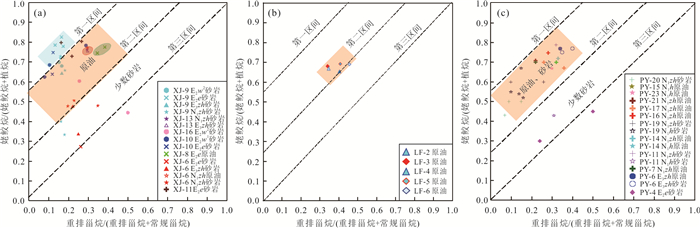
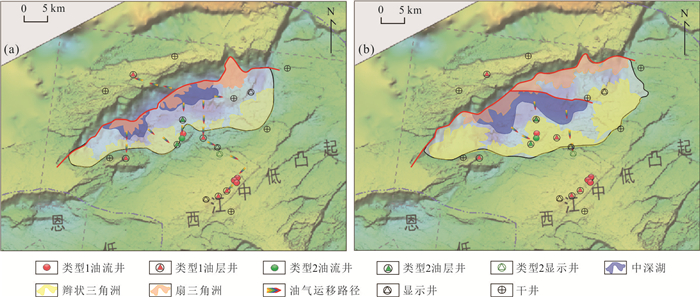
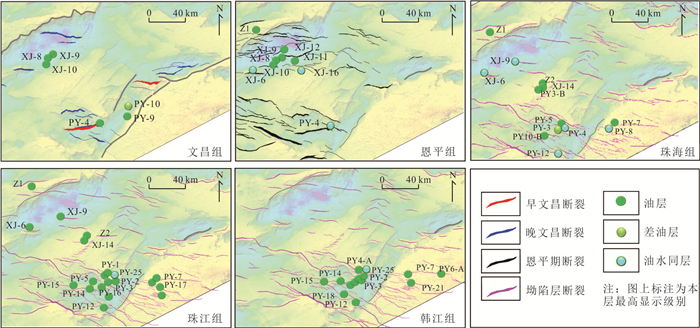
|
Bao, X. H., Ji, Y. B., Hu, Y. E., et al., 2017. Geochemical Characteristics, Origins, and Model of Lacustrine Source Rocks in the Zhu 1 Depression, Eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 101(9): 1543-1564. https://doi.org/10.1306/11071614117 |
|
Cai, G. F., Peng, G. R., Wu, J., et al., 2022. Sedimentary Filling Response to Detachment Structural Deformation in Shallow-Water Continental Shelf of Pearl River Mouth Basin: A Case Study of Enping Sag. Earth Science, 47(7): 2391-2409(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Cao, A. W., 1999. The Analysis of Hydrocarbon Potential in Xijiang Main Sag. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 11(3): 196-199(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Cao, Q. M., 2021. Formation Mechanism of Middle-Deep Sandstone Reservoir of Eocene in Zhu Ⅰ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Chen, W. C., Zhang, H. Y., Quan, Z. Z., et al., 2020. Paleogene Fault Structure Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of Xijiang Major Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 44(3): 57-69, 8(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2020.03.006 |
|
Cheng, Y. J., Wu, Z. P., Zhang, J., et al., 2020. Early Cenozoic Evolution of Fault System in Xijiang Sag and Its Implication to Clockwise Rotation of Extension Stress in Northern Margin of South China Sea. Earth Science, 45(6): 2199-2209(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Ding, L., Guo, G., Hao, J. R., et al., 2015. Characteristics of Paleogene Source Rocks of Wenchang Formation and Hydrocarbon Potential in Xijiang Sag, Zhu Ⅰ Depression. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 27(5): 21-26(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Du, J. Y., Shi, H. S., Zhu, M., et al., 2008. An Analysis of Hydrocarbon Accumulation and Exploration Potential under a Lower Geothermal Condition in Xijiang Sag. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 20(5): 287-292(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.05.001 |
|
Deng, P., Mei, L. F., Du, J. Y., et al., 2020. Characteristics and Genetic Development of a Low-Angle Boundary Normal Fault in Xijiang Main Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(3): 606-616(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Duan, Y., Wu, B. X., Zheng, C. Y., et al., 2005. Study on Hydrocarbon Generation Kinetics of Coal in Qinshui Basin, Shanxi Province. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(13): 1405-1411(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2005-50-13-1405 |
|
Feng, C. G., Liu, S. W., Wang, L. S., et al., 2009. Present-Day Geothermal Regime in Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(11): 2752-2762(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Fu, N., Ding, F., He, S. B., et al., 2007. Source Rocks Evaluation and Reservoir Characteristics Analysis in Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 19(5): 295-299, 305(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.05.002 |
|
Gao, Y. D., Lin, H. M., Wang, X. D., et al., 2021. Source Rock Distribution Pattern in an Episodic Rifting Sag and Later Stage Magmatiic Reformation: A Case from Panyu 4 Sag, Zhu Ⅰ Depression. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 41(3): 151-160(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Gao, C. L., Ji, Y. L., Jin, J., et al., 2017. Characteristics and Controlling Factors on Physical Properties of Deep Buried Favorable Reservoirs of the Qingshuihe Formation in Muosuowan Area, Junggar Basin. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(4): 990-1006(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, M., Lei, Y. C., Yu, S. M., et al., 2016. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Features and Exploration Inspiration of Low Geothermal Rifted Basins in Shallow Water Area of Northern South China Sea. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(4): 75-84(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.008 |
|
Hao, S. H., Mei, L. F., Shi, H. S., et al., 2021. Rift Migration and Transition during Multiphase Rifting: Insights from the Proximal Domain, Northern South China Sea Rifted Margin. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 123: 104729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104729 |
|
Jiang, J. Q., Li, J., Shi, J. N., et al., 2004. Geothermal Characteristics of Damintun Sag and Its Significance for Petroleum Accumulation. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 22(3): 541-546(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.025 |
|
Jin, J., Liu, M., Liu, Y. C., et al., 2021. Present-Day Temperature-Pressure Field and Its Controlling Factors of the Lower Composite Reservoir in the Southern Margin of Junggar Basin. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 56(1): 28-43(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Li, Z. S., Peng, G. R., Wu, J., et al., 2022. Accumulation Conditions and Modes of Neogene Hydrocarbons in Panyu 4 Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. World Geology, 41(2): 315-324(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liang, J., 2020. Geological Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Accumulation Mechanism of Paleogene Reservoir in Xijiang 33 Subsag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Sino-Global Energy, 25(4): 23-30(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liang, J., Liu, P., Chen, W. T., et al., 2022. Technology of Identification for Hydrocarbon Source and Its Application in Reformed Sag: A Case Study of Xijiang Main Sag. Marine Geology Frontiers, 38(6): 78-87(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liao, Z. B., 2013. Tectonic Evolution and Its Control on Hydrocarbon Accumulation Xijiang Main Sag, Zhu I Depression (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liu, C. Y., Zhou, P. B., Zeng, Y., et al., 2009. An Analysis of the Main Controls on Neogene Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Panyu 4 Sag. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 21(2): 91-94(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.02.004 |
|
Liu, P., Zhang, X. T., Du, J. Y., et al., 2018. Tectonic-Thermal Evolution Process and the Petroleum Geological Significance of Relatively Low Geothermal Gradient in a Rift Basin: an Example from Xijiang Main Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(2): 149-156(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liu, P., Zhang, X. T., Lin, H. M., et al., 2021. Distribution Mechanism of Oil and Gas in Xijiang Main Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 51(1): 52-64(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Liu, Z. F., Wu, K. Q., Ke, L., et al., 2017. Main Factors Controlling Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Northern Subsag Belt of the Zhu-1 Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 38(3): 561-569(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Ma, B. S., Qi, J. F., Chen, W. C., et al., 2020. Fault Interaction and Evolution during Two-Phase Rifting in the Xijiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea. Geological Journal, 55(2): 1128-1147. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3474 |
|
Ma, B. S., Qi, J. F., Wu, G. H., et al., 2022. Structural Variability and Rifting Process of the Segmented Cenozoic Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern Continental Margin of the South China Sea. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(6): 2074-2092. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.14983 |
|
Mi, L. J., 2018. Continuous Breakthroughs on Petroleum Exploration of the Eastern South China Sea with Innovative Understanding: Review of Recent Exploration Progress. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 30(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Meng, Z. P., Yu, Y. N., Li, G. F., et al., 2023. Geothermal Field Condition of Coal Reservoir and Its Genetic Mechanism of Low Geothermal Anomaly Area in the Qinshui Basin. Journal of China Coal Society, 48(1): 307-316(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Ma, A. L., Jin, Z. J., Li, H. L., et al., 2020. Secondary Alteration and Preservation of Ultra-Deep Ordovician Oil Reservoirs of North Shuntuoguole Area of Tarim Basin, NW China. Earth Science, 45(5): 1737-1753(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Pang, X., Zheng, J. Y., Mei, L. F., et al., 2021. Characteristics and Origin of Continental Marginal Fault Depressions under the Background of Preexisting Subduction Continental Margin, Northern South China Sea, China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(5): 1237-1250. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1876-3804(21)60106-4 |
|
Peng, G. R., Wen, H. H., Liu, C. Y., et al., 2013. Practice of Shallow Oil and Gas Exploration in Zhu I Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin: A Case from Panyu 4 Sag. Marine Geology Frontiers, 29(3): 22-28(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Peng, J. N., Luo, K. P., Liu, G. X., et al., 2018. Causes of Abnormal Thermal Evolution and Characteristics of Thermal Evolution in Sichuan Basin. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 40(5): 605-612(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., Moldowan, J. M., 2005. The Biomarker Guide, Secong Edition. Ⅱ. Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Systems and Earth History. Cambridge University Press, London. |
|
Shan, X. L., Yalikun Rexiti, Liu, P., et al., 2023. Sedimentary Response and Tectonic Significance of Zhuqiong Movement in Xijiang Main Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 53(2): 329-342(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Shi, H. S., Dai, Y. D., Liu, L. H., et al., 2015. Geological Characteristics and Distribution Model of Oil and Gas Reservoirs in Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(Suppl. 2): 120-133, 155(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Shi, H. S., Zhu, J. Z., Jiang, Z. L., et al., 2009. Hydrocarbon Resources Reassessment in Zhu Ⅰ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 21(1): 9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.01.002 |
|
Sun, Z. X., Zhang, W., Hu, B. Q., et al., 2006. Features of Heat Flow and the Geothermal Field of the Qinshui Basin. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(1): 130-134(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.01.018 |
|
Wu, X., Li, D., Zhu, X. X., et al., 2022. Influence of Geothermal Field on Ultra-Deep Ordovician Oil and Gas in Shunbei Field, Tarim Basin: A Case Study of Shunbei No. 5 Strike-Slip Fault. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 44(3): 402-412(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Yalikun Rexiti., 2022. Paleogene Sag Structure, Magmatic transformation, and Source Rock Distribution of Xijiang main Sag (Dissertation). Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Yang, X. W., Tian, J., Wang, Q. H., et al., 2021. Geological Understanding and Favorable Exploration Fields of Ultra-Deep Formations in Tarim Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(4): 17-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.002 |
|
Ye, Q., 2019. The Late Mesozoic Structure Systems in the Northern South China Sea Margin: Geodynamics and Their Influence on the Cenozoic Structures in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Ye, Q., Mei, L. F., Shi, H. S., et al., 2018a. A Low-Angle Normal Fault and Basement Structures within the Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Insights into Late Mesozoic to Early Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the South China Sea Area. Tectonophysics, 731-732: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.03.003 |
|
Ye, Q., Mei, L. F., Shi, H. S., et al., 2018b. The Late Cretaceous Tectonic Evolution of the South China Sea Area: An Overview, and New Perspectives from 3D Seismic Reflection Data. Earth-Science Reviews, 187: 186-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.09.013 |
|
Ye, Q., Mei, L. F., Shi, H. S., et al., 2020. The Influence of Pre-Existing Basement Faults on the Cenozoic Structure and Evolution of the Proximal Domain, Northern South China Sea Rifted Margin. Tectonics, 39(3): e2019TC005845. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019tc005845 |
|
Zhu, W. Q., Liang, J. S., Guo, G., et al., 2014. Main Control Factors and Models of Hydrocarbon Migration-Accumulation in Xijiang Major Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 26(6): 14-20(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Zhang, S. L., 2020. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Porous Tight Sandstone Reservoir in the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation, Upper Triassic, Central and Western Sichuan Basin (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Zheng, J. Y., Gao, Y. D., Zhang, X. T., et al., 2022. Tectonic Evolution Cycles and Cenozoic Sedimentary Environment Changes in Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Science, 47(7): 2374-2390(in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
蔡国富, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等, 2022. 珠江口盆地浅水陆架区拆离断陷的构造变形与沉积充填响应: 以恩平凹陷为例. 地球科学, 47(7): 2391-2409. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.215 |
|
曹爱武, 1999. 西江主洼生油潜力分析. 中国海上油气地质, 11(3): 196-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199903008.htm |
|
曹勤明, 2021. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷始新统中-深层砂岩储层形成机理(博士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学. |
|
陈玮常, 张洪宇, 全志臻, 等, 2020. 珠江口盆地西江主洼古近纪断裂构造与油气成藏. 东北石油大学学报, 44(3): 57-69, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2020.03.006 |
|
程燕君, 吴智平, 张杰, 等, 2020. 西江凹陷早新生代断裂演化及其对南海北缘应力场顺时针旋转的响应. 地球科学, 45(6): 2199-2209. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.250 |
|
丁亮, 郭刚, 郝建荣, 等, 2015. 珠一坳陷西江主洼古近系文昌组烃源岩特征及生烃潜力. 中国海上油气, 27(5): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201505003.htm |
|
杜家元, 施和生, 朱明, 等, 2008. 西江主洼相对低地温条件下油气成藏特征和勘探潜力分析. 中国海上油气, 20(5): 287-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.05.001 |
|
邓棚, 梅廉夫, 杜家元, 等, 2020. 珠江口盆地西江主洼低角度边界正断层特征及成因演化. 石油与天然气地质, 41(3): 606-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202003017.htm |
|
段毅, 吴保祥, 郑朝阳, 等, 2005. 山西沁水盆地煤生烃动力学研究. 科学通报, 50(13): 1405-1411. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.13.019 |
|
冯昌格, 刘绍文, 王良书, 等, 2009. 塔里木盆地现今地热特征. 地球物理学报, 52(11): 2752-2762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200911011.htm |
|
傅宁, 丁放, 何仕斌, 等, 2007. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷烃源岩评价及油气成藏特征分析. 中国海上油气, 19(5): 295-299, 305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.05.002 |
|
高崇龙, 纪友亮, 靳军, 等, 2017. 准噶尔盆地莫索湾地区清水河组深层优质储层特征及其物性控制因素. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(4): 990-1006. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201704003.htm |
|
高阳东, 林鹤鸣, 汪旭东, 等, 2021. 幕式裂陷控洼背景下的烃源岩分布及岩浆改造: 以珠一坳陷番禺4洼为例. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 41(3): 151-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202103014.htm |
|
何敏, 雷永昌, 于水明, 等, 2016. 南海北部浅水区低地温断陷成藏特征及勘探启示. 中国石油勘探, 21(4): 75-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.008 |
|
姜建群, 李军, 史建南, 等, 2004. 大民屯凹陷古今地温场特征及其成藏意义. 沉积学报, 22(3): 541-546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.025 |
|
靳军, 刘明, 刘雨晨, 等, 2021. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合现今温压场特征及其控制因素. 地质科学, 56(1): 28-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202101003.htm |
|
李振升, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等, 2022. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼新近系油气成藏条件及成藏模式. 世界地质, 41(2): 315-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2022.02.008 |
|
梁杰, 2020. 珠江口盆地西江33洼古近系油藏地质特征与成藏解剖. 中外能源, 25(4): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW202004006.htm |
|
梁杰, 刘培, 陈维涛, 等, 2022. 适用于改造型洼陷的烃源规模识别技术: 以西江主洼为例. 海洋地质前沿, 38(6): 78-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202206009.htm |
|
刘从印, 周平兵, 曾驿, 等, 2009. 番禺4洼地区新近系油气成藏主控因素分析. 中国海上油气, 21(2): 91-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200902004.htm |
|
刘培, 张向涛, 林鹤鸣, 等, 2021. 珠江口盆地西江主洼油气差异分布机制. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 51(1): 52-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202101005.htm |
|
刘培, 张向涛, 杜家元, 等, 2018. 低地温断陷构造-热演化过程及其石油地质意义: 以珠江口盆地西江主洼为例. 地质科技情报, 37(2): 149-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802021.htm |
|
刘志峰, 吴克强, 柯岭, 等, 2017. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷北部洼陷带油气成藏主控因素. 石油与天然气地质, 38(3): 561-569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201703016.htm |
|
廖宗宝, 2013. 珠一坳陷西江主洼构造演化及对油气成藏的控制作用(硕士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. |
|
米立军, 2018. 认识创新推动南海东部海域油气勘探不断取得突破: 南海东部海域近年主要勘探进展回顾. 中国海上油气, 30(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201801001.htm |
|
孟召平, 禹艺娜, 李国富, 等, 2023. 沁水盆地煤储层地温场条件及其低地温异常区形成机理. 煤炭学报, 48(1): 307-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202301023.htm |
|
马安来, 金之钧, 李慧莉, 等, 2020. 塔里木盆地顺北地区奥陶系超深层油藏蚀变作用及保存. 地球科学, 45(5): 1737-1753. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.157 |
|
彭光荣, 温华华, 刘从印, 等, 2013. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷浅层油气勘探实践及潜力探讨: 以番禺4洼为例. 海洋地质前沿, 29(3): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202206006.htm |
|
彭金宁, 罗开平, 刘光祥, 等, 2018. 四川盆地热演化异常成因及热场演化特征分析. 石油实验地质, 40(5): 605-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201805002.htm |
|
热西提·亚力坤, 2022. 西江主洼古近系洼陷结构、岩浆改造和烃源岩分布(硕士学位论文). 长春: 吉林大学 |
|
单玄龙, 热西提·亚力坤, 刘培, 等, 2023. 珠江口盆地西江主洼珠琼运动的沉积响应及构造意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 53(2): 329-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202302001.htm |
|
施和生, 代一丁, 刘丽华, 等, 2015. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气藏地质特征与分布发育基本模式. 石油学报, 36(增刊2): 120-133, 155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2015S2011.htm |
|
施和生, 朱俊章, 姜正龙, 等, 2009. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气资源再评价. 中国海上油气, 21(1): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200901003.htm |
|
孙占学, 张文, 胡宝群, 等, 2006. 沁水盆地大地热流与地温场特征. 地球物理学报, 49(1): 130-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200601018.htm |
|
吴鲜, 李丹, 朱秀香, 等, 2022. 塔里木盆地顺北油气田地温场对奥陶系超深层油气的影响: 以顺北5号走滑断裂带为例. 石油实验地质, 44(3): 402-412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202203004.htm |
|
杨学文, 田军, 王清华, 等, 2021. 塔里木盆地超深层油气地质认识与有利勘探领域. 中国石油勘探, 26(4): 17-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202104002.htm |
|
叶青, 2019. 南海北部陆缘晚中生代构造体系: 动力学以及对珠江口盆地新生代构造的制约(博士学位论文). 武汉: 中国地质大学. |
|
朱文奇, 梁建设, 郭刚, 等, 2014. 珠江口盆地西江主洼油气运聚主控因素及运聚模式. 中国海上油气, 26(6): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201406003.htm |
|
章顺利, 2020. 四川盆地中西部上三叠统须家河组二段孔隙型致密砂岩储层特征与形成机理(博士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学. |
|
郑金云, 高阳东, 张向涛, 等, 2022. 珠江口盆地构造演化旋回及其新生代沉积环境变迁. 地球科学, 47(7): 2374-2390. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.258 |









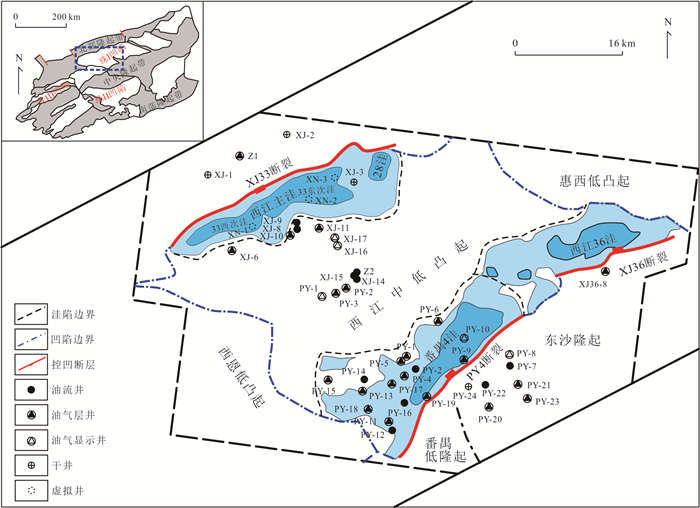
 下载:
下载: