Effect of Strike-Slip Activity of Basement Faults on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Dongying Sag
-
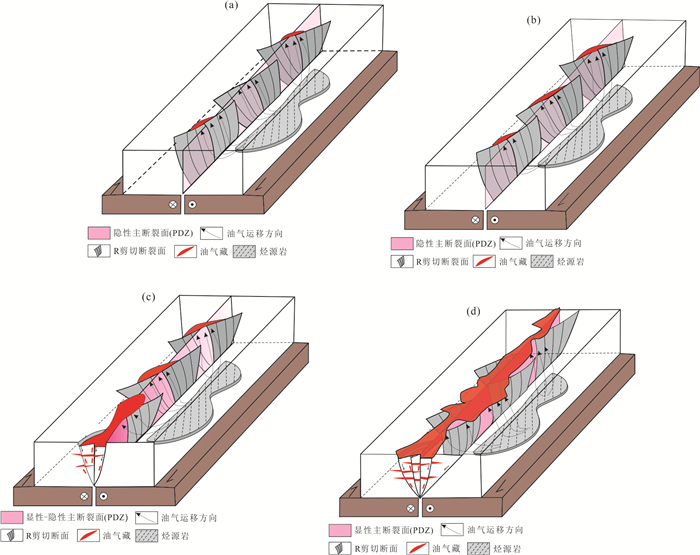
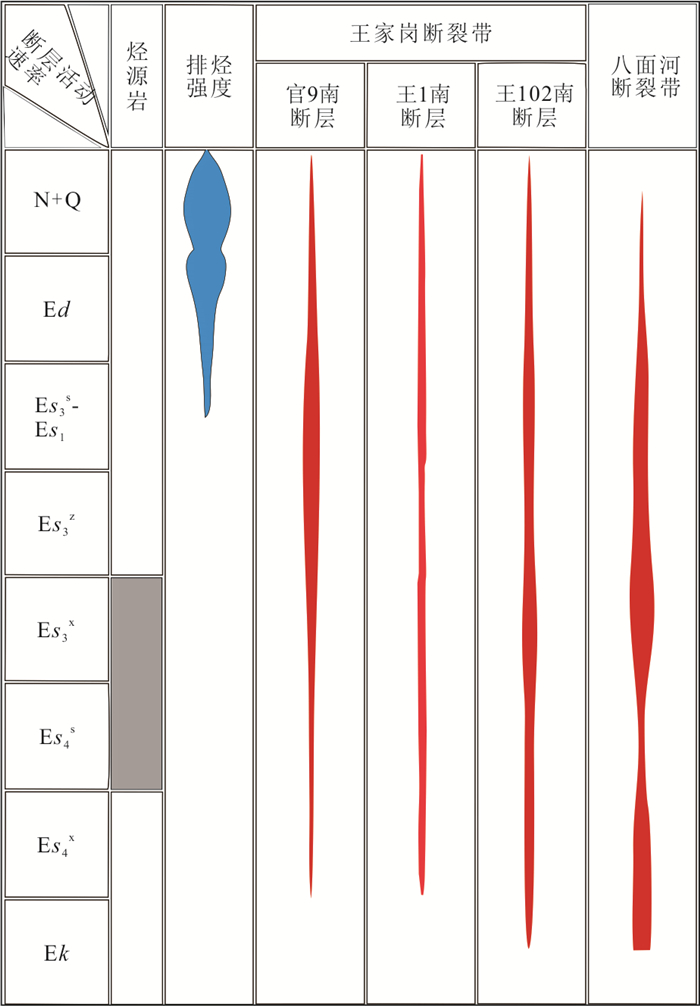
摘要: 弱变形构造带是沉积盆地盖层中客观存在的构造现象,并且与油气聚集关系密切,一般可以通过不同地质单元(次级断层、油藏、圈闭、相带、凹陷、岩体、潜山等)的有规律排列等现象进行识别.为了初步揭示盖层变形带变形强度与油气聚集规模这一问题,首先在渤海湾盆地初步识别出40条盖层变形带,然后应用变盖层厚度和变剪切强度的构造物理模拟实验方法研究基底断裂走滑活动对盆地沉积盖层产生断层的过程.应用SPSS软件,对基底走向滑动量、横向滑动量、实验盖层厚度、雁列缝长度等参数进行了多元二次函数拟合.根据东营凹陷八面河、王家岗地区古近系各时期地层厚度、构造图R剪切长度、实验估算的张扭角度,计算出了各个时期的基底断裂走滑量;在模拟实验各阶段充注染色石油,结合凹陷实例建立了基底断裂走滑早期R剪切单一通道运移‒孤立聚集、早中期R剪切主通道运移‒雁列串珠状聚集(王家岗)、P剪切主通道运移‒断续带状聚集、全通道运移‒连续带状聚等成藏模式(八面河);最后指出盖层变形带上的R剪切增压变形段,R、P剪切交汇段是油气勘探有利目标区.Abstract: The development stage of the fault deformation zone refers to the weak deformation (strong concealment) zone developed in the sedimentary cover of the basin, which is the product of the early and middle stages of the formation and evolution of the fault zone. It is difficult to identify because of the lack of obvious fracture surface (zone) and significant displacement. It has been found that the weakly deformed tectonic belt is an objective tectonic phenomenon in the sedimentary basin cover, and is closely related to oil and gas accumulation. It can be recognized by regular arrangement of different geological units (secondary faults, oil reservoirs, traps, facies belts, depressions, rock masses, buried hills, etc.). In order to reveal the deformation intensity and hydrocarbon accumulation scale of cap cover deformation zone, the key issue of oil and gas geology, this paper takes the Dongying Sag as the research object and applies variable caprock thickness and the structural physical simulation experiment method in which variable shear strength is used to study the process of basement fault strike-slip activity on the formation of faults in the sedimentary caprock of the basin. Using SPSS software, taking the sliding amount of the basement/the thickness of the experimental cover layer (DNBD) as the independent variable x1, the amount of lateral sliding/the thickness of the experimental cover layer as the independent variable x2 (x2=x1×tanα) and the length of the echelon seam/the thickness of the experimental cover as the dependent variable y, multivariate quadratic function fitting was performed. According to the strata thickness, shear length of structural map R and experimentally estimated tensional and torsion angles by experiment in different periods of Paleogene in Bamianhe (strong strike slip) and Wangjiagang (weak strike slip) areas of Dongying Sag, the strike-slip amounts of the basement faults of Bamianhe and Wangjiagang fault zones in each period were calculated. At each stage of the simulation experiment, dyed oil was charged, and combined with the sag examples, the accumulation models of the basement faults were established, such as Early R shear single-channel migration-isolated aggregation, Early and mid-term R shear main channel migration-geese and beaded aggregation, P shear main channel migration-intermittent zonal aggregation, full channel migration-continuous belt aggregation, etc.. Finally, it is pointed out that the R shear pressurized deformation section and the R and P shear intersection section in the deformation zone are favorable target areas for oil and gas exploration.
-
表 1 渤海湾盆地识别变形带
Table 1. Summary of identification of fault deformation zones in the Bohai Bay Basin
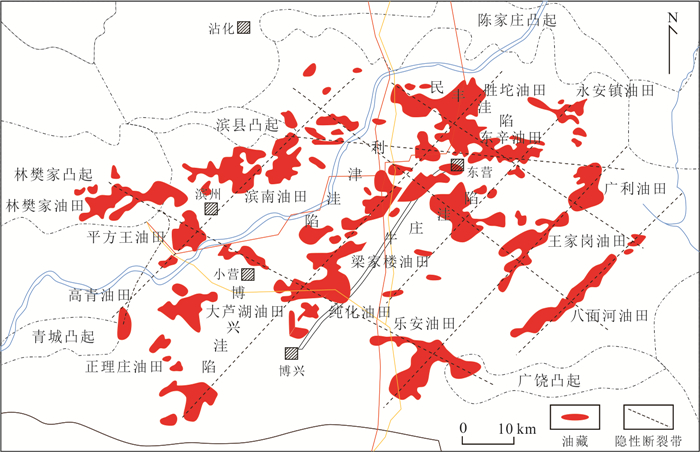
分布位置 断层名称 走向 长度(km) 宽度(km) 级别 东营凹陷 八面河变形带 北东向 18~20 < 10 圈闭级 东营凹陷 王家岗变形带 北东向 15~17 < 10 圈闭级 东营凹陷 滨南‒平方王变形带 北东向 22~26 < 12 凹陷级 东营凹陷 胜坨‒大芦湖变形带 北东向 25~29 < 15 凹陷级 东营凹陷 永安镇‒东辛‒梁家楼变形带 北东向 35~39 < 12 凹陷级 东营凹陷 胜坨‒东辛‒广利变形带 北西向 40~45 < 15 凹陷级 东营凹陷 滨南‒王家岗变形带 北西向 50~55 < 17 凹陷级 东营凹陷 林樊家‒纯化‒乐安变形带 北西向 65~70 < 20 凹陷级 东营凹陷 平方王‒正理庄‒金家变形带 南北向 35~40 < 15 凹陷级 惠民凹陷 肖庄‒临商变形带 北东东 40~45 < 10 凹陷级 惠民凹陷 夏口变形带 北东东 40~45 < 10 凹陷级 济阳坳陷 罗家‒胜坨‒乐安变形带 南北向 90~100 < 20 坳陷级 济阳坳陷 垦利‒渤南‒大王庄变形带 北西西 93~98 < 20 坳陷级 济阳坳陷 垦东变形带 北北东 24~30 < 10 凹陷级 济阳坳陷 滩海变形带 北西向 63~65 15~20 坳陷级 济阳坳陷 临盘‒玉皇庙‒英雄滩 北东向 102~107 < 20 坳陷级 青东凹陷 青东变形带 北北东向 31~35 1‒8 洼陷级 渤中坳陷 渤东变形带 北东向 40 30 洼陷级 渤中坳陷 蓬莱变形带 北北东 34 10 洼陷级 南堡凹陷 南堡2号‒林雀变形带 北西向 40~45 < 15 凹陷级 南堡凹陷 高柳‒蛤坨变形带 北西向 47~50 < 15 凹陷级 南堡凹陷 沙北变形带 北东向 32~35 < 12 凹陷级 南堡凹陷 南堡‒高柳变形带 北东向 31~35 < 12 凹陷级 南堡凹陷 沙垒田变形带 北东向 22~25 < 10 凹陷级 饶阳凹陷 赵黄庄变形带 北西向 22~25 < 10 凹陷级 黄骅坳陷 海河变形带 北西向 25~30 < 10 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 小站变形带 北西向 22~27 < 10 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 增福台变形带 北西向 22~27 < 15 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 埕北变形带 北西向 21~25 < 15 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 扣村变形带 北北西 32~38 < 20 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 北塘变形带 北北西 32~35 < 20 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 孔店‒小集‒乌马营变形带 北东向 110~120 < 24 坳陷级 黄骅坳陷 歧口变形带 北北东 170~180 > 100 坳陷级 渤海湾盆地 徐水‒安新变形带 北西向 130~140 < 30 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 衡水变形带 北西向 100~110 < 30 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 夏津‒腰站变形带 北西向 80~90 < 30 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 塘沽‒蓬莱变形带 北西向 160~180 < 50 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 回隆镇‒马陵变形带 北西向 60~70 < 30 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 秦皇岛‒旅顺变形带 北西向 40~50 20‒30 盆地级 渤海湾盆地 封丘‒兰考变形带 北西向 80~90 20‒30 盆地级 表 2 模型拟合度分析结果
Table 2. Model fit analysis results
R(%) R2(%) 调整R2(%) 标准估计的误差(%) 0.902 0.813 0.809 0.370 19 表 3 显著性分析结果
Table 3. Significance analysis results
平方和 df 均方 F Sig 回归 51.326 2 25.663 187.268 0 残差 11.785 86 0.137 总计 63.111 88 表 4 模型系数分析结果
Table 4. Model coefficient analysis results
非标准化系数 标准系数 t Sig B 标准误差 试用版 常量 0.184 0.092 2.004 0.048 走滑位移量 1.071 0.095 0.532 11.322 0 横向位移量 1.840 1.840 0.660 14.027 0 注:表格中的走滑位移量DNBD=基底断裂走滑位移量/盖层厚度,横向位移量HNBD=基底断裂横向位移量/盖层厚度. 表 5 八面河变形带走滑量计算结果
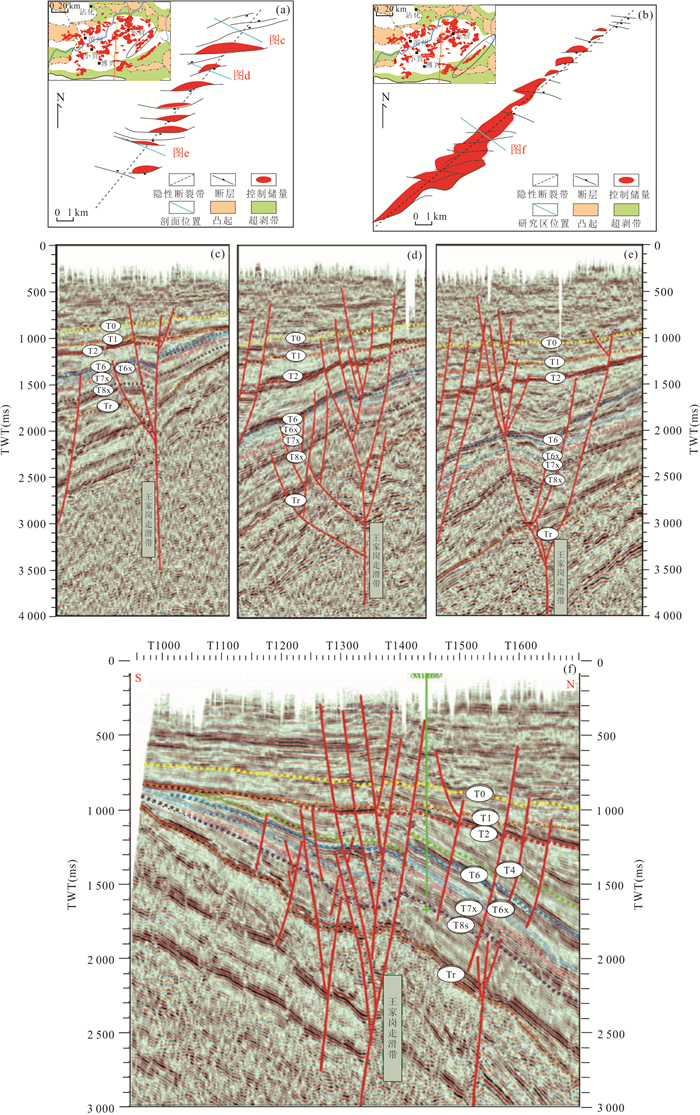
Table 5. Strike-slip calculation results of the Bamianhe fault trend zone
层位 地层厚度(m) 雁列式断层长度(km) 基底断裂走滑位移量(km) 基底断裂走滑位移量/盖层厚度 所处演化阶段 Es2-Ed ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ Es3 190 3.00,已贯通 1.62 8.48 显性阶段 Es4 260 2.76,已贯通 1.36 6.39 显性阶段 Ek 460 2.63,已贯通 1.34 2.89 显性阶段 表 6 王家岗变形带走滑量计算结果
Table 6. Calculation results of strike-slip in Wangjiagang fault trend zone
层位 地层厚度(m) 雁列式断层长度(km) 基底断裂走滑位移量(km) 基底断裂走滑位移量/盖层厚度 所处演化阶段 Es2-Ed ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ Es3 820 4.20 2.00 2.53 变形带阶段 Es4 650 3.00 1.59 2.22 变形带阶段 Ek 1 600 2.58 0.66 0.42 变形带阶段 表 7 盖层变形带变形强度与油气富集程度定量参数(累计注油量43 mL)
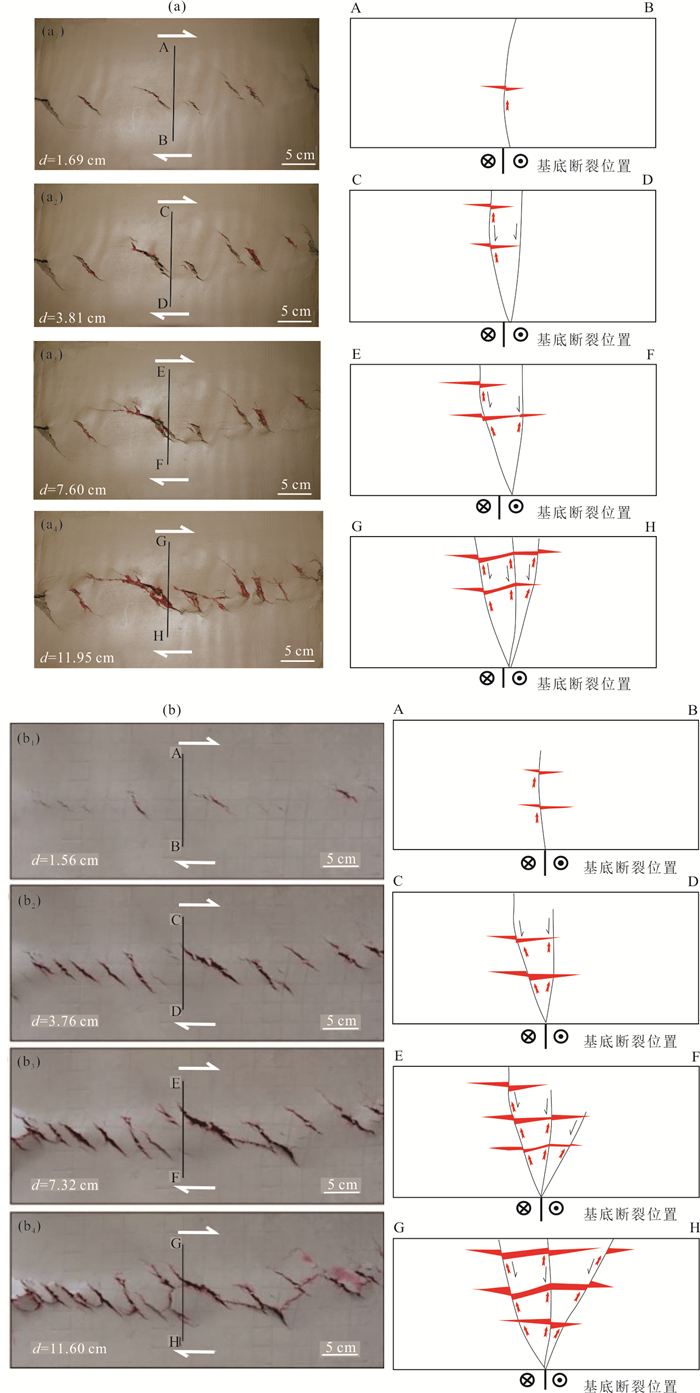
Table 7. Quantitative parameters of deformation strength and hydrocarbon enrichment degree of fault trend zone (cumulative oil injection volume 43 mL)
阶段 盖层变形带变形强度(cm) 注油量(mL) 损耗量(mL) 压力(kPa) 累计充注时间(min) 充注次数(次) 油注高度(cm) 圈闭面积充满度(%) a 1.69 6 2 70 3 2 0.20 10 b 3.81 11 2 70 7 3 1.60 20 c 7.6 14 5 45 9 3 1.93 45 d 11.95 14 6 15 10 2 2.27 70 表 8 盖层变形带变形强度与油气富集程度定量参数(累计注油量80 mL)
Table 8. Quantitative parameters of deformation strength and hydrocarbon enrichment degree of fault trend zone (cumulative oil injection volume 80 mL)
阶段 盖层变形带变形强度(cm) 注油量(mL) 损耗量(mL) 压力(kPa) 累计充注时间(min) 充注次数(次) 油注高度(cm) 圈闭面积充满度(%) A 1.56 12 4 90 3 2 1.64 20 B 3.76 20 4 90 7 3 2.32 55 C 7.32 24 10 70 9 3 3.10 75 D 11.60 24 10 45 10 2 3.35 90 -
Atmaoui, N., Kukowski, N., Stöckhert, B., et al., 2006. Initiation and Development of Pull-Apart Basins with Riedel Shear Mechanism: Insights from Scaled Clay Experiments. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 95(2): 225-238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0030-1 Bellahsen, N., Daniel, J. M., 2005. Fault Reactivation Control on Normal Fault Growth: An Experimental Study. Journal of Structural Geology, 27(4): 769-780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2004.12.003 Chi, Y. L., Zhao, W. Z., 2000. Strike-Slip Deformation during the Cenozoic and Its Influence on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 21(2): 14-20 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.02.003 Coelho, S., Passchier, C., Marques, F., 2006. Riedel-Shear Control on the Development of Pennant Veins: Field Example and Analogue Modelling. Journal of Structural Geology, 28(9): 1658-1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2006.05.009 Cunningham, W. D., Mann, P., 2007. Tectonics of Strike-Slip Restraining and Releasing Bends. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 290(1): 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp290.1 Davis, G. H., Bump, A. P., Garcı́a, P. E., et al., 2000. Conjugate Riedel Deformation Band Shear Zones. Journal of Structural Geology, 22(2): 169-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0191-8141(99)00140-6 Di, L. J., 2006. Controlling of Petrophysical Fractures on Extra-Low Permeability Oil and Gas Reservoirs in Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 33(6): 667-670 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.06.005 Dooley, T. P., Schreurs, G., 2012. Analogue Modelling of Intraplate Strike-Slip Tectonics: A Review and New Experimental Results. Tectonophysics, 574-575: 1-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.05.030 Fredman, N., Tveranger, J., Cardozo, N., et al., 2008. Fault Facies Modeling: Technique and Approach for 3-D Conditioning and Modeling of Faulted Grids. AAPG Bulletin, 92(11): 1457-1478. https://doi.org/10.1306/06090807073 Fu, G., Wang, Y. P., 2018. Controlling Factors of Hydrocarbon Enrichment with the Type of "below Source and Upper Reservoir" in Fault Concentrated Zones and Nearby. Lithologic Reservoirs, 30(2): 23-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fu, X. F., Fang, D. Q., Lü, Y. F., et al., 2005. Method of Evaluating Vertical Sealing of Faults in Terms of the Internal Structure of Fault Zones. Earth Science, 30(3): 328-336 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.03.008 Fusseis, F., Xiao, X., Schrank, C., et al., 2014. A Brief Guide to Synchrotron Radiation-Based Microtomography in (Structural) Geology and Rock Mechanics. Journal of Structural Geology, 65: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2014.02.005 Ghosh, N., Chattopadhyay, A., 2008. The Initiation and Linkage of Surface Fractures above a Buried Strike-Slip Fault: an Experimental Approach. Journal of Earth System Science, 117(1): 23-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0009-y Hardy, S., 2011. Cover Deformation above Steep, Basement Normal Faults: Insights from 2D Discrete Element Modeling. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(5): 966-972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.11.005 Hu, J. S., Sui, Z. Q., Liu, C. Z., 2009. Geologic Origin of Gravity Anomaly in Southern Dongying Depression. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 16(2): 39-42, 113 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2009.02.012 Hu, S. Y., Yu, Y. J., Dong, D. Z., et al., 2006. Control of Fault Activity on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Central Junggar Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 27(1): 1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00255.x Jiang, M. M., Fu, X. F., Shi, L., et al., 2022. Physical Analogue Experiment of Microstructure and Variation Law of Permeability within Faults in High-Porosity Sandstone. Earth Science, 47(5): 1805-1818 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, Y. L., Liu, H., Zhang, L., et al., 2005. Characteristics of Petroleum System in Dongying Depression. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 26(5): 33-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2005.05.007 Jiang, Y. L., Zhai, Q. L., Rong, Q. H., et al., 2003. Main Factors for Controlling Hydrocarbon Accumulation in South-West Part of Dongying Depression. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 27(4): 11-14, 36 (in Chinese with English abstract). Le Guerroué, E., Cobbold, P. R., 2006. Influence of Erosion and Sedimentation on Strike-Slip Fault Systems: Insights from Analogue Models. Journal of Structural Geology, 28(3): 421-430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2005.11.007 Li, H. Y., Niu, C. M., Xu, P., et al., 2021. Discovery of Bozhong 13-2 Archean Large Monoblock Volatile Buried Hill Oilfield and Its Oil and Gas Exploration Significance. Natural Gas Industry, 41(2): 19-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, H., Jiang, Y. L., Ren, J. L., 2009. Characteristics of Petroleum System and Oil-Source in Dongying Depression. Geological Journal of China Universities, 15(1): 93-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2009.01.009 Lu, K. Z., Qi, J. F., Dai, J. S., et al., 1997. Tectonic Model of Cenozoic Oil-Bearing Basin in Bohai Bay. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Luo, Q., 2010. Concept, Principle, Model and Significance of the Fault Controlling Hydrocarbon Theory. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 37(3): 316-324 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60035-3 Ma, B. J., Qi, J. F., Niu, S. Y., et al., 2009. The Influence of Basement Fault on the Deformation of Complex Cover Blocks in a Uniform Stress Field—Enlightenment from Sandbox Experiment. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(4): 105-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.04.011 Mollema, P. N., Antonellini, M. A., 1996. Compaction Bands: A Structural Analog for Anti-Mode Ⅰ Cracks in Aeolian Sandstone. Tectonophysics, 267(1-4): 209-228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00098-4 Morley, C. K., 1999. How Successful Are Analogue Models in Addressing the Influence of Pre-Existing Fabrics on Rift Structure? Journal of Structural Geology, 21(8-9): 1267-1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00075-9 Qi, J. F., 2004. Two Tectonic Systems in the Cenozoic Bohai Bay Basin and Their Genetic Interpretation. Chinese Geology, 31(1): 15-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.01.002 Qi, J. F., Deng, R. J., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2008. Structure of Tancheng-Lujiang Fault Zone in Cenozoic Basin in Bohai Sea. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 38(S1): 19-29 (in Chinese). Richard, P., 1991. Experiments on Faulting in a Two-Layer Cover Sequence Overlying a Reactivated Basement Fault with Oblique-Slip. Journal of Structural Geology, 13(4): 459-469. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8141(91)90018-E Richard, P., Krantz, R. W., 1991. Experiments on Fault Reactivation in Strike-Slip Mode. Tectonophysics, 188(1-2): 117-131. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(91)90318-M Richard, P., Mocquet, B., Cobbold, P. R., 1991. Experiments on Simultaneous Faulting and Folding above a Basement Wrench Fault. Tectonophysics, 188(1-2): 133-141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(91)90319-N Song, G. Q., Li, J. Y., Jia, G. H., et al., 2013. Structural Characteristics and Its Control on Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Kongdian Formation in the Wangjiagang Structural Zone, Dongying Depression. Oil & Gas Geology, 34(2): 207-214 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2013.02.003 Thomas, G. E., 1974. Lineament-Block Tectonics: Williston-Blood Creek Basin. AAPG Bulletin, 58: 1305-1322. https://doi.org/10.1306/83d9166e-16c7-11d7-8645000102c1865d Wang, W. F., Zhou, W. W., Shan, X. J., et al., 2015a. Characteristics of Hidden Fault Zone and Its Significance in Geology in Sedimentary Basin. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 46(6): 2236-2243 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, W. F., Zhou, W. W., Liu, Y. R., 2015b. Evolution of Subtle Fault Zone and Its Control Function of Reservoirs Forming in Jinhu Sag. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 50(3): 911-925 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Z. C., Zhao, W. Z., Li, Z. Y., et al., 2008. Role of Basement Faults in Gas Accumulation of Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 35(5): 541-547 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(09)60087-2 Xie, Y. H., 2021. Major Achievements in Oil and Gas Exploration of CNOOC in the 13th Five-Year Plan Period and Prospects in the 14th Five-Year Plan Period. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(1): 43-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, X. Y., Wang, W. F., 2020. The Recognition of Potential Fault Zone in Ordos Basin and Its Reservoir Control. Earth Science, 45(5): 1754-1768 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xue, Y. A., Li, H. Y., Xu, P., et al., 2021. Recognition of Oil and Gas Accumulation of Mesozoic Covered Buried Hills in Bohai Sea Area and the Discovery of BZ13-2 Oilfield. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 33(1): 13-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, W. Z., Hu, S. Y., Wang, Z. C., et al., 2003. Key Role of Basement Fault Control on Oil Accumulation of Yanchang Formation, Upper Triassic, Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 30(5): 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, W. W., Wang, W. F., An, B., et al., 2014a. Genetic Types of Potential Fault Zone and Its Significance on Hydrocarbon Accumulation. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(11): 1727-1734 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, W. W., Wang, W. F., An, B., et al., 2014b. Identification of Potential Fault Zones and Its Geological Significance in Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Science, 39(11): 1627-1638 (in Chinese with English abstract). 池英柳, 赵文智, 2000. 渤海湾盆地新生代走滑构造与油气聚集. 石油学报, 21(2): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200002002.htm 邸领军, 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地储集层物性断裂对超低渗油气藏的控制作用. 石油勘探与开发, 33(6): 667-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200606004.htm 付广, 王宇鹏, 2018. 断裂密集带及附近下生上储式油气富集的控制因素. 岩性油气藏, 30(2): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201802003.htm 付晓飞, 方德庆, 吕延防, 等, 2005. 从断裂带内部结构出发评价断层垂向封闭性的方法. 地球科学, 30(3): 328-336. http://www.earth-science.net/article/id/1414 胡加山, 隋志强, 刘成斋, 2009. 东营凹陷南部重力异常地质成因. 油气地质与采收率, 16(2): 39-42, 113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200902014.htm 胡素云, 蔚远江, 董大忠, 等, 2006. 准噶尔盆地腹部断裂活动对油气聚集的控制作用. 石油学报, 27(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200601000.htm 姜明明, 付晓飞, 石磊, 等, 2022. 高孔砂岩断层内部微观结构及渗透性变化规律物理模拟. 地球科学, 47(5): 1805-1818. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.113 蒋有录, 刘华, 张乐, 等, 2005. 东营凹陷含油气系统的划分及评价. 石油学报, 26(5): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200505006.htm 蒋有录, 翟庆龙, 荣启宏, 等, 2003. 东营凹陷博兴地区油气富集的主要控制因素. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 27(4): 11-14, 36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200304002.htm 李慧勇, 牛成民, 许鹏, 等, 2021. 渤中13-2大型整装覆盖型潜山油气田的发现及其油气勘探意义. 天然气工业, 41(2): 19-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202102005.htm 刘华, 蒋有录, 任景伦, 2009. 东营凹陷油‒源特征与含油气系统划分. 高校地质学报, 15(1): 93-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200901009.htm 陆克政, 漆家福, 戴俊生, 等, 1997. 渤海湾新生代含油气盆地构造模式. 北京: 地质出版社. 罗群, 2010. 断裂控烃理论的概念、原理、模式与意义. 石油勘探与开发, 37(3): 316-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201003010.htm 马宝军, 漆家福, 牛树银, 等, 2009. 统一应力场中基底断裂对盖层复杂断块变形的影响——来自砂箱实验的启示. 地学前缘, 16(4): 105-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200904013.htm 漆家福, 2004. 渤海湾新生代盆地的两种构造系统及其成因解释. 中国地质, 31(1): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200401001.htm 漆家福, 邓荣敬, 周心怀, 等, 2008. 渤海海域新生代盆地中的郯庐断裂带构造. 中国科学: 地球科学, 38(S1): 19-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1003.htm 宋国奇, 李继岩, 贾光华, 等, 2013. 东营凹陷王家岗构造带孔店组构造特征及其控藏作用. 石油与天然气地质, 34(2): 207-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201302013.htm 王伟锋, 周维维, 单新建, 等, 2015a. 沉积盆地隐性断裂带特征及其地质意义. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 46(6): 2236-2243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201506035.htm 王伟锋, 周维维, 刘玉瑞, 2015b. 张扭性盆地隐性断裂带识别、演化及控藏作用——以苏北盆地金湖凹陷为例. 地质科学, 50(3): 911-925. 汪泽成, 赵文智, 李宗银, 等, 2008. 基底断裂在四川盆地须家河组天然气成藏中的作用. 石油勘探与开发, 35(5): 541-547. 谢玉洪, 2021. 中国海油"十三五"油气勘探重大成果与"十四五"前景展望. 中国石油勘探, 26(1): 43-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202101004.htm 徐兴雨, 王伟锋, 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地隐性断裂识别及其控藏作用. 地球科学, 45(5): 1754-1768. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.175 薛永安, 李慧勇, 许鹏, 等, 2021. 渤海海域中生界覆盖型潜山成藏认识与渤中13-2大油田发现. 中国海上油气, 33(1): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202101002.htm 赵文智, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等, 2003. 鄂尔多斯盆地基底断裂在上三叠统延长组石油聚集中的控制作用. 石油勘探与开发, 30(5): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200305000.htm 周维维, 王伟锋, 安邦, 等, 2014a. 渤海湾盆地隐性断裂带成因类型特征及其对油气聚集的控制作用. 天然气地球科学, 25(11): 1727-1734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201411007.htm 周维维, 王伟锋, 安邦, 等, 2014b. 渤海湾盆地隐性断裂带识别及其地质意义. 地球科学, 39(11): 1627-1638. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.145 -









 下载:
下载: