40Ar/39Ar Ages of Gneiss and Granite from Huangling Uplift and Their Tectonic Significance
-
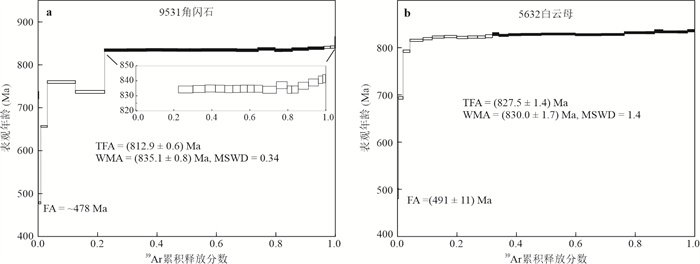
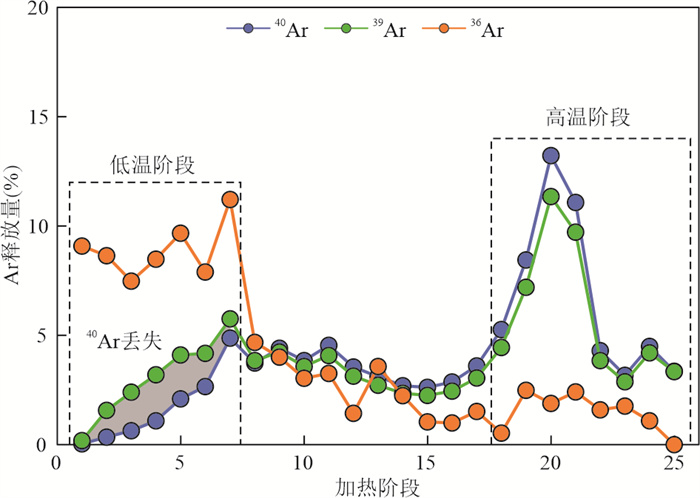
摘要: 黄陵花岗岩是研究扬子陆块构造演化和岩浆活动的关键对象,高精度的40Ar/39Ar定年可以为确定黄陵花岗岩的构造演化提供准确的年代学依据.采用40Ar/39Ar阶段加热技术分别测定了黄陵隆起核部变质岩中角闪石、黄陵庙花岗岩中白云母和黑云母单矿物的年龄. 角闪石40Ar/39Ar坪年龄(835.1±0.8)Ma,白云母坪年龄为(830.0±1.7)Ma,黑云母获得上凸型年龄谱,没有形成明显的年龄坪. 分析认为,角闪石年龄指示围岩受到花岗岩侵入烘烤重置的时间,白云母年龄指示黄陵花岗岩冷却至350 ℃的年龄,岩体侵入时间不晚于835 Ma,在835~830 Ma经历快速冷却事件,冷却速率为50 ℃/Ma. 黑云母低温阶段获得的年轻年龄216 Ma,记录了在晚三叠世黄陵地区缓慢差异隆升过程中发生的一期热事件.
-
关键词:
- 黄陵花岗岩 /
- 黄陵隆起 /
- 40Ar/39Ar定年 /
- 热扰动 /
- 地球化学
Abstract: The Huangling uplift, located in the front of the northeast corner of the Sichuan Basin, is composed mainly of Huangling granite. The granite is the geological record of the Jinning orogeny and the Rodinia supercontinent cracking in the Yangtze block, and it is critical for understanding the tectonic evolution and magmatic activity of the Yangtze block. To determine the formation time of the Huangling granite, abundant chronological data were published using isotope chronology methods such as U-Pb, K-Ar, and Rb-Sr. However, as a new chronology technique, 40Ar/39Ar is rarely used in studying Huangling granite. In this study, the age of amphibole in metamorphic rocks and muscovite and biotite in Huanglingmiao granite has been determined by 40Ar/39Ar stage heating technique. The plateau age of amphibole was (835.1±0.8) Ma, and the plateau age of muscovite was (830.0±1.7) Ma. The biotite sample yielded an age spectrum with an upward convex shape, and no obvious flat section was formed. It was concluded that the age of amphibole is much lower than the formation age and metamorphic age of metamorphic rocks, but slightly higher than the muscovite age of nearby granite, indicating the time when the surrounding rock was reset by granite baking and then cooled to 500 ℃. The muscovite age indicates the time Huangling granite cooled to 350 ℃. Both of them restrict the formation time of Huangling granite. Although no plateau age was obtained, the biotite sample gave a meaningful age of 216 Ma in the low-temperature steps, which probably indicates the occurrence time of thermal disturbance in the later stage. The collision and merging of the North China and Yangtze plates caused the slow uplift of the Huangling, and activity of the NNW-trending faults in the Huangling area, and caused the thermal effect enough to affect the Ar closure of the biotite. The high precision 40Ar/39Ar age provides accurate chronological support for determining the tectonic evolution history of Huangling granite.-
Key words:
- Huangling Granite /
- Huangling Uplift /
- 40Ar/39Ar dating /
- thermal events /
- geochemistry
-
表 1 黄陵隆起同位素年代学数据整理
Table 1. Compilation of isotopic ages for igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks in the Huangling Uplift
岩性(岩石组合) 矿物 年龄(Ma) 年代学方法 解释 文献 辉绿岩脉 锆石 2 842±11 U-Pb 岩浆锆石年龄,TTG花岗岩的形成时间 [1] 2 949±7 2 900±10 2 557 变质作用发生时间 辉绿岩脉 锆石 3 037±21 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,TTG古侵入体的形成时间 [2] 2 913 结晶锆石,脉岩形成时间 2 511 变质锆石,构造热事件时间 角闪岩 锆石 1 865~3 242 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,TTG花岗岩多期侵入时间 [3] 2 583±240 变质锆石,变质事件事件 奥长花岗片麻岩 锆石 3 051±12 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,TTG古侵入体的形成时间 [4] 2 739±18 变质锆石,片麻岩改造变质时间 2 947±5 奥长花岗岩的侵入年龄 2 895~2 938 岩浆锆石受后期元素活动扰动的时间 1 992±16 指示后期改造年龄 2 903±10 奥长花岗岩岩浆的侵入年龄 2 727±8 锆石变质增生边部年龄,指示变质活动 2 901±8 锆石核部年龄,指示古侵入体年龄 片麻岩 全岩 2 728±118 Sm-Nd 变质岩改造变质时间 [5] 斜长角闪岩 全岩 2 742±83 变质岩改造变质时间 角闪斜长混合岩 锆石 2 830±30 U-Pb 角闪斜长混合岩的改造变质时间 [6] 2 866±12 Pb-Pb 角闪斜长混合岩的改造变质时间 钾质花岗岩 锆石 1 840±4 U-Pb 钾质花岗岩的侵入时间 1 851±237 Pb-Pb 钾质花岗岩的侵入时间 黑云斜长变粒岩 锆石 2 913±4 Pb-Pb 变质岩改造变质时间 变基性岩 锆石 2 940±8 Rb-Sr 变质岩改造变质时间 钾长花岗质片麻岩 锆石 1 803±30 U-Pb 变质岩遭受构造-热事件改造的时间 [7] 片麻岩 锆石 2 015±15 U-Pb 变质锆石,改造变质时间 [8] 2 153±28 岩浆锆石 2 283~2602 辉绿岩脉 锆石 1 852±11 U-Pb 指示基性岩脉的侵入时间 [9] 混合岩 锆石 2 916~2947 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,指示原岩的形成时间 [10] 混合岩 锆石 3 113~3253 U-Pb 锆石继承核,指示原岩的形成时间 奥长花岗片麻岩 锆石 2 858±25 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,指示原岩的形成时间 英云闪长质片麻岩 锆石 2 893±29 U-Pb 岩浆锆石,指示原岩的形成时间 变沉积岩 锆石 1 974±25 U-Pb 指示了构造热事件 砂岩 锆石 3 802±8 U-Pb 碎屑锆石年龄,记录扬子陆块几期主要的构造活动时间 3 145~3 309 2 901~2 976 1 928~1 961 733~830 黄陵庙花岗岩、花岗斑岩 锆石 821±2 U-Pb 岩套的成岩年龄 816±5 814±5 809±5 806±6 800±5 砂岩 锆石 3 119.6~3 507.5 U-Pb 碎屑锆石,指示岩浆作用时间 [11] 大老岭二长花岗岩 锆石 846±15 U-Pb 捕获成因锆石 [12] 794±7 结晶锆石,大老岭花岗岩侵入时间 746±10 新生锆石的形成年龄,或发生部分重置的年龄 三斗坪英云闪长岩 锆石 795±8 U-Pb 三斗坪花岗岩侵入时间 734±17 指示后期热事件 618±13 指示更晚期的热事件或Pb丢失 晓峰浅成花岗岩 锆石 871±18 U-Pb 捕获成因锆石 737±13 晓峰花岗岩的侵入时间 黑云母花岗闪长岩 黑云母 823±7 K-Ar 黄陵庙花岗岩形成时间 [13] 锆石 819±7 U-Pb 黄陵庙花岗岩形成时间 818±5 黄陵庙花岗岩形成时间 黄陵庙花岗岩 全岩 808±35 Rb-Sr 黄陵庙花岗岩形成时间 [14] 大老岭花岗岩 全岩 786±17 Rb-Sr 大老岭花岗岩形成时间 晓峰花岗岩 全岩 750±57 Rb-Sr 晓峰花岗岩形成时间 中粒闪长岩 全岩及组成矿物 805±4 Rb-Sr 黄陵隆起整酸性岩浆活动区域结束,
基本稳定的时间[15] 807±2 全岩 834±35 三斗坪闪长岩 锆石 832±12 U-Pb 三斗坪岩体的形成年龄 全岩及组成矿物 805±5 Rb-Sr 三斗坪岩体的Rb-Sr同位素体系封闭年龄 黄陵庙似斑状黑云母花岗闪长岩 锆石 819 U-Pb 黄陵庙花岗岩的形成时间 全岩及组成矿物 800±2 Rb-Sr 黄陵庙花岗岩的Rb-Sr同位素体系封闭年龄 花岗岩 黑云母 780~789 K-Ar 太平溪和黄陵庙花岗岩的K-Ar黑云母封闭年龄 [16] 角闪石 738~799 白云母 799 花岗伟晶岩脉 微斜长石、白云母 807±2 Rb-Sr 岩脉的侵入时间 花岗闪长岩脉 独居石 801±24 U-Pb 岩脉的侵入时间 花岗岩 锆石 837±7 U-Pb 花岗岩的侵入时间 [17] 层凝灰岩 锆石 724±12 U-Pb 指示两期岩浆环带的存在,较年轻年龄指示莲沱组顶界年龄 锆石 787±7 三斗坪花岗岩 角闪石 844.0±4.2 40Ar/39Ar 三斗坪花岗岩的形成时间 [18] 辉长岩 锆石 857±11 U-Pb 岩石结晶年龄 [19] 橄榄辉长岩 锆石 854±14 U-Pb 岩石侵位年龄 三斗坪英云闪长岩 黑云母 838.7±4.0 40Ar/39Ar 黑云母封闭年龄 [20] 838.2±4.1 837.3±4.2 三斗坪英云闪长岩 角闪石 844.0±4.2 角闪石封闭年龄 黄陵庙花岗岩 锆石 815±9 U-Pb 黄陵庙岩套侵位时间 [21] 片麻岩 角闪石 835.1±0.8 40Ar/39Ar 角闪石受花岗岩侵入烘烤重置时间 本文 黄陵庙花岗岩 白云母 830.0±1.7 花岗岩冷却白云母封闭年龄 黑云母 216 花岗岩遭受后期热扰动时间 注:[1]赵敏等(2012);[2]魏君奇等(2009);[3]Wei et al.(2020);[4]高山等(2001);[5]凌文黎等(1998);[6]袁海华等(1991);[7]赵风清等(2006);[8]Li et al.(2016);[9]彭敏等(2009);[10]Zhang et al.(2006a, 2006b, 2006c);[11]柳小明等(2005);[12]凌文黎等(2006);[13]马国干等(1984);[14]马大铨等(2002);[15]冯定犹等(1991);[16]李志昌等(2002);[17]高维和张传恒(2009);[18]周忠友等(2007);[19]Jiang et al.(2018);[20]李益龙等(2007);[21]惠博等(2022); 年龄解释为对应文献中的解释 表 2 黄陵隆起样品信息
Table 2. Sample information of Huanglin Uplift
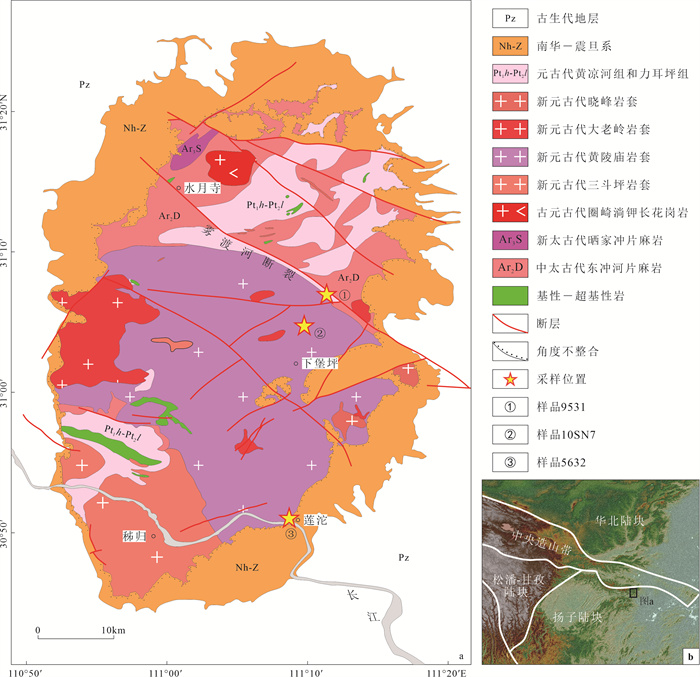
样品号 采样位置 纬度 经度 高程(m) 岩性 定年单矿物 9531 雾渡河镇花岩村 N31°06.542′ E111°11.386′ 580 片麻岩 角闪石 5632 莲沱镇莲沱大桥附近 N30°51.019′ E111°09.029′ 93 花岗岩 白云母 10SN7 雾渡河至下堡坪的公路旁 N31°04.898′ E111°09.456′ 990 花岗岩 黑云母 -
Feng, D. Y., Li, Z. C., Zhang, Z. C., 1991. Intrusive Ages and Isotopic Characteristics of Massives in the South of Huangling Granitoids. Hubei Geological, 5(2): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gao, S., Qiu, Y. M., Ling, W. L., et al., 2001. Studies on the Chronology of Single Grain Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb from the Kongling High Metamorphic Geologic Body- Discovery of the Continental Crust Material of the Yangtze Craton > 3.2 Ga. Science in China (Series D), 31(1): 27-35 (in Chinese). Gao, W., Zhang, C. H., 2009. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Ages of the Huangling Granite and the Tuff Beds from Liantuo Formation in the Three Gorges Area of Yangtze River, China and Its geological significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(1): 45-50 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.006 Ge, X., Shen, C. B., Mei, L. F., 2016. Low-Temperature Thermochronological Constraints on the Mesozoic-Cenozoic Paleotopograph in the Huangling Massif. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(4): 654-662 (in Chinese with English abstract). Harrison, T. M., McDougall, I., 1982. The Thermal Significance of Potassium Feldspar K-Ar Ages Inferred from 40Ar/39Ar Age Spectrum Results. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46: 1811-1820. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90120-x Hu, S. L., Liu, H. Y., Wang, S. S., et al., 1989. On the Age of Sinian Lower Boundary Infered from the New 40Ar/39Ar Data. Chinese Journal of Geology, 24(1): 16-25 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hui, B., Dong, Y. P., Sun, S. S., et al., 2022. Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Northern Margin of the Yangtze Plate: Constrains from Magmatic Events. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(9): 3034-3050 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, X. F., Peng, S. B., Han, Q. S., 2021. Petrogenesis and Geological Significance of ca. 860 Ma Dikes in Southern Huangling Anticline, Yangtze Craton. Earth Science, 46(6): 2117-2132 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, X. F., Peng, S. B., Kusky, T. M., et al., 2018. Petrogenesis and Geotectonic Significance of Early-Neoproterzoic Olivine-Gabbro within the Yangtze Craton: Constrains from the Mineral Composition, U-Pb Age and Hf Isotopes of Zircons. Journal of Earth Science, 29(1): 93-102. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s12583-018-0821-5 Lanphere, M., Dalrymple, G., 1976. Identification of Excess40Ar by the 40Ar/39Ar Age Spectrum Technique. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 32: 141-148. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/0012-821x(76)90052-2 Li, Y. H., Zheng, J. P., Xiong, Q., et al., 2016. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Paleoproterozoic MetapeliticRocks in the Archean Kongling Complex from the Northern Yangtze Craton, South China. Precambrian Research, 276: 158-177. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.01.028. Li, Y. L., Zhou, H. W., Li, X. H., et al., 2007. 40Ar-39Ar Plateau Ages of Biotite and Amphibole from Tonalite of Huangling Granitoids and Their Cooling Curve. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(5): 1067-1074 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Z. C., Wang, G. H., Zhang, Z. C., 2002. Isotopic Age Spectrum of the Huangling Granitic Batholith, Western Hubei. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 3: 19-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2002.03.004 Ling, W. L., Gao, S., Cheng, J. P., et al., 2006. Neoproterozoic Magmatic Events Within the Yangtze Continental Interior and Along Its Northern Margin and Their Tectonic Implication: Constraint from the ELA-ICPMS U-Pb Geochronology of Zircons from the Huangling and Hannan Complexes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(2): 387-396 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ling, W. L., Gao, S., Zheng, H. F., et al., 1998. The Sm-Nd Isotope Geochronology of the Kongling Complex in Huangling Region of the Yangtze Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(1): 3-5 (in Chinese). Liu, X. M., Gao, S., Ling, W. L., et al., 2005. 3.5 Ga Detrital Zircon from the Yangtze Craton and Its Geological Significance. Progress in Natural Science, 15(11): 1334-1337 (in Chinese). Lovera, O., Richter, F., Harrison, T., 1989. The 40Ar/39Ar Thermochronometry for Slowly Cooled Samples Having a Distribution of Diffusion Domain Sizes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 941: 17917-17935. https://doi.org/ 10.1029/JB094iB12p17917. Ma, D. Q., Du, S. H., Xiao, Z. F., 2002. The Origin of Huangling Granite Batholith. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 21(2): 151-161 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2002.02.009 Ma, D. Q., Li, Z. C., Xiao, Z. F., 1997. The Constitute, Geochronology and Geologic Evolution of the Kongling Complex, Western Hubei. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 18(3): 10-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, G. G., Li, H. Q., Zhang, Z. C., 1984. An Investigation of the Age Limits of the Sinian System in South China. Bulletin of Yichang Institute of Geology and Mineral ResourcesChinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 8: 1-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). Peng, M., 2010. Paleoproterozoic Magmatism of Yangtze Craton: Timing and Geological Implications (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Peng, M., Wu, Y. B., Wang, J., et al., 2009. Paleoproterozoic Mafic Dyke from Kongling Terrain in the Yangtze Craton and Its Implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(5): 641-647 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2009-54-5-641 Schneider, D. A., Cope, N., Holm, D. K., 2013. Thermochronology of the Mont Laurier Terrane, Southern Canadian Grenville Province, and Its Bearing on Defining Orogenic Architecture. Precambrian Research, 226: 43-58. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.11.006. Shen, C. B., Hu, D., Min, K., et al., 2020. Post-Orogenic Tectonic Evolution of the Jiangnan-Xuefeng Orogenic Belt: Insights from Multiple Geochronometric Dating of the Mufushan Massif, South China. Journal of Earth Science, 31(5): 905-918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1346-2. Shen, C. B., Mei, L. F., Min, K., et al., 2012. Multi-Chronometric Dating of the Huarong Granitoids from the Middle Yangtze Craton: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of Eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 52: 73-87. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.02.013. Shi, W. B., Wang, F., Yang, L. K., et al., 2020. 40Ar/39Ar Dating of Basic-Felsic Dikes in the Sulu Orogen, Shandong Peninsula, China: Evidence for the Destruction of the Southeastern North China Craton. Geological Journal, 55(7): 5574-5593. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/gj.3745. Sun, Z., Li, F. C., Lin, J., et al., 2021. The Rifting-Breakup Process of the Passive Continental Margin and Its Relationship with Magmatism: The Attribution of the South China Sea. Earth Science, 46(3): 770-789(in Chinese with English abstract). Wei, J. Q., Wang, J. X., Wang, X. D., et al., 2009. Dating of Mafic Dikes from Kongling Group in Huangling Area and Its Implications. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39(3): 466-471 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wei, J. Q., Wei, Y. X., Wang, J. X., et al., 2020. Geochronological Constraints on the Formation and Evolution of the Huangling Basement in the Yangtze Craton, South China. Precambrian Research, 342. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105707. Xiong, C. Y., Wei, C. S., Jin, G. F., et al., 1998. Basic Characteristics and Metallogenetic Regularity of the Gold Ore Deposits in the Middle Core of Huangling Anticline, Western Hubei Province. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 1: 3-5 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, D. L., Peng, L. H., Liu, H., et al., 2013. Meso-Cenozoic Tectono-Sedimentary Response of Multiphased Uplifts of Huangling Anticline, Central China. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 29(2): 90-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yuan, H. H., Zhang, Z. L., Liu, W., et al., 1991. Direct Dating Method of Zircon Grains by 207Pb/206Pb. Mineralogy and Petrology, 11(2): 72-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G. W., Guo, A. L., Wang, Y. J., et al., 2013. Tectonics of South China Continent and Its Implications. Science China: Earth Sciences, 56: 1804-1828, https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11430-013-4679-1 Zhang, S. B., Wu, P., Zheng, Y. F., 2019. Mafic Magmatic Records of Rodinia Amalgamation in the Northern Margin of the South China Block. Earth Science, 44(12): 4157-4166 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, S. B., Zheng, Y. F., Wu, Y. B., et al., 2006a. Zircon Isotope Evidence for ≥3.5 Ga Continental Crust in the Yangtze Craton of China. Precambrian Research, 146(1): 16-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.002. Zhang, S. B., Zheng, Y. F., Wu, Y. B., et al., 2006b. Zircon U–Pb Age and Hf Isotope Evidence for 3.8 Ga Crustal Remnant and Episodic Reworking of Archean Crust in South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 252(1): 56-71. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.09.027. Zhang, S. B., Zheng, Y. F., Wu, Y. B., et al., 2006c. Zircon U-Pb Age and Hf-O Isotope Evidence for Paleoproterozoic Metamorphic Event in South China. Precambrian Research, 151(3): 265-288. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.08.009. Zhao, F. Q., Zhao, W. P., Zuo, Y. C., et al., 2006. Zircon U-Pb Ages of the Migmatites from Kongling Complex. Geological Survey and Research, 29(2): 81-85 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2006.02.001 Zhao, M., Wei, J. Q., Wang, J. X., 2012. Zircon U-Pb Age and Hf Isotope Composition from Yemadong Mafic Dikes in the Huangling Area. Geology and Mineral Researchs of South China, 28(2): 124-131 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, Z. Y., Yang, J. X., Zhou, H. W., et al., 2007. Significance on Hubei Huangling Complex in the Rodinia Super-Continent of Evolution. Resources Environment and Engineering, 21(4): 380-384 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200704004.htm 冯定犹, 李志昌, 张自超, 1991. 黄陵花岗岩类岩基南部岩体侵入时代和同位素特征. 湖北地质, 5(2): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK199102000.htm 高山, Qiu Y., 凌文黎, 等, 2001. 崆岭高级变质地体单颗粒锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究──扬子克拉通 > 3.2 Ga陆壳物质的发现. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 31(1): 27-35. 高维, 张传恒, 2009. 长江三峡黄陵花岗岩与莲沱组凝灰岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其构造地层意义. 地质通报, 28(1): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200901007.htm 葛翔, 沈传波, 梅廉夫, 2016. 低温热年代对黄陵隆起中新生代古地形的约束. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(4): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201604003.htm 胡世玲, 刘鸿允, 王松山, 等, 1989. 据40Ar/39Ar快中子年龄新资料讨论震旦系底界年龄. 地质科学, 24(1): 16-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198901002.htm 惠博, 董云鹏, 孙圣思, 等, 2022. 扬子板块北缘新元古代构造属性的岩浆事件制约. 地质学报, 96(9): 3034-3050. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202209005.htm 蒋幸福, 彭松柏, 韩庆森, 2021. 扬子克拉通黄陵背斜南部~860 Ma岩墙的成因及地质意义. 地球科学, 46(6): 2117-2132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106012.htm 李益龙, 周汉文, 李献华, 等, 2007. 黄陵花岗岩基英云闪长岩的黑云母和角闪石40Ar-39Ar年龄及其冷却曲线. 岩石学报, 23(5): 1067-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200705020.htm 李志昌, 王桂华, 张自超, 2002. 鄂西黄陵花岗岩基同位素年龄谱. 华南地质与矿产, 3: 19-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC200203003.htm 凌文黎, 高山, 程建萍, 等, 2006. 扬子陆核与陆缘新元古代岩浆事件对比及其构造意义——来自黄陵和汉南侵入杂岩ELA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素年代学的约束. 岩石学报, 22(2): 387-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200602011.htm 凌文黎, 高山, 郑海飞, 等, 1998. 扬子克拉通黄陵地区崆岭杂岩Sm-Nd同位素地质年代学研究. 科学通报, 43(1): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199801021.htm 柳小明, 高山, 凌文黎, 等, 2005. 扬子克拉通35亿年碎屑锆石的发现及其地质意义. 自然科学进展, 15(11): 1334-1337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200511011.htm 马大铨, 杜绍华, 肖志发, 2002. 黄陵花岗岩基的成因. 岩石矿物学杂志, 21(2): 151-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200202008.htm 马大铨, 李志昌, 肖志发, 1997. 鄂西崆岭杂岩的组成、时代及地质演化. 地球学报, 18(3): 10-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB703.001.htm 马国干, 李华芹, 张自超, 1984. 华南地区震旦纪时限范围的研究. 中国地质科学院宜昌地质矿产研究所所刊, 8: 1-29. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198412001003.htm 彭敏, 2010. 扬子板块古元古代岩浆事件年龄及其地质意义(硕士学位论文). 武汉: 中国地质大学. 彭敏, 吴元保, 汪晶, 等, 2009. 扬子崆岭高级变质地体古元古代基性岩脉的发现及其意义. 科学通报, 54(5): 641-647. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200905018.htm 孙珍, 李付成, 林间, 等, 2021. 被动大陆边缘张-破裂过程与岩浆活动: 南海的归属. 地球科学, 46(3): 770-789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202103002.htm 魏君奇, 王建雄, 王晓地, 等, 2009. 黄陵地区崆岭群中基性岩脉的定年及意义. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 39(3): 466-471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200903016.htm 熊成云, 韦昌山, 金光富, 等, 1998. 鄂西黄陵背斜核部中段金矿基本特征及成矿规律. 华南地质与矿产, 1: 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC199801004.htm 徐大良, 彭练红, 刘浩, 等, 2013. 黄陵背斜中新生代多期次隆升的构造-沉积响应. 华南地质与矿产, 29(2): 90-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201302002.htm 袁海华, 张志兰, 刘炜, 等, 1991. 直接测定颗粒锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄的方法. 矿物岩石, 11(2): 72-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS199102012.htm 张少兵, 吴鹏, 郑永飞, 2019. 罗迪尼亚超大陆聚合在华南陆块北缘的镁铁质岩浆岩记录. 地球科学, 44(12): 4157-4166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201912026.htm 赵风清, 赵文平, 左义成, 等, 2006. 崆岭杂岩中混合岩的锆石U-Pb年龄. 地质调查与研究, 29(2): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200602000.htm 赵敏, 魏君奇, 王建雄, 2012. 黄陵野马洞基性岩脉中锆石的U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成. 华南地质与矿产, 28(2): 124-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201202006.htm 周忠友, 杨金香, 周汉文, 等, 2007. 湖北黄陵杂岩在Rodinia超大陆演化中的意义. 资源环境与工程, 21(4): 380-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200704004.htm -
 dqkxzx-49-2-700-附表.docx
dqkxzx-49-2-700-附表.docx

-









 下载:
下载: