Hydrocarbon Accumulation Characteristics and Controlling Mechanism of Strike-Slip Faults in Jinghe Oilfield, Ordos Basin
-
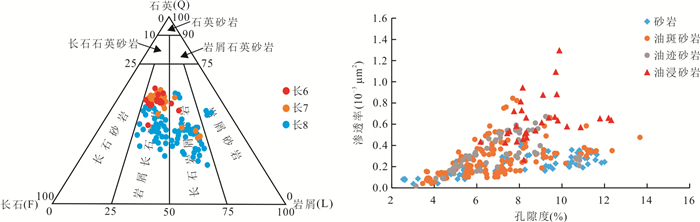
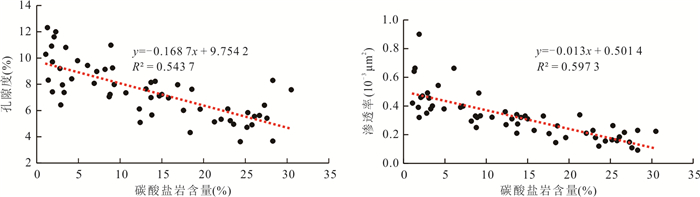
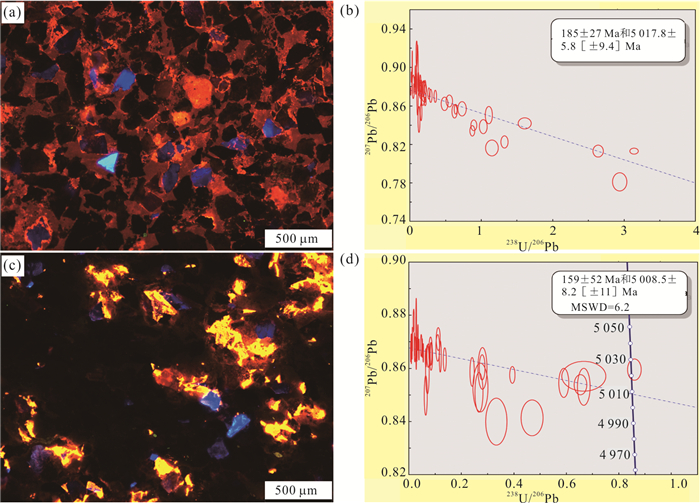
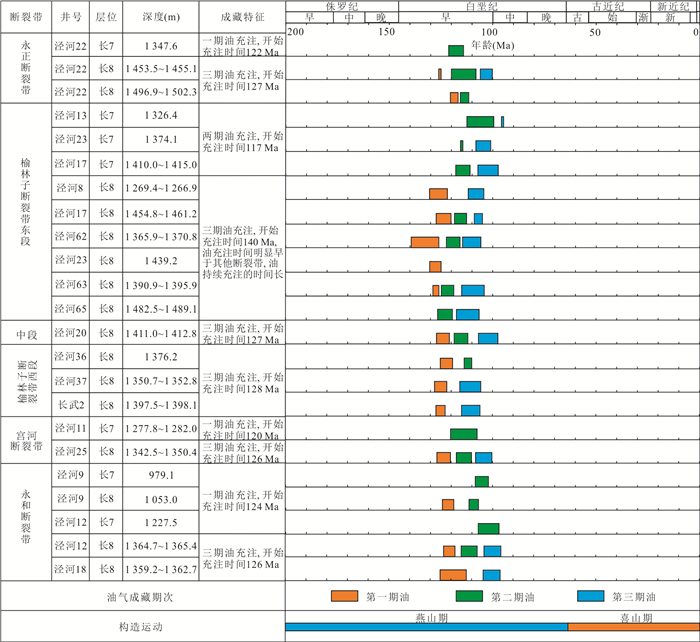
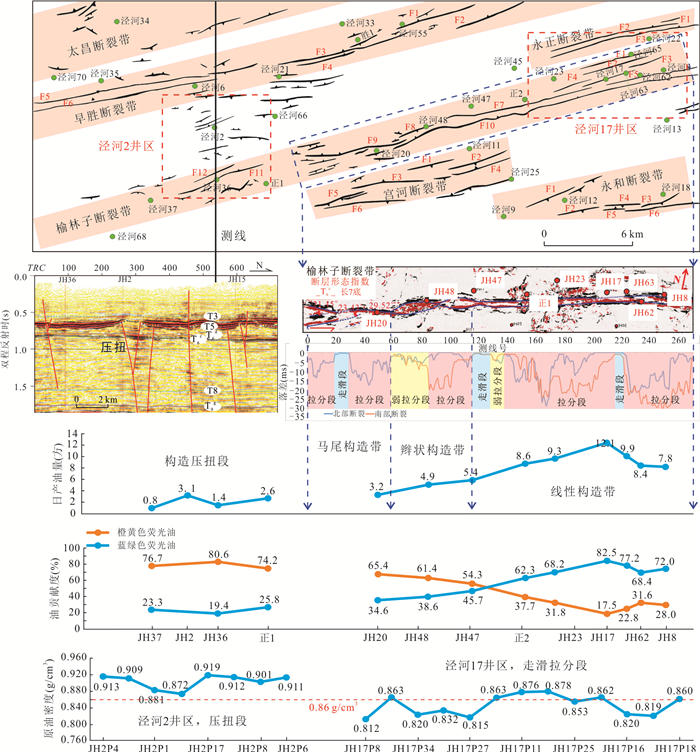
摘要: 近年来,泾河油田围绕走滑断裂带断缝体油藏勘探取得重要突破,揭示了新的油气勘探领域.深入理解走滑断裂带油气成藏特征及控藏机制则是厘定断缝体型油藏富集规律的重要前提.利用流体包裹体技术结合方解石超低浓度U-Pb定年对储层成岩作用和油气充注过程进行了系统研究,探讨了走滑断裂带油气分布特征及控制因素.结果表明:研究区储层主要发育两期早期方解石胶结(185±27 Ma和159±52 Ma)以及相对较晚的橙黄色、蓝绿色和蓝色荧光三期油连续充注(140.1~96.8 Ma),具有“先致密、后成藏”的特征.走向上,走滑断裂带原油物性具有“东低西高”、产量具有“东高西低”、油气成藏时间均具有“东早西晚”的分段特点;垂向上,走滑断裂带流体活动也存在明显差异,长6、长7段储层碳酸盐胶结作用较弱,以蓝绿色和蓝色荧光晚期油充注为主;而长8段碳酸岩盐胶结作用较强,表现为三期油充注、多期油成藏的特征.总体上,走滑断裂控制了研究区油气整体由东向西高效侧向运移,但由于走向上构造应力的变化局部控制了油气沿走滑断裂带分段差异富集(单井产量高低).长6-长7储层原始物性差以及长7段大套泥页岩的发育,限制了走滑断裂垂向流体输导能力,导致流体主要在长8段优势聚集,分层差异富集.研究结果可为进一步明确研究区的断缝体油藏的分布规律及成藏模式提供重要支撑.Abstract: In recent years, Jinghe oilfield has made important breakthroughs in the exploration of fault-fracture body reservoirs around strike-slip fault zones, revealing new fields for hydrocarbon exploration. Deeply understanding of the characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and control mechanism in strike-slip fault zone is an important prerequisite for determining the enrichment model of fault-fracture type reservoirs. In this paper, reservoir diagenesis and hydrocarbon charging process have been systematically studied using fluid inclusion technique and calcite ultra-low concentration U-Pb dating and the hydrocarbon distribution characteristics and controlling factors in strike-slip fault zones are also discussed. The results show that there are mainly two stages of early calcite cementation (185±27 Ma and 159±52 Ma, respectively) and the relatively late stage of orange-yellow, blue-green and blue fluorescent oil charge (140.1-96.2 Ma). In strike-slip fault zones, the physical property of crude oil is low in the east and high in the west, the oil production is high in the east and low in the west, and the oil accumulation time is early in the east and late in the west. The carbonate cementation in the Chang 6 and Chang 7 members is weak, and the late blue-green and blue fluorescence oil charges are dominant, but the carbonate cementation of Chang 8 member is intense, which is characterized by three stages of oil charging. On the whole, the strike-slip fault controls the lateral migration of hydrocarbon with high efficiency, but the differences of hydrocarbon enrichment along the strike-slip fault zone is partly controlled by the variation of tectonic stress. The poor original physical property of Chang 6-Chang 7 reservoir and the development of large shale in Chang 7 member limit the vertical fluid transporting ability of strike-slip fault, which leads to fluid predominance and differential accumulation in Chang 8 member. The research results can provide important support for further determining the distribution pattern and oil reservoir-forming model for fault-fracture body reservoirs in the study area.
-
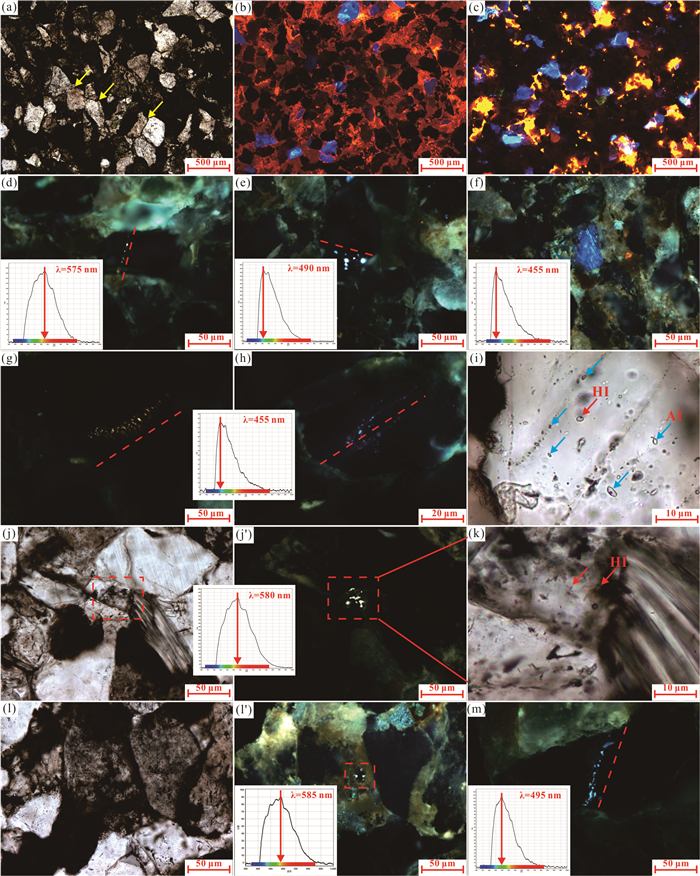
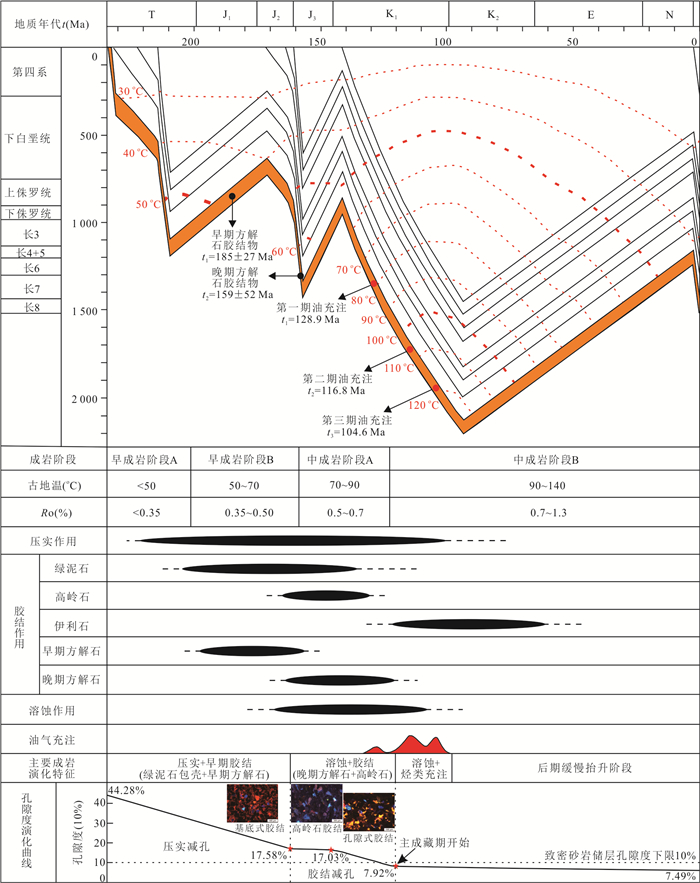
图 4 泾河油田延长组典型阴极发光及显微荧光照片
a.JH22井,深度1 496.9 m,石英颗粒呈线-凹凸接触(黄色箭头);b.JH25井,深度1 354.8 m,早期方解石呈基底式胶结,发橘红色阴极光;c.JH63井,深度1 387.8 m,晚期方解石呈孔隙式胶结,溶蚀作用明显;d.JH45井,深度1 454.8 m,穿石英颗粒裂纹中发橙黄色荧光油包裹体;e.JH22井,深度1 502.3 m,石英颗粒内裂纹中发蓝绿色荧光油包裹体;f.JH17井,深度1 415.0 m,长石解理缝中见蓝色荧光油包裹体;g.JH25井,深度1 342.6 m,石英颗粒内裂纹中发橙黄色荧光油包裹体;h~i.JH25井,深度1 413.6 m,穿石英颗粒裂纹中发蓝色荧光油包裹体,HI油包裹体,AI盐水包裹体;j~k.JH9井,深度1 053.0 m,方解石胶结物内橙黄色荧光油包裹体;l~l'.JH9井,深度1 053.0 m,长石溶孔内橙黄色荧光油包裹体;m.JH12井,深度1 364.7 m,穿石英颗粒裂纹中蓝绿色荧光油包裹体
Fig. 4. The typical cathodoluminescence and micro-fluorescence graphs of Yanchang Formation in Jinghe oilfield
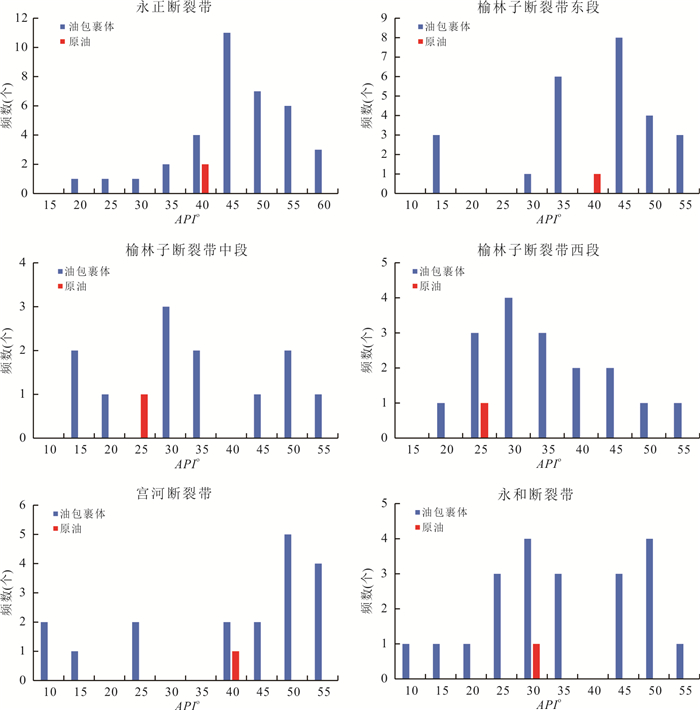
图 5 泾河油田不同断裂带包裹体均一温度分布
a.永正断裂带,长8段,1 453.5~1 455.8 m;b.榆林子断裂带东段,长8段,1 365.9~1 390.8 m;c.榆林子断裂带中段,长8段,1 411.0~1 412.8 m;d.榆林子断裂带西段,长8段,1 350.7~1 376.2 m;e.宫河断裂带,长8段,1 342.5~1 350.4 m;f.永和断裂带,1 359.2~1365.4 m
Fig. 5. The homogeneous temperature distribution of inclusions in different fault zones in Jinghe oilfield
-
Blanchet, A., Pagel, M., Walgenwitz, F., et al., 2003. Micro-spectrofluorimetric and Microthermometric Evidence for Variability in Hydrocarbon Fluid Inclusions in Quartz Overgrowths: Implications for Inclusion Trapping in the Alwyn North Field, North Sea. Organic Geochemistry, 34(11): 1477-1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.08.003 Choi, J. H., Edwards, P., Ko, K., et al., 2016. Definition and Classification of Fault Damage Zones: A Review and a New Methodological Approach. Earth-Sci. Rev. 152: 70-87. Chen, H. H., Zhu, X. M., Chen, C. F., et al., 2018. The Coupling Relationship of Reservoir Densification History and Hydrocarbon Emplacement in Tight Sandstone Reservoir: A Case Study of the Chang 8 Oil Member, Yanchang Formation, Southern Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 36(2): 401-414(in Chinese with English abstract). Coogan, L. A., Parrish, R. R., Roberts, N. M. W., 2016. Early Hydrothermal Carbon Uptake by the Upper Oceanic Crust: Insight from In Situ U-Pb Dating. Geology, 44(2): 147-150. https://doi.org/10.1130/g37212.1 Deng, S., Li, H. L., Zhang, Z. P., et al., 2018. Characteristics of Differential Activities in Major Strike-Slip Fault Zones and Their Control on Hydrocarbon Enrichment in Shunbei Area and Its Surroundings, Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 39(5): 878-888(in Chinese with English abstract). Deng, X. Q., Liu, X. S., Li, S. X., 2009. The Relationship between Compacting History and Hydrocarbon Accumulating History of the Super-Low Permeability Reservoirs in the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 30(2): 156-161(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.02.005 Faulkner, D. R., Jackson, C. A. L., Lunn, R. J., et al., 2010. A Review of Recent Developments Concerning the Structure, Mechanics and Fluid Flow Properties of Fault Zones. Journal of Structural Geology, 32(11): 1557-1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2010.06.009 Fu, J. H., Deng, X. Q., Wang, Q., et al., 2017. Compaction and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 8 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China: Evidence from Geochemistry and Fluid Inclusions. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(1): 48-57(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30007-1 Fu, S. Y., Liao, Z. W., Chen, A. Q., et al., 2020. Reservoir Characteristics and Multi-Stage Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Southwestern Ordos Basin, NW China. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 38(2): 348-371. https://doi.org/10.1177/0144598719870257 Guo, Y. Q., Hui, L., Zhang, X. N., et al., 2018. Sedimentary System Characteristics and Lake Basin Evolution of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 48(4): 593-602(in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, Z. Q., Zhang, L. R., Chu, M. J., et al., 2008. Pre-Jurassic Palaeogeomorphic Control on the Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Lower Yan'an Formation in Southern Ordos Basin. Journal of Palaeogeography, 10(1): 63-71(in Chinese with English abstract). He, F. Q., Liang, C. C., Lu, C., et al., 2020. Identification and Description of Fault-Fracture Bodies in Tight and Low Permeability Reservoirs in Transitional Zone at the South Margin of Ordos Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(4): 710-718(in Chinese with English abstract). He, F. Q., Qi, R., Wang, F. B., et al, 2021. Tectonic Genesis of Triassic Yanchang Formation Valley Systems, Southern Ordos Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 42(5): 1056-1062(in Chinese with English abstract). He, F. Q., Qi, R., Yuan, C. Y., et al., 2023. Further Understanding of the Relationship between Fault Characteristic and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Binchang Area, Ordos Basin. Earth Science (in press)(in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, J., Cao, J. K., Zhuang, Y. P., et al., 2021. Characteristics and Evaluation of Chang 7 Source Rocks in Yanchang Formation in Xunyi Exploration Area in Southern Ordos Basin. Mineral Resources and Geology, 35(4): 708-716 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, W., Liang, J. P., Zhao, B., et al., 2013. Main Controlling Factors of Tight Oil Accumulations in the Fuyu Layer of Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Northern Songliao Basin. Journal of Palaeogeography, 15(5): 635-644(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=GDLX201305010&dbcode=CJFD&year=2013&dflag=pdfdown Jiao, F. Z., 2017. Significance of Oil and Gas Exploration in NE Strike-Slip Fault Belts in Shuntuoguole Area of Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 38(5): 831-839(in Chinese with English abstract). Kang, Y., Chen, G., Zhang, W. G., et al., 2021. Diagenetic Densification of Chang 8 Sandstone Reservoirs and Its Relationship with Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Tiebiancheng Area, Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(2): 64-75(in Chinese with English abstract). Kim, Y. S., Sanderson, D. J., 2006. Structural Similarity and Variety at the Tips in a Wide Range of Strike-Slip Faults: A Review. Terra Nova, 18(5): 330-344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3121.2006.00697.x Li, C. S., Zhang, W. X., Lei, Y., et al., 2021. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Oil Accumulation in Chang 9 Member in Longdong Area, Ordos Basin. Earth Science, 46(10): 3560-3574(in Chinese with English abstract). Lin, A. M., Yamashita, K., 2013. Spatial Variations in Damage Zone Width along Strike-Slip Faults: An Example from Active Faults in Southwest Japan. Journal of Structural Geology, 57: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2013.10.006 Liu, M. J., Liu, Z., Liu, J. J., et al., 2014. Coupling Relationship between Sandstone Reservoir Densification and Hydrocarbon Accumulation: A Case from the Yanchang Formation of the Xifeng and Ansai Areas, Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(2): 168-175(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y. Q., Deng, S., 2022. Structural Analysis of Intraplate Strike-Slip Faults with Small to Medium Displacement: A Case Study of the Shunbei 4 Fault, Tarim Basin. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 51(1): 124-136(in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, L. Y., Qiu, G. Q., Liu, C. Y., et al., 2020. The Relationship between Reservoir Densification and Petroleum Accumulation of the Yanchang Formation in the Honghe Oilfield, Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 38(3): 620-634 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, Q. Y., Cao, Z. C., Jiang, H. S., et al., 2020. Source-Connectivity of Strike Slip Fault Zone and Its Relationship with Oil and Gas Accumulation in Tahe-Shunbei Area, Tarim Basin. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 25(4): 327-334 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2020.04.005 Ping, H. W., Chen, H. H., Jia, G. H., 2017. Petroleum Accumulation in the Deeply Buried Reservoirs in the Northern Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: New Insights from Fluid Inclusions, Natural Gas Geochemistry, and 1-D Basin Modeling. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 80: 70-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.11.023 Ping, H. W., Chen, H. H., Song, G. Q., et al., 2012. Contributions Degree of Petroleum Charging to Oil and Gas Accumulation and Its Significance. Earth Science, 37(1): 163-170 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ping, H. W., Chen, H. H., Zhai, P. Q., et al., 2019. Petroleum Charge History in the Baiyun Depression and Panyu Lower Uplift in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea: Constraints from Integration of Organic Geochemical and Fluid Inclusion Data. AAPG Bulletin, 103(6), 1401-1442. https://doi.org/10.1306/11151817369 Ping, H. W., Li, C. Q., Chen, H. H., et al., 2020. Overpressure Release: Fluid Inclusion Evidence for a New Mechanism for the Formation of Heavy Oil. Geology, 48(8): 803-807. https://doi.org/10.1130/g47227.1 Qi, L. X., 2016. Oil and Gas Breakthrough in Ultra-Deep Ordovician Carbonate Formations in Shuntuoguole Uplift, Tarim Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(3): 38-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.03.004 Ren, D. Z., Sun, W., Qu, X. F., et al., 2016. Characteristic of Diagenesis and Pore Dense Evolution of Chang 6 Reservoir of Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 47(8): 2706-2714 (in Chinese with English abstract). Roberts, N. M. W., Walker, R. J., 2016. U-Pb Geochronology of Calcite-Mineralized Faults: Absolute Timing of Rift-Related Fault Events on the Northeast Atlantic Margin. Geology, 44(7): 531-534. https://doi.org/10.1130/g37868.1 Smith, D. A., 1980. Sealing and Nonsealing Faults in Louisiana Gulf Coast Salt Basin. AAPG Bulletin, 64(2): 145-172. https://doi.org/10.1306/2f918946-16ce-11d7-8645000102c1865d Wu, G. H., Ma, B. S., Han, J. F., et al., 2021. Origin and Growth Mechanisms of Strike-Slip Faults in the Central Tarim Cratonic Basin, NW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(3): 510-520 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380421600484 Xu, H., Guo, X. W., Cao, Z. C., et al., 2021. Application of Minimum Homogenization Temperatures of Aqueous Inclusions in Calcite Veins to Determine Time of Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Ordovician of Tahe Oilfield: Evidence from In-Situ Calcite U-Pb Dating by Laser Ablation. Earth Science, 46(10): 3535-3548 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, J. Y., Xu, X., 2016. Fracture Identification in Honghe Oilfield, Ordos Basin. Well Logging Technology, 40(5): 572-577 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, H. J., Deng, X. L., Zhang, Y. T., et al, 2020. Great Discovery and Its Significance of Exploration for Ordovician Ultra-Deep Fault-Controlled Carbonate Reservoirs of Well Manshen 1 in Tarim Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 25(3): 13-23(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.002 Yang, Y. N., Zhou, S. X., Li, J., et al., 2017. Geochemical Characteristics of Source Rocks and Oil-Source Correlation of Yanchang Formation in Southern Ordos Basin, China. Natural Gas Geoscience, 28(4): 550-565 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410518308374 Yin, X. D., Jiang, S., Wu, P., et al., 2021. Features of the Acid and Alkaline Diagenetic Environment of Tight Sandstones and the Control of the Reservoir Physical Properties: A Case Study of the Linxing and Shenfu District, Eastern Ordos Basin. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(1): 142-151(in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, Z., Liu, Z. L., Peng, N., et al., 2019. Study on Sedimentary Faciess Features of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, in the Western Margin, Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 37(1): 163-176(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817218302629 Yun, L., Cao, Z. C., 2014. Hydrocarbon Enrichment Pattern and Exploration Potential of the Ordovician in Shunnan Area, Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 35(6): 788-797 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, Y., Wang, Y. B., Zhong, D. K., et al., 2018. Study on the Relationship between Tight Sandstone Reservoir Diagenetic Evolution and Hydrocarbon Reservoirs Filling: A Case from the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 3(2): 106-118(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y. Y., Ren, Z. L., He, F. Q., et al, 2020. Meso-Cenozoic Structural Characteristics and Their Reservoir Controls of Structural Transition Area in China Craton: A Case Study of Yanchang Formation in Zhenjing Area of Southwestern Ordos Basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(11): 3537-3549 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.11.18 Zou, C. N., Zhu, R. K., Wu, S. T., et al., 2012. Types, Characteristics, Genesis and Prospects of Conventional and Unconventional Hydrocarbon Accumulations: Taking Tight Oil and Tight Gas in China as an Instance. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(2): 173-187 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.203 陈贺贺, 朱筱敏, 陈纯芳, 等, 2018. 致密砂岩储层致密化与成藏史耦合关系研究: 以鄂尔多斯南部镇原-泾川地区延长组长8油层组为例. 沉积学报, 36(2): 401-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201802017.htm 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等, 2018. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系. 石油与天然气地质, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm 邓秀芹, 刘新社, 李士祥, 2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组超低渗透储层致密史与油藏成藏史. 石油与天然气地质, 30(2): 156-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200902009.htm 付金华, 邓秀芹, 王琪, 等, 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长8储集层致密与成藏耦合关系: 来自地球化学和流体包裹体的证据. 石油勘探与开发, 44(1): 48-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701007.htm 郭艳琴, 惠磊, 张秀能, 等, 2018. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组沉积体系特征及湖盆演化. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 48(4): 593-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201804016.htm 郭正权, 张立荣, 楚美娟, 等, 2008. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部前侏罗纪古地貌对延安组下部油藏的控制作用. 古地理学报, 10(1): 63-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200801011.htm 何发岐, 梁承春, 陆骋, 等, 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘过渡带致密-低渗油藏断缝体的识别与描述. 石油与天然气地质, 41(4): 710-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004006.htm 何发岐, 齐荣, 王付斌, 等, 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部三叠系延长组沟谷体系构造成因. 石油与天然气地质, 42(5): 1056-1062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202105005.htm 何发岐, 齐荣, 袁春艳, 等, 2023. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部地区断裂构造与油气成藏关系再认识-以彬长地区为例. 地球科学(待刊). 侯娟, 曹建康, 庄一鹏, 等, 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部旬-宜探区延长组长7烃源岩特征及评价. 矿产与地质, 35(4): 708-716. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD202104013.htm 黄薇, 梁江平, 赵波, 等, 2013. 松辽盆地北部白垩系泉头组扶余油层致密油成藏主控因素. 古地理学报, 15(5): 635-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201305010.htm 焦方正, 2017. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区北东向走滑断裂带的油气勘探意义. 石油与天然气地质, 38(5): 831-839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201705001.htm 康昱, 陈刚, 张卫刚, 等, 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油区铁边城区块长8储层成岩致密化及其与油气成藏关系. 地质科技通报, 40(2): 64-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202102008.htm 李程善, 张文选, 雷宇, 等, 2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长9油层组砂体成因与油气差异分布. 地球科学, 46(10): 3560-3574. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.007 刘明洁, 刘震, 刘静静, 等, 2014. 砂岩储集层致密与成藏耦合关系: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西峰-安塞地区延长组为例. 石油勘探与开发, 41(2): 168-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201402006.htm 刘雨晴, 邓尚, 2022. 板内中小滑移距走滑断裂发育演化特征精细解析: 以塔里木盆地顺北4号走滑断裂为例. 中国矿业大学学报, 51(1): 124-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202201012.htm 马立元, 邱桂强, 刘春燕, 等, 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田延长组储层致密化与石油成藏的关系. 沉积学报, 38(3): 620-634. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202003015.htm 马庆佑, 曹自成, 蒋华山, 等, 2020. 塔河-顺北地区走滑断裂带的通源性及其与油气富集的关系. 海相油气地质, 25(4): 327-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ202004005.htm 平宏伟, 陈红汉, 宋国奇, 等, 2012. 油气充注成藏贡献度及其意义. 地球科学, 37(1): 163-170. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2012.016 漆立新, 2016. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒隆起奥陶系碳酸盐岩超深层油气突破及其意义. 中国石油勘探, 21(3): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603004.htm 任大忠, 孙卫, 屈雪峰, 等, 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长6储层成岩作用特征及孔隙度致密演化. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 47(8): 2706-2714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201608023.htm 邬光辉, 马兵山, 韩剑发, 等, 2021. 塔里木克拉通盆地中部走滑断裂形成与发育机制. 石油勘探与开发, 48(3): 510-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103008.htm 徐豪, 郭小文, 曹自成, 等, 2021. 运用方解石中流体包裹体最小均一温度确定塔河油田奥陶系油气成藏时间: 来自激光原位方解石U-Pb年龄的证据. 地球科学, 46(10): 3535-3548. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.376 许君玉, 许新, 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田裂缝识别. 测井技术, 40(5): 572-577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS201605010.htm 杨海军, 邓兴梁, 张银涛, 等, 2020. 塔里木盆地满深1井奥陶系超深断控碳酸盐岩油气藏勘探重大发现及意义. 中国石油勘探, 25(3): 13-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202003002.htm 杨亚南, 周世新, 李靖, 等, 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延长组烃源岩地球化学特征及油源对比. 天然气地球科学, 28(4): 550-565. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201704009.htm 尹相东, 蒋恕, 吴鹏, 等, 2021. 致密砂岩酸性和碱性成岩环境特征及对储层物性的控制: 以鄂尔多斯盆地临兴和神府地区为例. 地质科技通报, 40(1): 142-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101015.htm 尹泽, 刘自亮, 彭楠, 等, 2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘上三叠统延长组沉积相特征研究. 沉积学报, 37(1): 163-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201901017.htm 云露, 曹自成, 2014. 塔里木盆地顺南地区奥陶系油气富集与勘探潜力. 石油与天然气地质, 35(6): 788-797. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406008.htm 赵岳, 王延斌, 钟大康, 等, 2018. 致密砂岩储集层成岩演化与致密油充注成藏关系研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组为例. 矿业科学学报, 3(2): 106-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKX201802002.htm 张园园, 任战利, 何发岐, 等, 2020. 克拉通盆地构造转折区中-新生界构造特征及其控藏意义-以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部镇泾地区延长组为例. 岩石学报, 36(11): 3537-3549. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202011018.htm 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等, 2012. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例. 石油学报, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htm -









 下载:
下载: