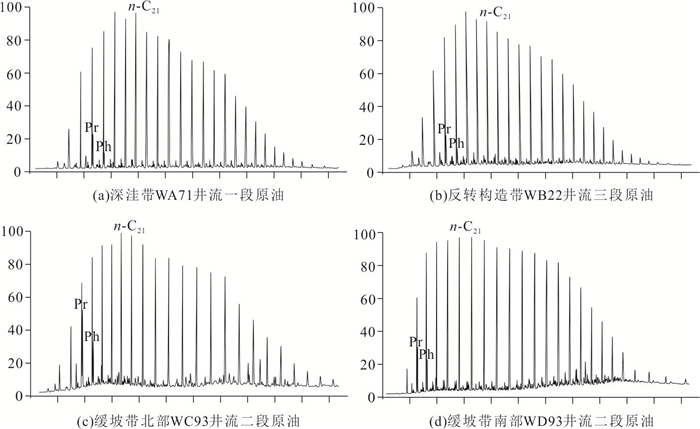
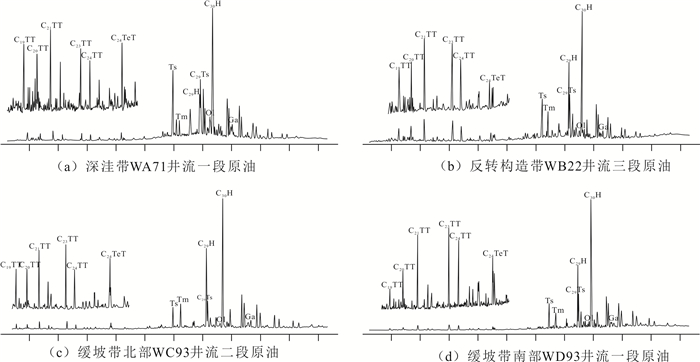
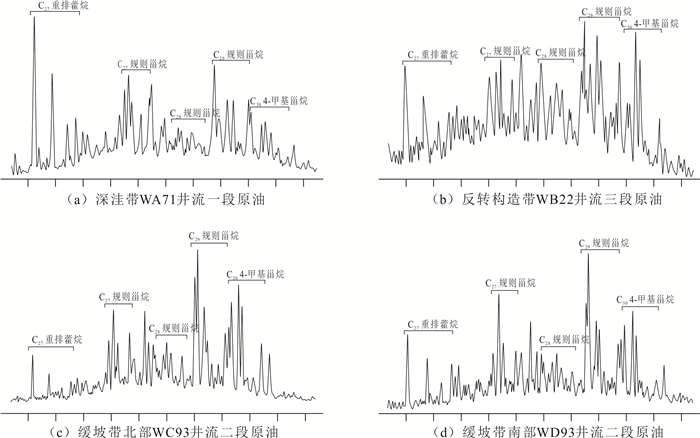
Geochemical Characteristics and Oil-Source Rock Correlation of Crude Oil in Wushi Sag, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea
-
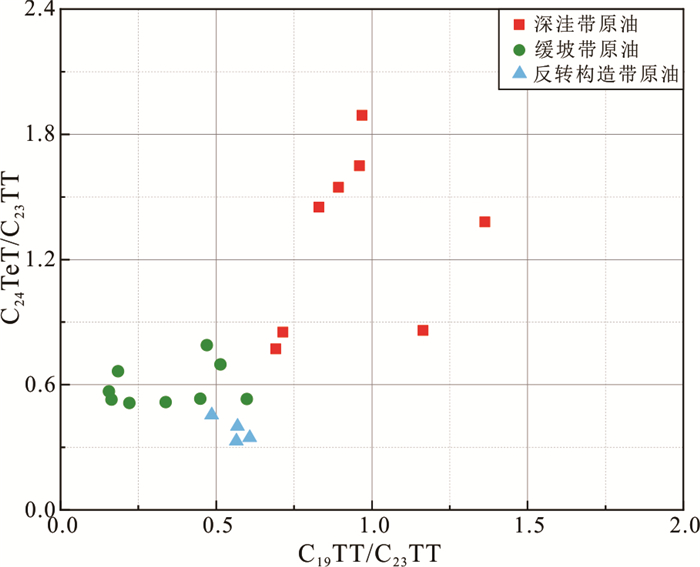
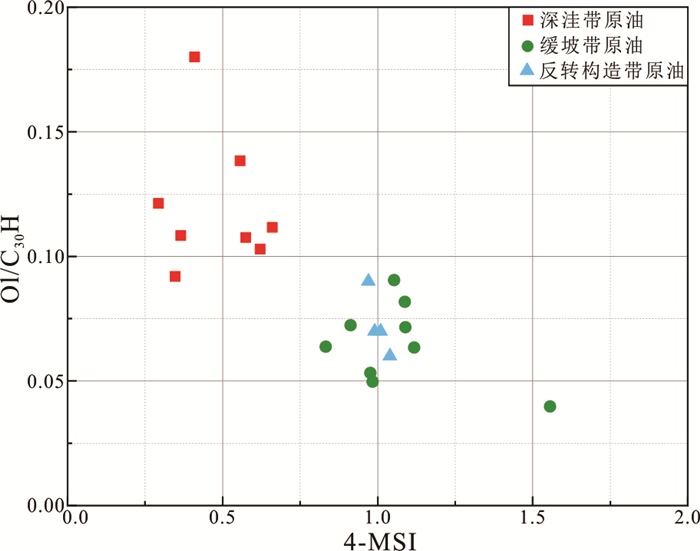
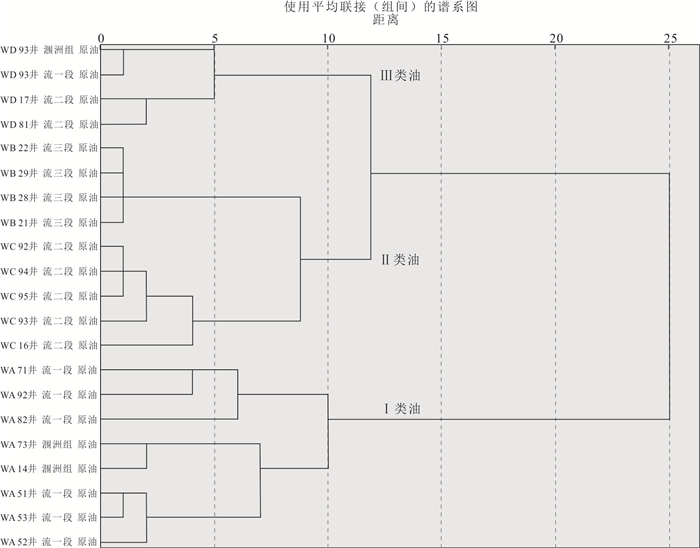
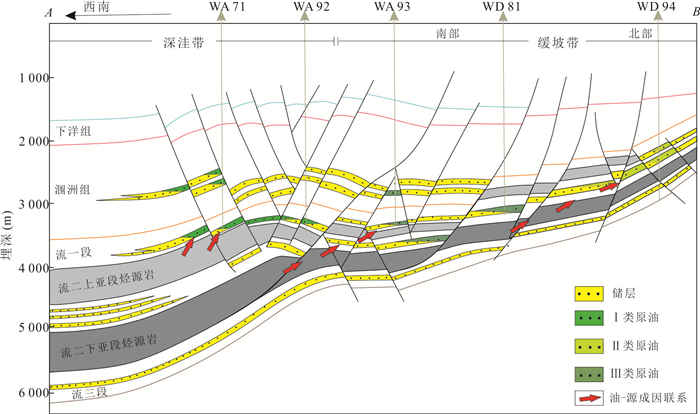
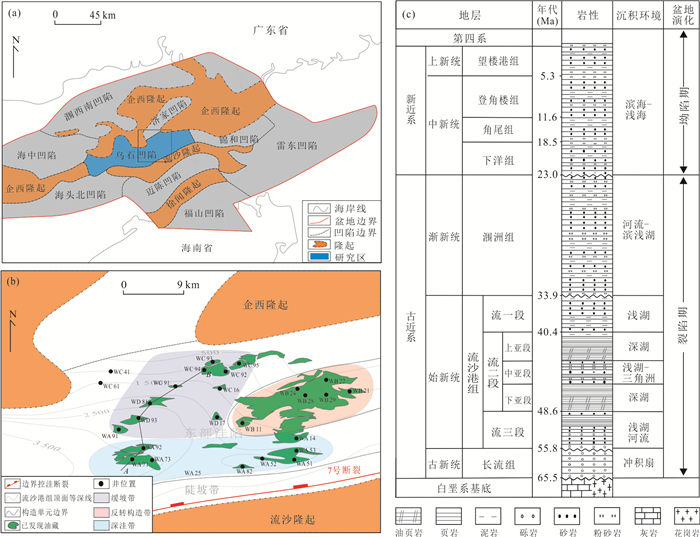
摘要: 为了探究乌石凹陷的油气来源,对原油及烃源岩样品进行地球化学分析.研究结果表明,乌石凹陷原油可分为3类:Ⅰ类原油分布在深洼带的涠洲组和流沙港组一段储层,成熟度整体偏高,C19三环萜烷、C24四环萜烷、奥利烷丰度均相对较高,C23三环萜烷、C30 4-甲基甾烷丰度相对较低,体现出水生低等生物与陆源高等植物双重输入的特征.Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类原油主要分布在反转构造带和缓坡带的流沙港组二段、三段储层中,成熟度整体低于Ⅰ类原油,C19三环萜烷、C24四环萜烷、奥利烷丰度均较低,C23三环萜烷、C30 4-甲基甾烷丰度相对较高,表明其母质来源以低等水生生物为主.相对Ⅱ类原油,Ⅲ类原油的Pr/Ph值更低,全油稳定碳同位素偏轻.油源对比表明,Ⅰ类原油主要来源于流沙港组二上亚段烃源岩;Ⅱ类及Ⅲ类原油均来自流沙港组二下亚段烃源岩.Abstract: To study the genetic relationship between oil and source rock in Wushi sag, geochemical analyses of crude oil and source rock samples were carried out in this paper. The results show that crude oils in Wushi sag can be classified into three groups: group Ⅰ crude oil is distributed in the Weizhou Formation and 1-member of Liushagang Formation reservoir in the deep sag belt. The maturity of this crude oil is relatively high, and the abundances of C19 tricyclic terpenes, C24 tetracyclic terpenes, and oleanane are relatively high, while the abundances of C23 tricyclic terpenes and C30 4-methylsteranes are relatively low, which reflects the characteristics of double input of lower aquatic organisms and terrigenous higher plants. Group Ⅱ and group Ⅲ crude oil is mainly distributed in the 2-member and 3-member of the Liushagang Formation reservoir in the reversal tectonic belt and gentle slope belt, and their maturity is overall lower than that of group Ⅰ crude oil. The abundances of C19 tricyclic terpanes, C24 tetracyclic terpanes, and oleanane of these oils are relatively low, and the abundances of C23 tricyclic terpanes and 4-methylsteranes are relatively high, indicating their parent material is mainly from lower aquatic organisms. The difference between the two groups of crude oils mainly lies in the Pr/Ph value and the stable carbon isotope characteristics of whole oil. Compared with group Ⅱ crude oil, group Ⅲ crude oil has a lower Pr/Ph value and lighter stable carbon isotope. The oil-source rock correlation shows that the group Ⅰ crude oil mainly comes from the upper sub-member of 2-member of Liushagang Formation source rock. Both group Ⅱ and group Ⅲ oils are derived from the lower sub-member of the 2-member of Liushagang Formation source rock.
-
表 1 乌石凹陷不同构造带原油物性及族组分统计
Table 1. Statistical data of physical properties and group components of crude oil in different structural belts of Wushi sag
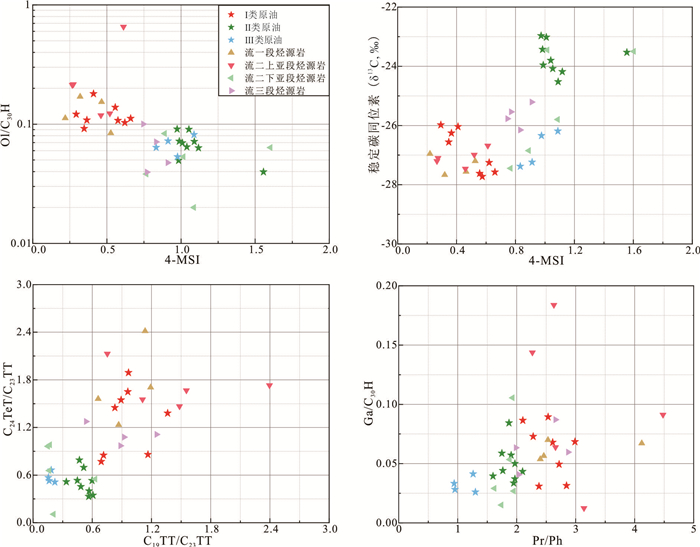
构造带 密度(g/cm3) 粘度(mPa·s) 含硫量(%) 含蜡量(%) 胶质+沥青质(%) 饱和烃(%) 芳烃(%) 非烃+沥青质(%) 原油类型 深洼带 0.797~0.862 1.30~16.09 0.03~0.25 6.93~21.1 2.38~6.90 72.72~88.68 7.66~18.55 3.06~11.95 轻质油 0.828(16) 4.416(16) 0.1(16) 14.068(16) 4.66(14) 80.66(16) 12.66(16) 6.68(16) 反转构造带 0.806~0.850 3.31~8.96 0.03~0.14 11.7~19.1 1.70~6.91 75.92~86.16 3.86~14.91 3.94~12.77 0.822(8) 5.09(8) 0.06(8) 9.91(8) 3.26(7) 81.32(8) 11.08(8) 7.60(8) 缓坡带 0.852~0.935 14.31~491.1 0.14~0.35 4.83~31.9 4.68~32.7 46.83~79.35 11.80~28.07 8.67~32.62 中质‒重质油 0.899(13) 168.31(11) 0.23(12) 16.1(13) 15.33(13) 63.4(13) 18.8(13) 17.8(13) 注:0.797~0.862分别表示最小值、最大值;0.828(16)分别表示平均值、样品数. 表 2 乌石凹陷不同构造带原油生物标志物参数及稳定碳同位素值
Table 2. Biomarker parameters and stable carbon isotopes of crude oil in different structural belts of Wushi sag
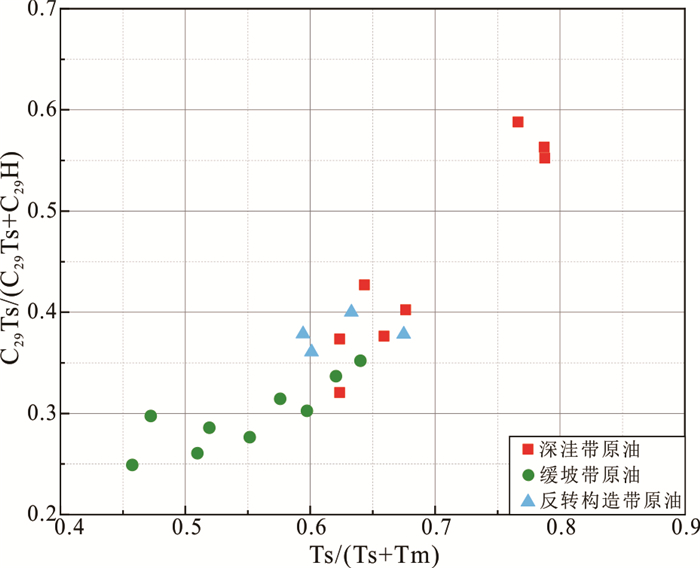
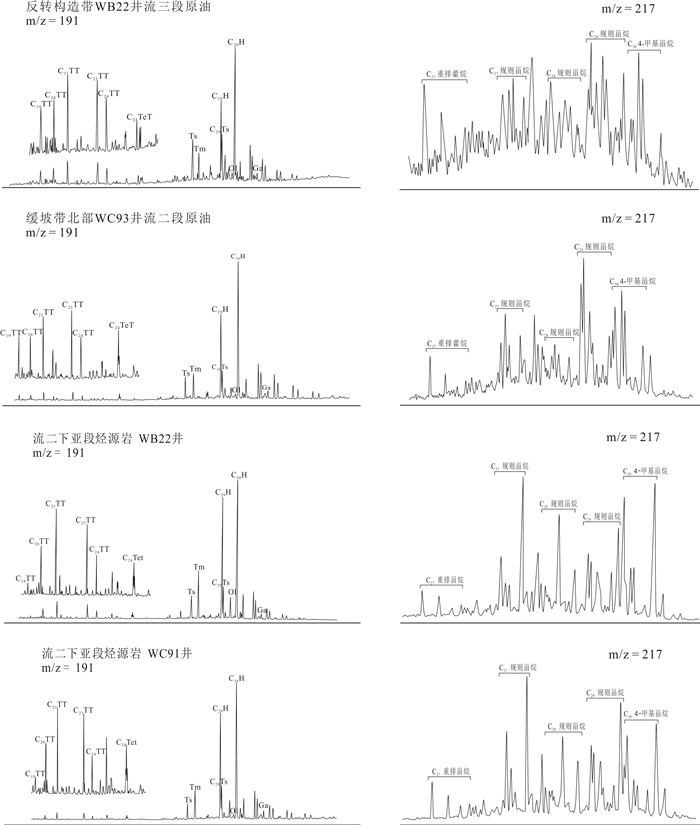
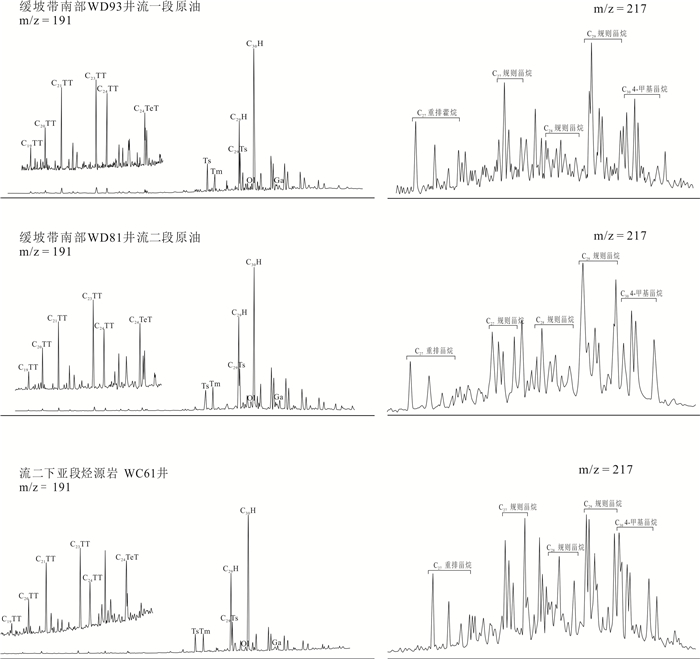
构造带 井号 储层 Pr/Ph CPI C19TT/C23TT C24TeT/C23TT Ts/(Ts+Tm) C29Ts/(C29Ts+C29H) Ol/C30H Ga/C30H 4-MSI δ13C全油(‰) 原油族群 深洼带 WA71 流一段 2.10 1.08 1.36 1.38 0.77 0.59 0.12 0.09 0.29 ‒25.98 Ⅰ WA73 涠洲组 2.38 1.08 0.69 0.77 0.64 0.43 0.09 0.03 0.35 ‒26.56 Ⅰ WA92 流一段 2.53 1.11 1.16 0.86 0.79 0.55 0.18 0.09 0.41 ‒26.04 Ⅰ WA82 流一段 2.61 1.14 0.83 1.45 0.79 0.56 0.10 0.07 0.62 ‒27.25 Ⅰ WA14 涠洲组 2.72 1.10 0.71 0.85 0.62 0.32 0.11 0.05 0.37 ‒26.26 Ⅰ WA51 流一段 2.84 1.18 0.97 1.89 0.62 0.37 0.11 0.03 0.57 ‒27.72 Ⅰ WA52 流一段 2.28 1.12 0.89 1.55 0.66 0.38 0.11 0.07 0.66 ‒27.57 Ⅰ WA53 流一段 2.99 1.16 0.96 1.65 0.68 0.40 0.14 0.07 0.56 ‒27.62 Ⅰ 反转构造带 WB21 流三段 1.87 1.03 0.61 0.35 0.67 0.38 0.09 0.08 0.97 ‒22.97 Ⅱ WB22 流三段 1.97 1.07 0.57 0.40 0.59 0.38 0.07 0.05 1.01 ‒23.02 Ⅱ WB28 流三段 2.10 1.08 0.49 0.45 0.63 0.40 0.07 0.04 0.99 ‒23.96 Ⅱ WB29 流三段 1.75 1.12 0.56 0.33 0.60 0.36 0.06 0.06 1.04 ‒23.80 Ⅱ 缓坡带北部 WC16 流二段 1.60 1.12 0.34 0.52 0.60 0.30 0.04 0.04 1.56 ‒23.53 Ⅱ WC92 流二段 1.77 1.15 0.45 0.53 0.51 0.26 0.06 0.04 1.12 ‒24.18 Ⅱ WC93 流二段 1.91 1.15 0.47 0.79 0.46 0.25 0.05 0.06 0.98 ‒23.43 Ⅱ WC94 流二段 1.95 1.11 0.51 0.70 0.52 0.29 0.07 0.03 1.09 ‒24.52 Ⅱ WC95 流二段 1.97 1.10 0.60 0.53 0.58 0.31 0.09 0.04 1.05 ‒24.08 Ⅱ 缓坡带南部 WD93 涠洲组 0.94 1.08 0.16 0.53 0.62 0.34 0.07 0.03 0.91 ‒27.24 Ⅲ WD93 流一段 1.26 1.06 0.16 0.57 0.64 0.35 0.06 0.04 0.83 ‒27.38 Ⅲ WD17 流二段 0.95 1.08 0.22 0.51 0.55 0.28 0.08 0.03 1.09 ‒26.19 Ⅲ WD81 流二段 1.30 1.16 0.18 0.66 0.47 0.30 0.05 0.03 0.98 ‒26.34 Ⅲ 表 3 乌石凹陷流沙港组烃源岩总有机碳含量、热解参数、镜质体反射率统计
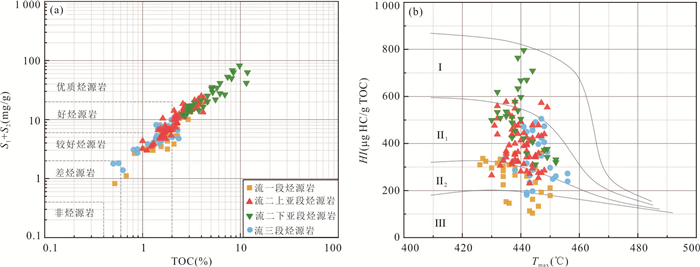
Table 3. Total organic carbon content, pyrolysis parameters and vitrinite reflectance of source rocks in Liushagang Formation, Wushi sag
烃源岩层 总有机碳(%) 产油潜率 S1+S2(mg/g) 热解最大峰温 Tmax(℃) 氢指数HI(mg/g) 镜质体反射率 Ro(%) 流一段 0.52~4.04 0.82~17.74 426~450 104~360 0.52~0.73 1.71(27) 5.06 (27) 438 (27) 250 (27) 流二上亚段 1.00~4.45 3.00~24.91 430~449 231~579 0.47~0.89 2.30 (68) 10.52 (68) 440 (68) 396 (68) 流二下亚段 2.56~11.8 11.58~81.4 430~452 311~796 0.49~0.88 5.50 (29) 31.08 (29) 440 (29) 510 (29) 流三段 0.50~2.72 1.38~12.18 434~456 181~505 0.46~0.92 1.61 (30) 6.24 (30) 445 (30) 342 (30) 注:1.71(27)分别表示平均值、样品数. 表 4 乌石凹陷流沙港组烃源岩生物标志物参数及干酪根稳定碳同位素统计
Table 4. Biomarker parameters and stable carbon isotopes of source rock of Liushagang Formation in Wushi sag
井号 烃源岩层 Pr/Ph Ga/C30H Ol/C30H C19TT/C23TT C24TeT/C23TT 4-MSI δ13C干酪根(‰) WA51 流一段 2.40 0.05 0.11 0.87 1.23 0.22 ‒26.96 WA51 流一段 2.53 0.07 0.17 0.66 1.56 0.32 ‒27.67 WA53 流一段 4.12 0.07 0.15 1.14 2.41 0.46 ‒27.56 WA71 流一段 2.46 0.06 0.08 1.19 1.70 0.53 ‒27.20 WA25 流二上亚段 3.14 0.01 0.21 1.48 1.47 0.27 ‒27.20 WA51 流二上亚段 2.66 0.06 0.12 0.75 2.13 0.52 ‒26.99 WA73 流二上亚段 2.27 0.14 0.22 1.55 1.67 0.27 ‒27.10 WA91 流二上亚段 4.48 0.09 0.66 2.40 1.73 0.61 ‒26.68 WA92 流二上亚段 2.63 0.18 0.12 1.11 1.55 0.46 ‒27.46 WB11 流二下亚段 1.93 0.11 0.08 0.63 0.55 0.89 ‒26.85 WB22 流二下亚段 1.74 0.01 0.02 0.15 0.96 1.09 ‒25.80 WB22 流二下亚段 1.62 0.03 0.06 0.21 0.11 1.60 ‒23.50 WC61 流二下亚段 1.88 0.05 0.04 0.17 0.98 0.77 ‒27.45 WC91 流二下亚段 1.95 0.03 0.05 0.16 0.66 1.02 ‒23.45 WB24 流三段 2.04 0.04 0.07 0.54 1.28 0.83 ‒26.15 WC41 流三段 2.87 0.06 0.10 0.89 0.97 0.75 ‒25.77 WC41 流三段 2.66 0.09 0.04 0.92 1.08 0.77 ‒25.54 WC91 流三段 1.99 0.06 0.05 1.25 1.11 0.91 ‒25.21 -
Fang, R., Littke, R., Zieger, L., et al., 2019. Changes of Composition and Content of Tricyclic Terpane, Hopane, Sterane, and Aromatic Biomarkers throughout the Oil Window: A Detailed Study on Maturity Parameters of Lower Toarcian Posidonia Shale of the Hils Syncline, NW Germany. Organic Geochemistry, 138: 103928. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2019.103928 Gan, J., Yang, X.B., Hu, L., et al., 2019. Hydrocarbon Generation Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Differential Accumulation Model in Wushi Sag. Geological Science and Technology Information, 38(3): 174-179 (in Chinese with English abstract). Golyshev, S.I., Verkhovskaya, N., Burkova, V.N., et al., 1991. Stable Carbon Isotopes in Source-Bed Organic Matter of West and East Siberia. Organic Geochemistry, 17: 277-291. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(91)90091-W Hackley, P.C., Parris, T.M., Eble, C.F., et al., 2021. Oil-Source Correlation Studies in the Shallow Berea Sandstone Petroleum System, Eastern Kentucky. AAPG Bulletin, 105: 517-542. doi: 10.1306/08192019077 Hao, X., Ren, Y.J., Xu, X.D., et al., 2016. Composition Characteristics and Geochemical Significance of Aromatic Hydrocarbon in Crude Oils in Eastern Wushi Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 37(6): 674-680 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, D.J., Feng, Z.H., 2011. Oil and Gas Geochemistry. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 201-242 (in Chinese). Hu, C.H., Lu, H.O., Huang, Y. X., 2021. Geochemical Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of Heavy Oil in Wushi Sag. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 28(9): 111-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, L., Yang, X. B., Xu, X. F., et al., 2016. Main Controlling Factors and Accumulation Models of Hydrocarbon in Wushi Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin, South China Sea. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 36(2): 121-127 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, B.J., Tian, H., Wilkins, R.W.T., et al., 2013. Geochemical Characteristics, Palaeoenvironment and Formation Model of Eocene Organic-Rich Shales in the Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea. Marine Petroleum Geology, 48: 77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.012 Huang, B.J., Xiao, X.M., Zhang, M.Q., 2003. Geochemistry, Grouping and Origins of Crude Oils in the Western Pearl River Mouth Basin, Offshore South China Sea. Organic Geochemistry, 34: 993-1008. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(03)00035-4 Huang, B.J., Zhu, W.L., Tian, H., et al., 2017. Characterization of Eocene Lacustrine Source Rocks and Their Oils in the Beibuwan Basin, Offshore South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 101: 1395-1423. doi: 10.1306/10171615161 Lan, L., Li, Y.C., Wang, K., et al., 2019. Biomarker Parameters for Effectively Distinguishing Source Rocks in Bozhong Sag. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(1): 35-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0066-y Li, F.L., Lü, L., Ma, W.K., et al., 2021. Geochemical Characteristics of Source Rocks in Liushagang Formation of Wushi Sag. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 45(1): 31-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, R.W., 1988. Geological Occurrence and Paleoenvironmental Significance of Gammacerane. Chinese Science Bulletin, 33(20): 1574-1576 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1988-33-20-1574 Li, X.S., Gan, J., Zhang, Y.C., et al., 2015. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Regularity and Exploration Prospects of Fault Lacustrine Basins in Western South China Sea. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 27(4): 22-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y. C., Lan, L., Wang, K., et al., 2019. Differences in Lacustrine Source Rocks of Liushagang Formation in the Beibuwan Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(12): 1451-1459 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y.C., Wang, K., Lan, L., 2020. Oil and Gas Differences and Their Controlling Factors of the Main Sags in the Beibuwan Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 32(5): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). Moldowan, J. M., Dahl, J., Huizinga, B. J., et al., 1994. The Molecular Fossil Record of Oleanane and Its Relation to Angiosperms. Science, 265(5173): 768-771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.265.5173.768 Parandavar, M., Sadouni, J., 2021. Evaluation of Organic Matter Richness of Eocene Strata Based on Calcareous Nannofossils and Rock-Eval Analysis in North Dezful, Iran. Journal of Earth Science, 32(4): 1022-1034. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1091-6 Peters, K.E., Walters, C.C., Moldowan, J.M., 2005. The Biomarker Guide. In: Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Exploration and Earth History. University of Cambridge Press, Cambridge, 475-1155. Philp, R. P., Gilbert, T. D., 1986. Biomarker Distributions in Australian Oils Predominantly Derived from Terrigenous Source Material. Organic Geochemistry, 10(1-3): 73-84. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(86)90010-0 Talbot, M.R., 1990. A Review of the Palaeohydrological Interpretation of Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Ratios in Primary Lacustrine Carbonates. Chemical Geology, 80: 261-279. Talbot, M. R., Livingstone, D. A., 1989. Hydrogen Index and Carbon Isotopes of Lacustrine Organic Matter as Lake Level Indicators. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 70(1-3): 121-137. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(89)90084-9 Tao, S. Z., Wang, C. Y., Du, J. G., et al., 2015. Geochemical Application of Tricyclic and Tetracyclic Terpanes Biomarkers in Crude Oils of NW China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 67: 460-467. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.030 Ten Haven, H. L., De Leeuw, J. W., Rullkötter, J., et al., 1987. Restricted Utility of the Pristane/Phytane Ratio as a Palaeoenvironmental Indicator. Nature, 330(6149): 641-643. doi: 10.1038/330641a0 Wang, Y. J., Cai, C., Xiao, Y., et al., 2021. Geochemical Characteristics and Oil-Source Correlation of Crude Oils of Buried Hills in Shulu Sag, Jizhong Depression. Earth Science, 46(10): 3629-3644 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, X.D., Zhang, Y.C., Huang, Y.W., et al., 2013. Major Controlling Factors for Development of Oil Shale in Liushagang Formation of Wushi Sag, Beibuwan Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(S2): 66-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Y.Z., Huang, Z.L., Zhao, Z., et al., 2022. Geochemical Characteristics and Oil Source Correlation of Paleo-reservoirs in Biluocuo Area, Qiangtang Basin. Earth Science, 47(5): 1834-1848 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, X.M., Zou, M.S., Zhang, H., et al., 2016. Main Controls on the Distribution of the 3rd Member of Liushagang Formation in Eastern Wushi Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 38(6): 757-764 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G.C., Xie, X, J., Wang, W.Y., et al., 2013. Tectonic Types of Petroliferous Basins and Its Exploration Potential in the South China Sea. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(4): 611-627 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, M., Liu, C.L., Tian, J.X., et al., 2020. Characteristics of Crude Oil Geochemical Characteristics and Oil Source Comparison in the Western Part of Qaidam Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 31(1): 61-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, W.L., Zhang, G.C., Zhong, K., 2016. Oil and Gas Exploration Progress of China National Offshore Oil Corporation during the 12th Five-Year Plan and the Prospect during the 13th Five-Year Plan. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(4): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). 甘军, 杨希冰, 胡林, 等, 2019. 乌石凹陷烃源岩生烃特征及差异成藏模式. 地质科技情报, 38(3): 174-179. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0318 郝鑫, 任拥军, 徐新德, 等, 2016. 北部湾盆地乌石凹陷东部原油芳香烃组成特征及地球化学意义. 新疆石油地质, 37(6): 674-680. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201606009.htm 侯读杰, 冯子辉, 2011. 油气地球化学. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 201-242. 胡晨晖, 鲁海鸥, 黄英鑫, 2021. 乌石凹陷重质油地球化学特征及成因分析. 石化技术, 28(9): 111-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJS202109051.htm 胡林, 杨希冰, 徐雪丰, 等, 2016. 南海北部湾盆地乌石凹陷成藏主控因素与成藏模式. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(2): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201602020.htm 兰蕾, 李友川, 王柯, 等, 2019. 一组有效区分渤中凹陷烃源岩的生物标志化合物参数. 石油学报, 40(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201901002.htm 李福来, 吕琳, 马文宽, 等, 2021. 乌石凹陷流沙港组烃源岩地球化学特征. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 45(1): 31-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202101004.htm 李任伟, 1988. 伽马蜡烷的地质产状及古环境意义. 科学通报, 33(20): 1574-1576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198820015.htm 李绪深, 甘军, 张迎朝, 等, 2015. 南海西部海域断陷湖盆油气聚集规律及勘探前景. 中国海上油气, 27(4): 22-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201504003.htm 李友川, 兰蕾, 王柯, 等, 2019. 北部湾盆地流沙港组湖相烃源岩的差异. 石油学报, 40(12): 1451-1459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201912003.htm 李友川, 王柯, 兰蕾, 2020. 北部湾盆地主要凹陷油气差异性及其控制因素. 中国海上油气, 32(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202005001.htm 王元杰, 蔡川, 肖阳, 等, 2021. 冀中坳陷束鹿凹陷潜山原油地球化学特征与油源对比. 地球科学, 46(10): 3629-3644. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.030 徐新德, 张迎朝, 黄义文, 等, 2013. 北部湾盆地乌石凹陷流沙港组油页岩发育的主控因素. 石油学报, 34(S2): 66-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2009.htm 杨易卓, 黄志龙, 赵珍, 等, 2022. 羌塘盆地毕洛错地区古油藏地球化学特征与油源对比. 地球科学, 47(5): 1834-1848. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.008 曾小明, 邹明生, 张辉, 等, 2016. 北部湾盆地乌石凹陷东区流沙港组三段储层物性主控因素及分布规律. 石油实验地质, 38(6): 757-764. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201606009.htm 张功成, 谢晓军, 王万银, 等, 2013. 中国南海含油气盆地构造类型及勘探潜力. 石油学报, 34(4): 611-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201304001.htm 张迈, 刘成林, 田继先, 等, 2020. 柴达木盆地西部地区原油地球化学特征及油源对比. 天然气地球科学, 31(1): 61-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202001006.htm 朱伟林, 张功成, 钟锴, 2016. 中国海洋石油总公司"十二五"油气勘探进展及"十三五"展望. 中国石油勘探, 21(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201604001.htm -









 下载:
下载: