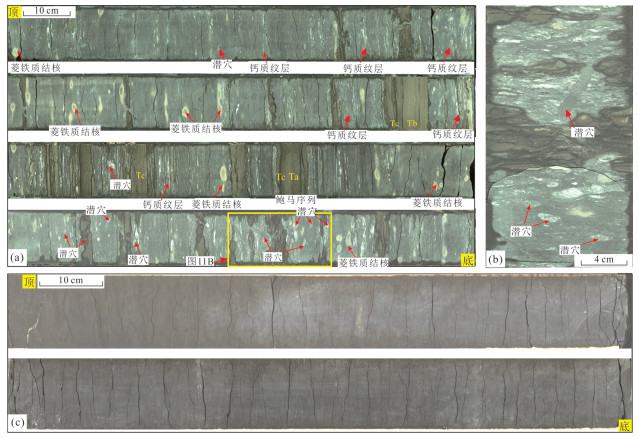
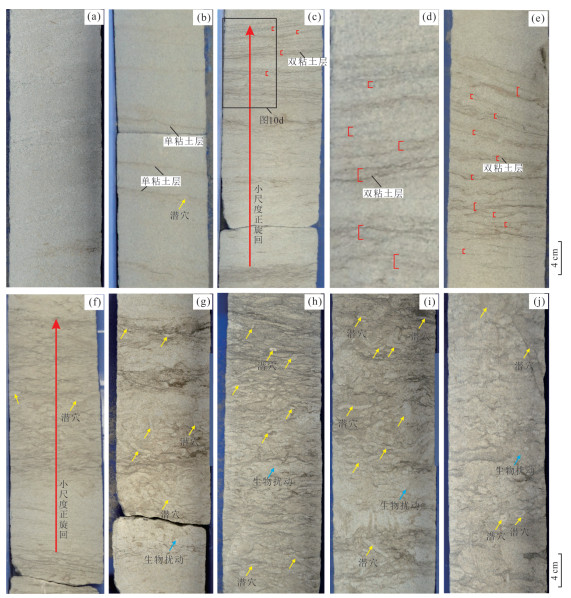
图 10 W2井潮流改造重力流水道沉积的岩性组合和沉积构造(井位见图 1)
a. 3 337.4 m,灰白色块状细砂岩;b. 3 336.5 m,灰白色细砂岩,夹少量深灰色泥质纹层显示单粘土层,局部见生物潜穴沿泥质纹层分布;c、d. 3 339.5 m,灰白色细砂岩向上变细为粉砂岩夹泥质纹层,显示小尺度正旋回,泥质纹层成对出现,显示双粘土层;e. 3 349.5 m,灰白色细砂岩,下部和上部呈块状,中部夹较多泥质纹层显示双粘土层;f. 3 347.2 m,灰白色细砂岩,向上变细且夹薄层泥质纹层,显示小尺度正旋回,上部含丰富的潜穴和生物扰动构造;g. 3 340.7 m,灰白色块状细砂岩夹少量泥质纹层,较多生物潜穴;h、i、j. 分别为3 340.0 m、3 340.4 m、3 341.2 m,灰白色粉‒细砂岩,夹较多泥质纹层,丰富的潜穴和强烈的生物扰动构造. 典型潜穴构造用黄箭头指出
Fig. 10. Lithological assemblages and sedimentary structures representing tide current-reworked gravity flow channel deposits in Well W2
图 11 浅海相与深海相泥岩沉积特征对比(井位见图 1)
a、b. W2井2 543.0~2 547.0 m,深灰色泥岩,夹少量递变‒平行‒波状层理粉‒细砂岩”(Ta、Tb、Tc),含较多菱铁矿结核和生物潜穴化石;c. W3井3 002.0~3 004.0 m,深灰色水平层理泥岩
Fig. 11. Sedimentary characteristics of mudstone deposited in shallow sea comparing with in deep sea
-
Bouma, A.H., 1962. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits: A Graphic Approach to Facies Interpretation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 264. Breien, H., de Blasio, F. V., Elverhoi, A., et al., 2010. Transport Mechanisms of Sand in Deep-Marine Environments: Insights Based on Laboratory Experiments. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 80(11): 975-990. https://doi.org/10.2110/jsr.2010.079 Cai, L.L., Liu, C.C., Lü, M., et al., 2016. The Development Characteristics of Deep Water Channel and Sedimentary Reservoir Prediction in Lower Congo Basin, West Africa. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 28(2): 60-70 (in Chinese with English abstract). Catuneanu, O., 2006. Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy. Elsevier Science Ltd., Amsterdam, 105-245. Haq, B. U., Hardenbol, J., Vail, P. R., 1987. Chronology of Fluctuating Sea Levels since the Triassic. Science, 235(4793): 1156-1167. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.235.4793.1156 He, W.J., Xie, J.Y., Liu, X.Y., et al., 2011. Foraminiferal Biostratigraphy and Sedimentary Environment Reconstruction Based on Paleontological Data from Bore Hole DF1-1-11, Yinggehai Basin. Journal of Stratigraphy, 35(1): 81-87 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, Y.B., Gao, Z.Z., Li, J.M., et al., 1998. Internal-Tide Deposits of the Late Ordovician in Tonglu, Zhejiang. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 16(1): 1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, Y.T., Wen, L., Yao, G.Q., et al., 2018. Sedimentary Characteristics of Thick Fine-Grained Shallow-Marine Gravity Flow Deposits from Huangliu Formation in Dongfang Area, Yinggehai Basin, China. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 39(3): 290-303 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, Y.T., Yao, G.Q., Zhu, H.T., et al., 2016. Reworking of Gravity Flow Sandbody by Bottom-Current from Huangliu Formation in Dongfang Area of Yinggehai Basin, Northwestern South China Sea. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(7): 855-866 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Zheng, R.C., Zhu, G.J., et al., 2012. Deep-Water Tractive Deposition in Zhujiang Formation Baiyun Sag, Zhujiang River Mouth Basin and Its Geological Implications. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(1): 127-135 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, B.J., Pang, X., Wang, J.H., et al., 2019. Sedimentary System Response Process and Hydrocarbon Exploration Significance of Crust Thinning Zone at Extensional Continental Margin of Deep-Water Area in Pearl River Mouth Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(S1): 124-138 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, B.J., Pang, X., Yan, C.Z., et al., 2011. Evolution of the Oligocene-Miocene Shelf Slope-Break Zone in the Baiyun Deep-Water Area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin and Its Significance in Oil-Gas Exploration. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 32(2): 234-242 (in Chinese with English abstract). Marr, J. G., Harff, P. A., Shanmugam, G., et al., 2001. Experiments on Subaqueous Sandy Gravity Flows: The Role of Clay and Water Content in Flow Dynamics and Depositional Structures. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 113(11): 1377-1386. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(2001)1131377: eossgf>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1377:EOSSGF>2.0.CO;2 Myrow, P. M., Hiscott, R. N., 1991. Shallow-Water Gravity-Flow Deposits, Chapel Island Formation, Southeast Newfoundland, Canada. Sedimentology, 38(5): 935-959. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1991.tb01880.x Okay, S., Jupinet, B., Lericolais, G., et al., 2011. Morphological and Stratigraphic Investigation of a Holocene Subaqueous Shelf Fan, North of the İstanbul Strait in the Black Sea. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 20: 287-305. https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1001-16 Pang, X., Zhu, M., Liu, B.J., et al., 2014. The Mechanism of Gravity Flow Deposition in Baiyun Sag Deepwater Area of the Northern South China Sea. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 35(4): 646-653 (in Chinese with English abstract). Posamentier, H. W., Kolla, V., 2003. Seismic Geomorphology and Stratigraphy of Depositional Elements in Deep-Water Settings. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 73(3): 367-388. https://doi.org/10.1306/111302730367 Posamentier, H.W., Walker, R.G., 2006. Deep-Water Turbidites and Submarine Fans. In: Posamentier, H.W., Walker, R.G., eds., Facies Models Revisited. Society for Sedimentary Geology, Tulsa, 397-520. Qin, G.Q., 1996. Application of Microfossils in the Study of Sequence Stratigraphy in the Late Cenozoic in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 16(4): 1-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Shanmugam, G., 1996. High-Density Turbidity Currents: Are They Sandy Debris Flows? Journal of Sedimentary Research, 66(1): 2-10. https://doi.org/10.1306/d426828e-2b26-11d7-8648000102c1865d doi: 10.1306/D426828E-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D Shanmugam, G., 2000. 50 Years of the Turbidite Paradigm (1950s-1990s): Deep-Water Processes and Facies Models—A Critical Perspective. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 285-342. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2 Shanmugam, G., 2012. New Perspective on Deep-Water Sandstones: Origin, Recognition, Initiation, and Reservoir Quality. Handbook of Petroleum Exploration and Production. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 524. Shepard, F. P., Marshall, N. F., McLoughlin, P. A., et al., 1978. Currents in Submarine Canyons and Other Seavalleys. AAPG Studies in Geology, 8: 1-13. Shi, H.S., He, M., Zhang, L.L., et al., 2014. Hydrocarbon Geology, Accumulation Pattern and the Next Exploration Strategy in the Eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 26(3): 11-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tokuhashi, S., 1996. Shallow-Marine Turbiditic Sandstones Juxtaposed with Deep-Marine Ones at the Eastern Margin of the Niigata Neogene Backarc Basin, Central Japan. Sedimentary Geology, 104(1-4): 99-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/0037-0738(95)00123-9 Vail, P.R., 1992. The Evolution of Seismic Stratigraphy and the Global Sea-Level Curve. In: Dott, R.H. Jr., ed., Eustasy: The Historical Ups and Downs of a Major Geological Concept. Geological Society of America Memoir, 180: 83-91. Villa, E., Bahamonde, J.R., 2001. Accumulations of Ferganites (Fusulinacea) in Shallow Turbidite Deposits from the Carboniferous of Spain. The Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 31(3): 173-190. https://doi.org/10.2113/31.3.173 Walker, R. G., 1978. Deep-Water Sandstone Facies and Ancient Submarine Fans: Models for Exploration for Stratigraphic Traps. AAPG Bulletin, 62: 932-966. https://doi.org/10.1306/c1ea4f77-16c9-11d7-8645000102c1865d Wang, H., Chen, S., Gan, H.J., et al., 2015. Accumulation Mechanism of Large Shallow Marine Turbidite Deposits: A Case Study of Gravity Flow Deposits of the Huangliu Formation in Yinggehai Basin. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 21-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J., Luan, X.W., He, B.S., et al., 2021. Characteristics and Genesis of Faults in Southwestern Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea. Earth Science, 46(3): 916-928 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J. H., Guan, Z. L., la Croix, A. D., et al., 2020. Seismic Geomorphology of Shallow-Water Lacustrine Deltas in the Paleocene Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 120: 104561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104561 Wang, J. H., Pang, X., Liu, B. J., et al., 2018. The Baiyun and Liwan Sags: Two Supradetachment Basins on the Passive Continental Margin of the Northern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 95: 206-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.05.001 Wang, J. H., Xie, X. N., Pang, X., et al., 2017. Storm-Reworked Shallow-Marine Fans in the Middle Triassic Baise Area, South China. Sedimentary Geology, 349: 33-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.12.007 Wu, J., Zhang, X.Z., Bai, H.J., et al., 2021. Miocene Tidal Control System and Its Exploration Significance of Lithologic Trap in Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Science, 46(10): 3673-3689 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, H.J., Guo, S.S., Liu, B., et al., 2013. Gravity Flow and Internal Wave and Internal Tide Deposits in Upper Miocene of SE Area, Yinggehai Basin. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 35(6): 626-633 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, W., Gao, X. Z., Wang, Y. M., et al., 2015a. Seismic Geomorphology and Lithology of the Early Miocene Pearl River Deepwater Fan System in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 68: 449-469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.09.006 Zhou, W., Wang, Y. M., Gao, X. Z., et al., 2015b. Architecture, Evolution History and Controlling Factors of the Baiyun Submarine Canyon System from the Middle Miocene to Quaternary in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 67: 389-407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.015 蔡露露, 刘春成, 吕明, 等, 2016. 西非下刚果盆地深水水道发育特征及沉积储层预测. 中国海上油气, 28(2): 60-70. 何卫军, 谢金有, 刘新宇, 等, 2011. 莺歌海盆地DF1-1-11井有孔虫生物地层与沉积环境研究. 地层学杂志, 35(1): 81-87. 何幼斌, 高振中, 李建明, 等, 1998. 浙江桐庐晚奥陶世内潮汐沉积. 沉积学报, 16(1): 1-7. 黄银涛, 文力, 姚光庆, 等, 2018. 莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组细粒厚层重力流砂体沉积特征. 石油学报, 39(3): 290-303. 黄银涛, 姚光庆, 朱红涛, 等, 2016. 莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组重力流砂体的底流改造作用. 石油学报, 37(7): 855-866. 李云, 郑荣才, 朱国金, 等, 2012. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷珠江组深水牵引流沉积特征及其地质意义. 海洋学报(中文版), 34(1): 127-135. 柳保军, 庞雄, 王家豪, 等, 2019. 珠江口盆地深水区伸展陆缘地壳减薄背景下的沉积体系响应过程及油气勘探意义. 石油学报, 40(S1): 124-138. 柳保军, 庞雄, 颜承志, 等, 2011. 珠江口盆地白云深水区渐新世‒新世陆架坡折带演化及油气勘探意义. 石油学报, 32(2): 234-242. 庞雄, 朱明, 柳保军, 等, 2014. 南海北部珠江口盆地白云凹陷深水区重力流沉积机理. 石油学报, 35(4): 646-653. 秦国权, 1996. 微体古生物在珠江口盆地新生代晚期层序地层学研究中的应用. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 16(4): 1-18. 施和生, 何敏, 张丽丽, 等, 2014. 珠江口盆地(东部)油气地质特征、成藏规律及下一步勘探策略. 中国海上油气, 26(3): 11-22. 王华, 陈思, 甘华军, 等, 2015. 浅海背景下大型浊积扇研究进展及堆积机制探讨: 以莺歌海盆地黄流组重力流为例. 地学前缘, 22(1): 21-34. 王嘉, 栾锡武, 何兵寿, 等, 2021. 南海北部珠江口盆地西南段断裂特征与成因讨论. 地球科学, 46(3): 916–928. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.381 吴静, 张晓钊, 白海军, 等, 2021. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷中新统潮控体系及其岩性圈闭勘探意义. 地球科学, 46(10): 3673-3689. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.017 杨红君, 郭书生, 刘博, 等, 2013. 莺歌海盆地SE区上中新统重力流与内波内潮汐沉积新认识. 石油实验地质, 35(6): 626-633. -










 下载:
下载: