Evaluation of Geochemical Geothermometers with Borehole Geothermal Measurements: A Case Study of the Xiong'an New Area
-
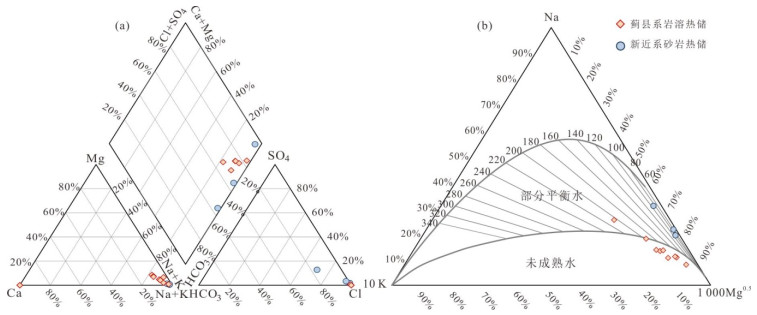
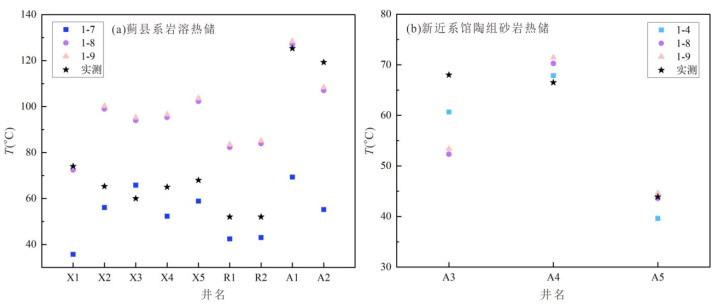
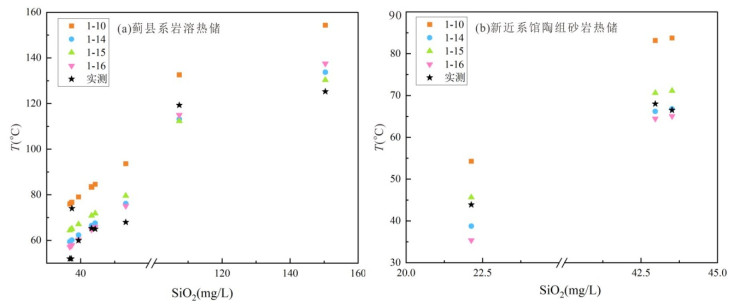
摘要: 地球化学温度计是估算深部热储温度的常用方法,在没有钻孔或钻孔深度未达到地热储层时被广泛使用.但是过去地球化学温度计的计算结果主要用于与井口温度进行对比,而与钻孔实测温度之间的对比研究工作相对较少,这不利于温度计计算结果的可靠性评估.为此,本文选择勘探相对成熟的华北平原冀中坳陷雄安新区的12口地热井开展工作,通过现场水温测定、钻孔地温测量、地热水采集与测试的手段,在水岩相互作用程度判定和矿物化学热力学平衡模拟基础上,利用地球化学温度计估算地热水的热储温度,对比钻孔实测温度和温度计计算结果的误差,进而给出研究区不同热储的最适温度计方法.研究结果表明:(1)研究区内井口温度 < 70 ℃时,井口温度落在热储层顶底板钻孔实际温度的区间范围内.但井口温度超过100 ℃时,受降温、减压、相分离、CO2脱气、SiO2沉淀等因素影响,井口温度明显低于热储层顶板温度,更低于热储层底板温度,在地球化学温度计可靠性评估时需格外注意.(2)蓟县系岩溶热储地热水未达到水岩平衡,阳离子温度计不适用,新近系砂岩热储馆陶组地热水达到部分平衡,阳离子、SiO2温度计均具可行性;针对不同储层,通过与实测温度对比发现玉髓溶解度温度计最适合岩溶热储,平均误差6.2 ℃;Na-K温度计和玉髓温度计最适合砂岩热储,平均误差分别为6.0 ℃和3.4 ℃.(3)在使用地球化学温度计时建议结合地层信息或岩石特征及井口温度进行筛选;在无实测温度情况下,对于同一地质构造单元,可根据不同采样深度的地球化学温度计计算结果了解地下深部温度情况,指导地热资源勘探工作.研究成果对于流体温度计应用及地热资源可持续开发利用具有重要意义.Abstract: The geochemical geothermometer is a common method for estimating the temperature of deep thermal reservoirs, which is widely used where no boreholes are drilled or the borehole depths do not reach the geothermal reservoir. However, the calculation results of the geochemical geothermometer were generally compared to the wellhead temperature in the previous studies. Comparison studies with the measured temperature of the borehole are few, which results in uncertainty of the geothermometers. In this study, 12 geothermal wells in the geothermal field with detailed research basis and abundant data in Xiong'an New Area, Jizhong depression, North China Plain, were selected to evaluate the reliability of the geothermometer in conjunction with water temperature measurement, borehole logging, and geothermal water collection and analysis. Nineteen geochemical geothermometers were used to estimate the thermal storage temperature of geothermal water after the evolution of water-rock interaction and multimineral thermodynamic equilibrium simulation. And then the results were compared with the measured borehole temperature and wellhead temperature. Results show that when the wellhead temperature in the study area is less than 70 ℃, the wellhead temperature falls within the range of the actual borehole temperature from the thermal reservoir roof to the floor. However, when the wellhead temperature exceeds 100 ℃, the wellhead temperature is lower than the thermal reservoir roof temperature and much lower to the bottom plate temperature. They are affected by several factors such as cooling, decompression, phase separation, CO2 degassing, and SiO2 precipitation during the transport process, which should be paid great attention in the future. Secondly, the geothermal water in Jixian karst-fissured reservoir belongs to immature water, and the cation geothermometer is not applicable, while the geothermal water in the porous Neogene sandstone reservoir is mainly located in a partial equilibrium area which implies the feasibility of both cation and SiO2 geothermometer. The borehole temperatures were used to verify the suitable geothermometers. It is found that the chalcedony solubility geothermometer is suitable for Jixian karst-fissured reservoir with a deviation of 6.2 ℃, while the Na-K geothermometer and chalcedony geothermometer are suitable for the porous Neogene sandstone reservoir with a deviation of 6.0 ℃ and 3.4 ℃, respectively. Finally, a variety of geothermometers are recommended to be selected with constraints of stratigraphic information, rock characteristics, wellhead temperature, and so on. And if the borehole logging is not available, underground temperature can be roughly understood with geochemical geothermometers at different sampling depths under the same geological structural unit. Our results have significant implications for the application of geochemical geothermometers and sustainable management of geothermal resources.
-
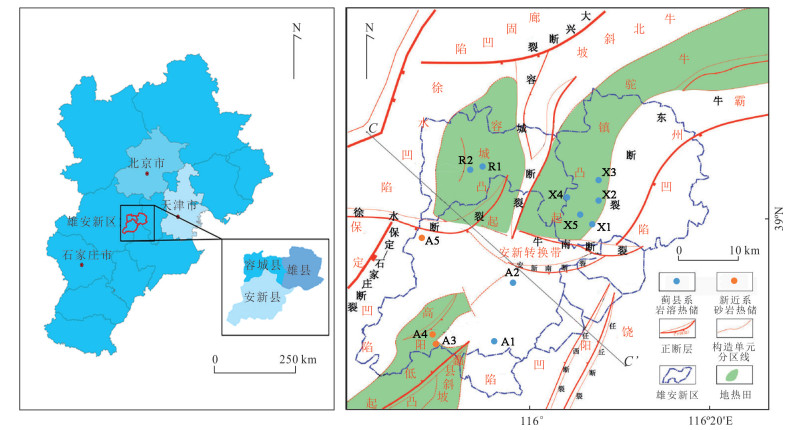
图 1 研究区位置及采样点位置分布(据吴爱民等,2018)
Fig. 1. Location of the study area and distribution map of sampling points (after Wu et al., 2018)
表 1 研究区地热水主要组分
Table 1. Main components of geothermal water in the study area
样品
编号地层 Cl‒
(mg/L)SO42‒
(mg/L)HCO3‒ (mg/L) CO32‒
(mg/L)K+
(mg/L)Na+
(mg/L)Mg2+
(mg/L)Ca2+
(mg/L)SiO2
(mg/L)X1 Jxw 529.00 19.30 462.00 30.70 21.10 458.00 25.70 45.60 37.44 X2 Jxw 1 029.51 0.00 581.37 0.00 54.46 786.69 21.03 46.64 43.21 X3 Jxw 891.30 0.00 696.68 0.00 51.45 680.66 27.22 16.86 39.36 X4 Jxw 1 151.00 0.09 669.00 0.00 51.80 864.00 25.00 54.60 44.28 X5 Jxw 1 121.34 0.00 624.61 0.00 62.19 839.03 21.60 48.88 53.27 R1 Jxw 1 075.00 0.09 681.00 0.00 38.60 793.00 38.10 73.50 36.80 R2 Jxw 1 137.00 0.09 610.00 25.40 40.00 802.00 35.90 75.70 37.22 A1 Jx 1 271.00 5.41 448.70 17.65 63.99 920.60 4.30 17.01 150.36 A2 Jxw 1 041.00 12.77 540.70 0.00 47.83 769.20 9.10 35.50 107.42 A3 Ng 381.00 10.20 33.10 391.00 2.84 413.00 2.86 11.10 42.97 A4 Ng 569.00 41.42 550.40 0.00 4.60 560.60 1.47 8.64 43.51 A5 Ng 139.00 76.42 421.40 18.02 1.16 296.80 1.13 3.95 22.13 表 2 热储温度估算结果(℃)
Table 2. Estimation results of reservoir temperature (℃)
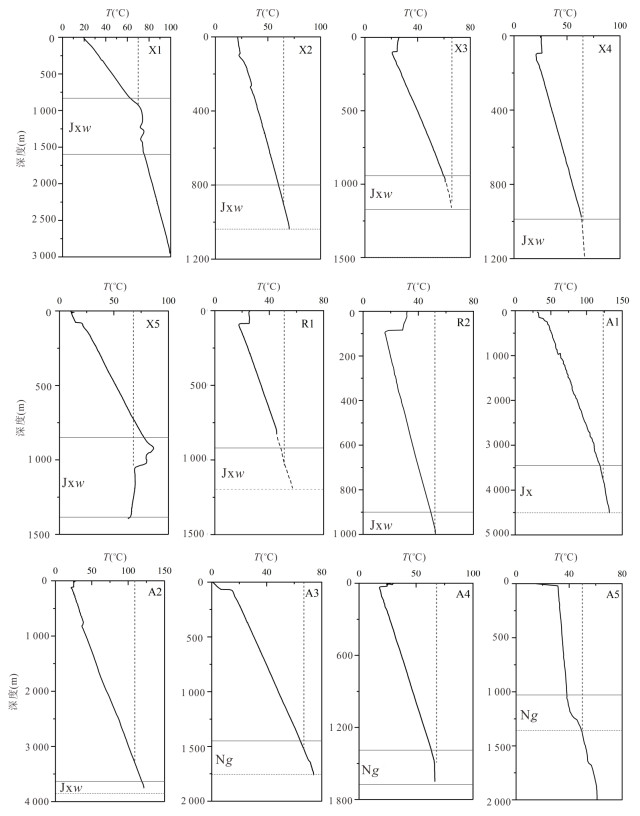
井名 井深
(m)地层 阳离子温度计 石英温度计 顶底板
温度范围实测
温度井口
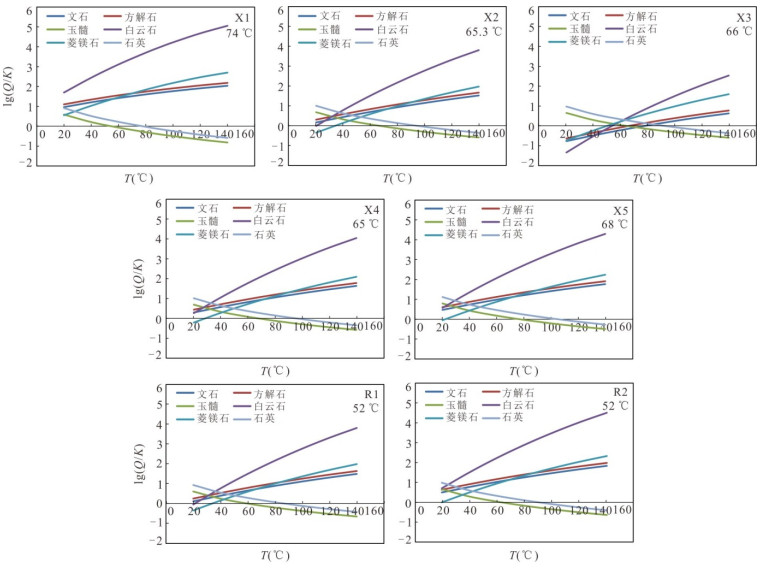
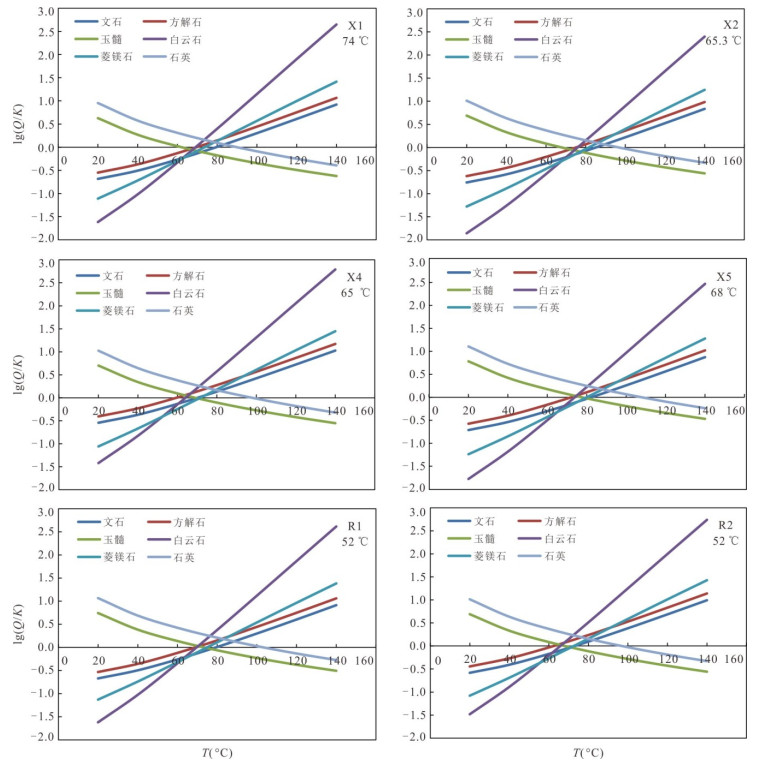
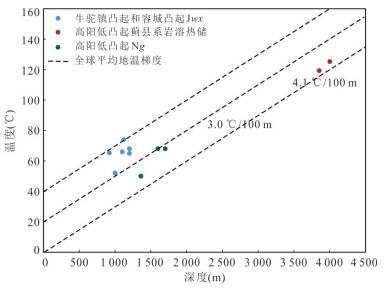
温度1-1 1-2 1-3 1-4 1-5 1-6 1-7 1-8 1-9 1-10 1-11 1-12 1-13 1-14 1-15 1-16 1-17 1-18 1-19 X1 3 000 Jxw 117.1 144.0 127.4 158.5 146.6 177.2 35.7 72.4 73.6 76.7 89.9 88.8 91.3 60.1 65.1 58.0 38.7 -7.2 -25.1 63.0~75.2 74 70 X2 1 600 Jxw 151.3 182.1 160.3 187.4 174.8 204.6 56.1 99.0 100.3 83.4 95.4 95.1 96.8 66.5 70.9 64.7 44.9 -1.4 -19.7 60.4~70.3 65.3 63 X3 1 508 Jxw 159.5 191.2 168.1 194.1 181.4 210.9 65.8 94.0 95.3 79.1 91.8 91.0 93.2 62.3 67.1 60.3 40.8 -5.2 -23.2 60.5~66.0 66 66 X4 1 506 Jxw 138.5 167.9 148.0 176.7 164.4 194.5 52.3 95.3 96.6 84.6 96.4 96.2 97.7 67.6 71.9 65.9 46.0 -0.4 -18.8 64~66 65 65 X5 1 500 Jxw 157.6 189.1 166.3 192.6 179.9 209.5 58.8 102.3 103.6 93.6 103.8 104.8 105.1 76.1 79.6 75.1 54.3 7.4 -11.5 65.0~86.1 68 68 R1 1 914 Jxw 121.4 148.8 131.5 162.2 150.2 180.7 42.4 82.3 83.5 76.0 89.2 88.0 90.6 59.4 64.4 57.2 38.0 -7.9 -25.7 48~54 52 51 R2 1 863 Jxw 123.3 150.9 133.4 163.8 151.8 182.3 43.0 83.9 85.1 76.5 89.6 88.5 91.0 59.9 64.9 57.7 38.5 -7.4 -25.3 49~52 52 52 A1 4 507 Jx 151.7 182.5 160.6 187.7 175.1 204.8 69.3 127.0 128.4 154.3 152.1 161.3 152.8 133.7 130.3 137.5 111.0 61.6 38.9 118.7~131.8 125.3 123.4 A2 3 853 Jxw 141.7 171.4 151.1 179.4 167.0 197.0 55.2 107.0 108.4 132.6 135.1 141.2 136.1 113.1 112.3 115.0 90.6 41.9 20.6 118.5~120.0 119.3 109.2 A3 1 614 Ng 10.3 26.9 22.5 60.7 51.1 82.1 2.1 52.3 53.4 83.2 95.2 94.9 96.5 66.2 70.6 64.4 44.6 -1.7 -19.9 64~72 68 67 A4 1 583 Ng 17.7 35.0 29.9 67.9 58.1 89.2 11.7 70.3 71.4 83.8 95.7 95.4 97.0 66.8 71.1 65.1 45.2 -1.2 -19.5 63.3~68.0 68 68 A5 1 195 Ng -11.0 3.8 1.2 39.6 30.6 61.1 -6.5 43.6 44.6 54.3 70.8 67.3 72.4 38.8 45.6 35.4 18.0 -26.4 -42.9 38.4~50.0 50 50 -
Arnórsson, S., 1983. Chemical Equilibria in Icelandic Geothermal Systems—Implications for Chemical Geothermometry Investigations. Geothermics, 12(2/3): 119-128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(83)90022-6 Chai, R., 2010. Selection of Geothermometers and Estimate of the Temperature of Geothermal Reservior in Pingdingshan 8th Mine. Coal Geology & Exploration, 38(1): 58-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, M. X., 1988. North China Geothermal. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Chenaker, H., Houha, B., Vincent, V., 2018. Hydrogeochemistry and Geothermometry of Thermal Water from North-Eastern Algeria. Geothermics, 75: 137-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.04.009 Fournier, R. O., 1977. Chemical Geothermometers and Mixing Models for Geothermal Systems. Geothermics, 5(1-4): 41-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(77)90007-4 Fournier, R. O., Truesdell, A. H., 1973. An Empirical Na-K-Ca Geothermometer for Natural Waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 37(5): 1255-1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4 Giggenbach, W. F., 1988. Geothermal Solute Equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca Geoindicators. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12): 2749-2765. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3 Guo, S., Wang, W. Y., Wang, Z., et al., 2016. The Analysis between Temperature of Geothermal Reservoirs and Fractures in Beijing Plain. Urban Geology, 11(1): 42-47 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2016.01.009 Guo, S., Zhu, C. Q., Qiu, N. S., et al., 2019. Present Geothermal Characteristics and Influencing Factors in the Xiongan New Area, North China. Energies, 12(20): 1-22. Jiang, B. L., Li, Z. C., Yu, C., 2022. Application of Geochemical Temperature Scale in Jiyuan Wulongkou Geothermal Area. Journal of Hebei GEO University, 45(1): 83-88, 105 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kharaka, Y. K., Mariner, R. H., 1989. Chemical Geothermometers and Their Application to Formation Waters from Sedimentary Basins. In: Naeser, N. D., McCulloh, T. H., eds., Thermal History of Sedimentary Basins. Springer, New York. Kong, Y. L., Pang, Z. H., Pang, J. M., et al., 2020. Fault-Affected Fluid Circulation Revealed by Hydrochemistry and Isotopes in a Large-Scale Utilized Geothermal Reservoir. Geofulids. 2020(24): 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2604025. Kong, Y. L., Pang, Z. H., Shao, H. B., et al., 2017. Optimization of Well-Doublet Placement in Geothermal Reservoirs Using Numerical Simulation and Economic Analysis. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(3): 118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6404-4 Li, W. W., Rao, S., Tang, X. Y., et al., 2014. Borehole Temperature Logging and Temperature Field in the Xiongxian Geothermal Field, Hebei Province. Chinese Journal of Geology, 49(3): 850-863 (in Chinese). Liu, M. L., He, T., Wu, Q. F., et al., 2020. Hydrogeochemistry of Geothermal Waters from Xiong'an New Area and Its Indicating Significance. Earth Science, 45(6): 2221-2231 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, Z. Q., Song, H. J., Cheng, H. Z., 2020. Application of Geothermometer Estimate Geothermal Reservoir Temperature of Radon Geothermal Spring in Dasunzhuang, Pingyin County, Jinan City. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 42(1): 42-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2020.01.007 Pang, J. M., Pang, Z. H., Lü, M., et al., 2018. Geochemical and Isotopic Characteristics of Fluids in the Niutuozhen Geothermal Field, North China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(1): 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7171-y Pang, Z. H., Kong, Y. L., Pang, J. M., et al., 2017. Geothermal Resources and Development in Xiongan New Area. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 32(11): 1224-1230 (in Chinese with English abstract). Pang, Z. H., Yang, F. T., Luo, L., 2013. Determination Method of Reservoir Temperature in Geothermal Field. In: Ding, Z. L., ed., Methods of Solid Earth Science Research. Science Press, Beijing, 219-242 (in Chinese). Sun, Y. Y., Liu, S. K., Jing, Y. L., 2020. Selection of Geothermometer and Estimation of Reservoir Temperature in Chenzhou Geothermal Field. Resource Information and Engineering, 35(1): 36-39 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J. Y., Pang, Z. H., Kong, Y. L., et al., 2020. Status and Prospects of Geothermal Clean Heating Industry in China. Science and Technology for Development, 16(Z1): 294-298 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, P., Chen, X. H., Shen, L. C., et al., 2016. Reservoir Temperature of Geothermal Anomaly Area and Its Environmental Effect in Tibet. Geology in China, 43(4): 1429-1438 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, S. F., Liu, J. R., Pang, Z. H., 2010. Preliminary Analysis of Temperature and Recharge Characteristics of Hot Fields in Beijing. The 26th Annual Meeting of Chinese Geophysical Society, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y. C., Li, L., Wen, H. G., et al., 2022. Geochemical Evidence for the Nonexistence of Supercritical Geothermal Fluids at the Yangbajing Geothermal Field, Southern Tibet. Journal of Hydrology, 604: 127243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127243 Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Yu, Y., et al., 2007. Application of Geothermometers to Calculation of Temperature of Geothermal Reservoirs. Geoscience, 21(4): 605-612 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003 Wang, Z. T., Zhang, C., Jiang, G. Z., et al., 2019. Present-Day Geothermal Field of Xiongan New Area and Its Heat Source Mechanism. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(11): 4313-4322 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, A. M., Ma, F., Wang, G. L., et al., 2018. A Study of Deep-Seated Karst Geothermal Reservoir Exploration and Huge Capacity Geothermal Well Parameters in Xiongan New Area. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(5): 523-532 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, H. M., Zhou, L. D., Guo, Y., 2006. Application of Cation Temperature Scale in Medium-Low Temperature Geothermal Resource. Journal of Heilongjiang Institute of Science and Technology, 16(1): 27-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xing, Y. F., Wang, H. Q., Li, J., et al., 2022. Chemical Field Characteristics of Geothermal Water in Xiong'an New Area, and Analysis on the Influencing Factors. Geology in China, 49(6): 1711-1722 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, P. H., Cheng, Q., Xie, S. Y., et al., 2017. Hydrogeochemistry and Geothermometry of Deep Thermal Water in the Carbonate Formation in the Main Urban Area of Chongqing, China. Journal of Hydrology, 549: 50-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.054 Yuan, L. J., Yang, F. T., 2017. Temperature Distribution Characteristic of Jixian Reservoir in Beijing Depression. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(1): 179-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Z. W., Yao, L., Sun, Y. Y., 2014. Preliminary Study on the Application of Geochemical Geothermometry in Geothermal Storage Calculation: A Case of Thermal Anomalies in Hunan. The 2014 Hunan Geological Society Annual Conference, Changsha (in Chinese). Zhao, J. Y., 2020. Study on Spatial Structure and Hydrothermal Differentiation Process of Deep Thermal Reservoir in Xiongan New Area (Dissertation). Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, X. L., Guo, J. Q., 1996. Silica Geothermometer and Its Related Problems. Groundwater, 18(2): 85-88 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, X., Wang, G. L., Ma, F., et al., 2023. Hydrogeochemistry of Geothermal Waters from Taihang Mountain-Xiong'an New Area and Its Indicating Significance. Earth Science, 48(3): 1093-1106 (in Chinese with English abstract). 柴蕊, 2010. 平顶山八矿地热温标的选取及热储温度估算. 煤田地质与勘探, 38(1): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2010.01.014 陈墨香, 1988. 华北地热. 北京: 科学出版社. 郭帅, 王维逸, 王治, 等, 2016. 浅析北京平原区热储温度与断裂关系. 城市地质, 11(1): 42-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2016.01.009 姜宝良, 李志超, 余晨, 2022. 地热温标在济源五龙口地热田的应用. 河北地质大学学报, 45(1): 83-88, 105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDX202201013.htm 李卫卫, 饶松, 唐晓音, 等, 2014. 河北雄县地热田钻井地温测量及地温场特征. 地质科学, 49(3): 850-863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201403013.htm 刘明亮, 何曈, 吴启帆, 等, 2020. 雄安新区地热水化学特征及其指示意义. 地球科学, 45(6): 2221-2231. 雄安新区地热水化学特征及其指示意义 卢兆群, 宋会军, 程洪柱, 2020. 应用地热温标估算济南市平阴县大孙庄氡温泉热储温度. 化工矿产地质, 42(1): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2020.01.007 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 庞菊梅, 等, 2017. 雄安新区地热资源与开发利用研究. 中国科学院院刊, 32(11): 1224-1230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201711009.htm 庞忠和, 杨峰田, 罗璐, 2013. 地热田储层温度的确定方法. 见: 丁仲礼主编, 固体地球科学研究方法. 北京: 科学出版社, 219-242. 孙杨艳, 刘声凯, 景营利, 2020. 郴州地热田地热温标的选取和热储温度估算. 资源信息与工程, 35(1): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJW202001010.htm 汪集旸, 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 等, 2020. 我国地热清洁取暖产业现状与展望. 科技促进发展, 16(Z1): 294-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJCJ2020Z1010.htm 王鹏, 陈晓宏, 沈立成, 等, 2016. 西藏地热异常区热储温度及其地质环境效应. 中国地质, 43(4): 1429-1438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201604027.htm 王树芳, 刘久荣, 庞忠和, 2010. 北京地区热田热储温度和补给特征初步分析. 北京: 中国地球物理学会第26届年会. 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 等, 2007. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度. 现代地质, 21(4): 605-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200704003.htm 王朱亭, 张超, 姜光政, 等, 2019. 雄安新区现今地温场特征及成因机制. 地球物理学报, 62(11): 4313-4322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201911026.htm 吴爱民, 马峰, 王贵玲, 等, 2018. 雄安新区深部岩溶热储探测与高产能地热井参数研究. 地球学报, 39(5): 523-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805002.htm 吴红梅, 周立岱, 郭宇, 2006. 阳离子温标在中低温地热中的应用研究. 黑龙江科技学院学报, 16(1): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI200601007.htm 邢一飞, 王慧群, 李捷, 等, 2022. 雄安新区地热水的化学场特征及影响因素分析. 中国地质, 49(6): 1711-1722. 袁利娟, 杨峰田, 2017. 北京迭断陷内蓟县系热储层温度分布特征. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(1): 179-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201701017.htm 张志卫, 姚砾, 孙杨艳, 2014. 地球化学温标在热储计算中的应用初探: 以湖南部分热异常点为例. 长沙: 2014年湖南省地质学会学术年会. 赵佳怡, 2020. 雄安新区深部热储空间结构与水热分异过程研究(博士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质科学院. 郑西来, 郭建青, 1996. 二氧化硅地热温标及其相关问题的处理方法. 地下水, 18(2): 85-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU199602022.htm 朱喜, 王贵玲, 马峰, 等, 2023. 太行山-雄安新区蓟县系含水层水文地球化学特征及意义. 地球科学, 48(3): 1093-1106. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.207 -









 下载:
下载: