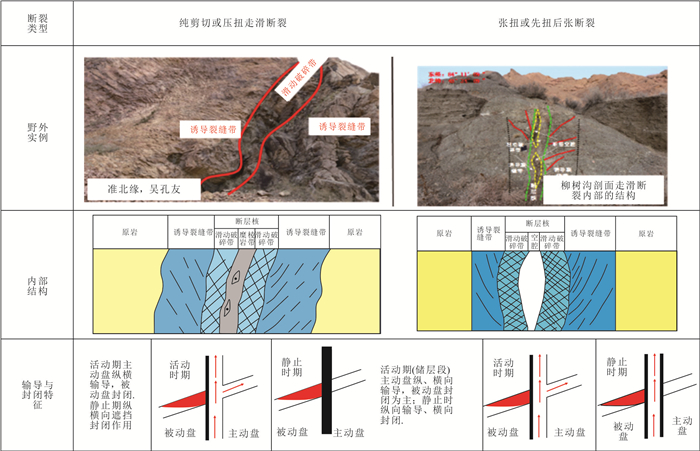
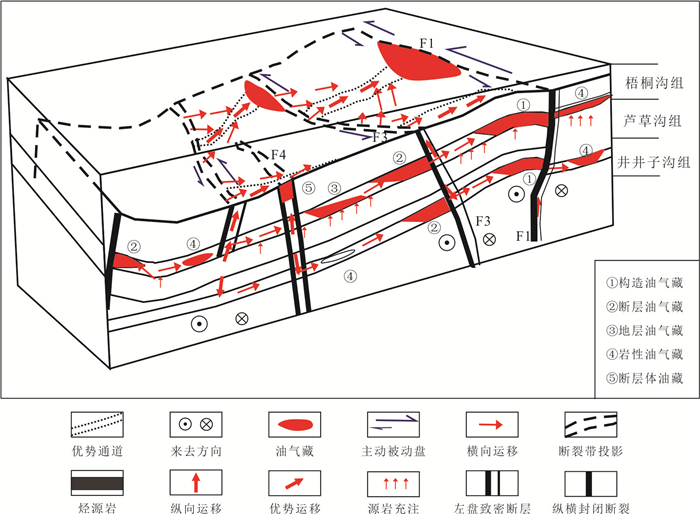
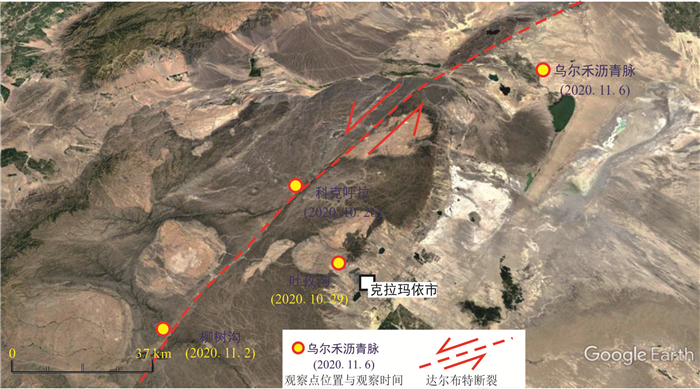
Internal Structural Units, Differential Characteristics of Permeability and Their Transport, Shielding and Reservoir Control Modes of Strike-Slip Faults
-
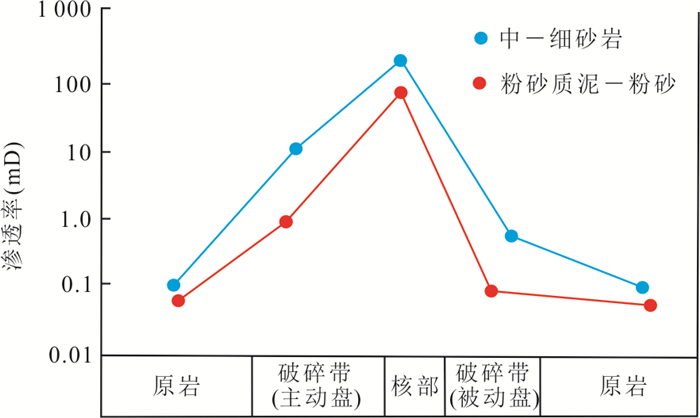
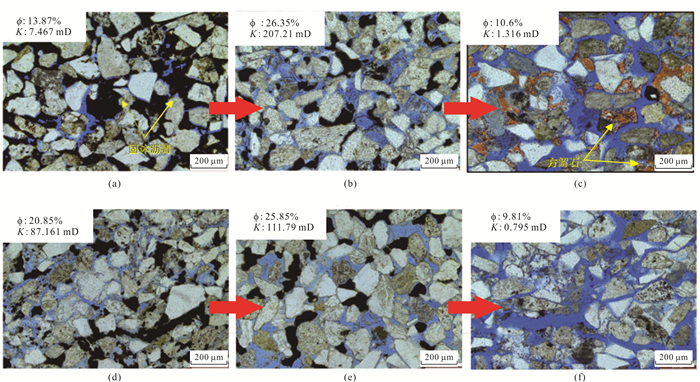
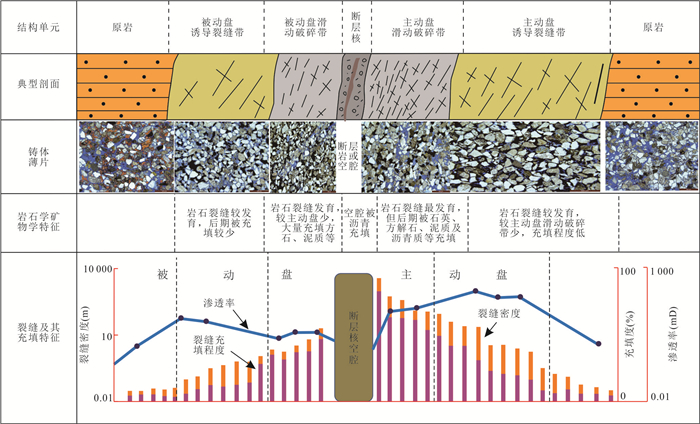
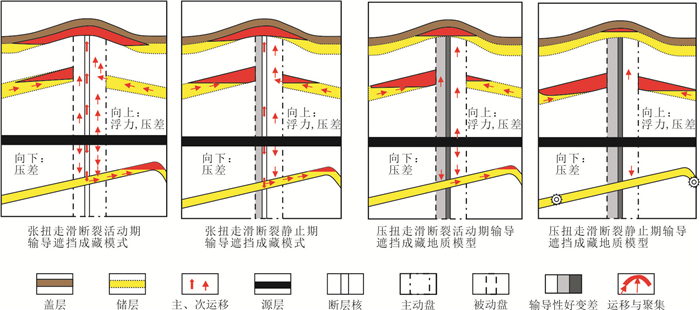
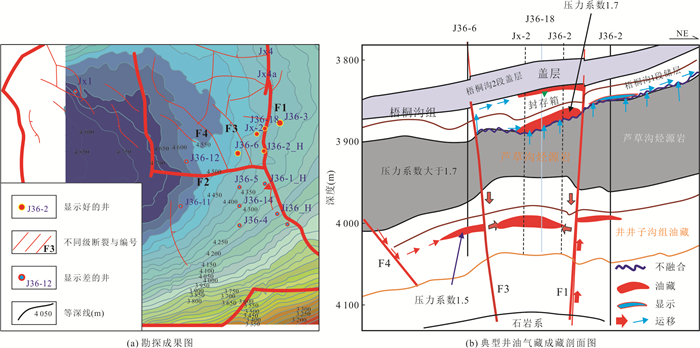
摘要: 走滑断裂及其控藏规律已经成为油气勘探的热点,但不同类型走滑断裂内部结构单元、输导特征及其控藏规律,目前还不甚清楚.通过野外精细表征、物理模拟实验和典型实例剖析,揭示走滑断裂内部结构及其控藏特征:走滑断裂内部结构包括断层核、其两侧的滑动破碎带和诱导裂缝带3个单元5个带;张扭性走滑断裂的断层核输导性最好、其次是滑动破碎带,再次是诱导裂缝带;压扭或纯扭性走滑断裂的断层核封闭性最好,其次是诱导裂缝带,滑动破碎带输导性最好.张扭性走滑断裂纵横向输导性要好于压扭和纯扭性走滑断裂,主动盘输导性好于被动盘,活动时期的输导性好于静止时期.走滑断裂的主动盘以输层油气垂向运移为主、被动盘以横向遮挡油气为特征.构建了准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷西部走滑断裂的控藏模式.Abstract: Strike-slip faults and their reservoir-controlling rules have become the focus of oil and gas exploration, but the internal structural units, transport characteristics and reservoir-controlling rules of different types of strike-slip faults are still unclear. Through detailed fields characterization, physical simulation experiments and typical case analysis, the internal structure of the strike-slip fault and its reservoir control characteristics are revealed. The internal structure of the strike-slip fault includes three units and five zones, including the fault core, the sliding fracture zone on both sides and the induced fracture zone. The fault core of tension-shear strike-slip fault has the best transport, followed by the slip fracture zone and the induced fracture zone. The fault core of compressional or pure torsional strike-slip fault has the best sealing property, followed by induced fracture zone and slip fracture zone. The longitudinal and horizontal transport of tension-shear strike-slip faults is better than that of compression-torsional and pure torsional strike-slip faults. The transport of active disks is better than that of passive disks. The transport of active disks is better than that of static faults. The active disk of the strike-slip fault is characterized by vertical migration of oil and gas in the transport layer while the passive disk is characterized by transverse blocking of oil and gas. The reservoir controlling model of the western strike-slip fault in Jimsar sag, Junggar basin was constructed.
-
Key words:
- strike-slip fault /
- internal structure /
- permeability /
- transmissibility /
- shield /
- control accumulation mode /
- petroleum geology
-
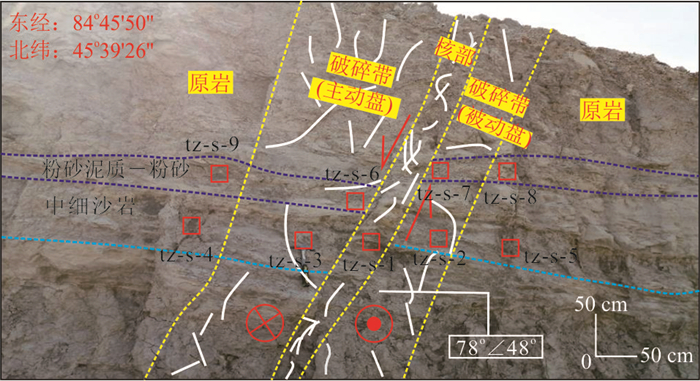
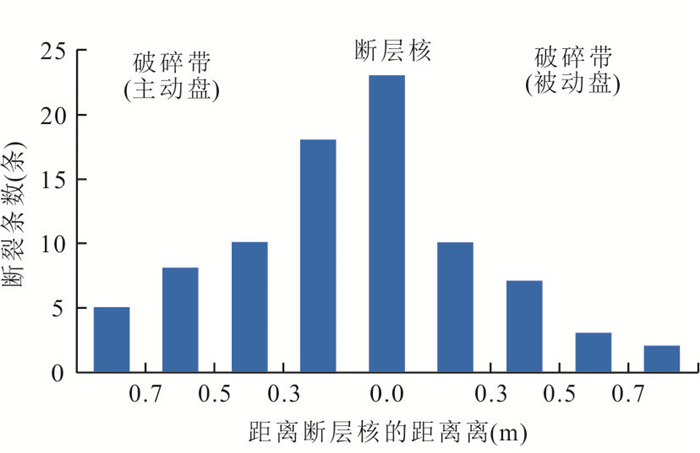
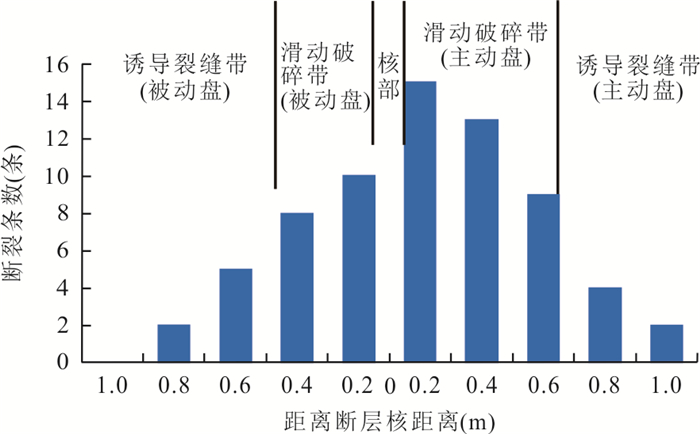
表 1 吐孜沟剖面观察点3走滑断裂裂缝要素统计
Table 1. Statistical of strike-slip fracture elements at observation point 3 of Tuzigou profile
剖面名称 观察点序号 断裂结构 裂缝条数(条) 裂缝开度(mm) 裂缝密度
(条/m2)裂缝充填性 吐孜沟剖面 观察带3 破碎带
(主动盘)42 1~4 10 少部分充填 破碎带
(被动盘)23 0.2~2.0 3 大部分充填 表 2 乌尔禾1号走滑断裂南端和中南端不同结构单元裂缝
Table 2. Fracture statistics of different structural units in the southern and middle southern parts of Wuerhe No.1 strike-slip fault
剖面名称 断裂名称 断裂结构 裂缝条数
(条)裂缝开度
(mm)裂缝密度
条/m2)裂缝充填性 乌尔禾沥青脉观测剖面 1号走滑断裂南端 滑动破碎带(主动盘) 10 0.2~2.0 10 大部分充填胶结 诱导裂缝带(被动盘) 7 0.1~1.0 7 少量充填胶结 1号走滑断裂中南段 滑动破碎带(主动盘) 22 0.2~4.0 22 大部分充填胶结 诱导裂缝带(主动盘) 10 0.12 10 少量充填胶结 表 3 实验模型1各模拟内容参数
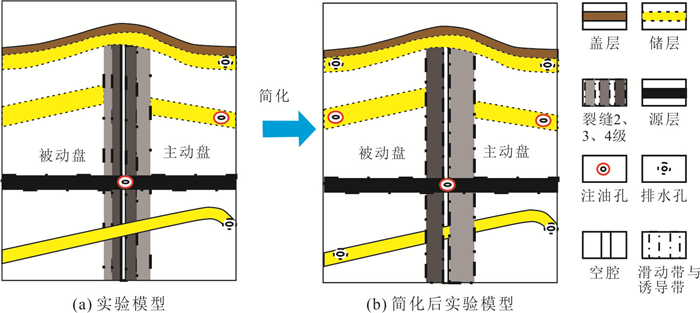
Table 3. Simulation content parameters of experimental model 1
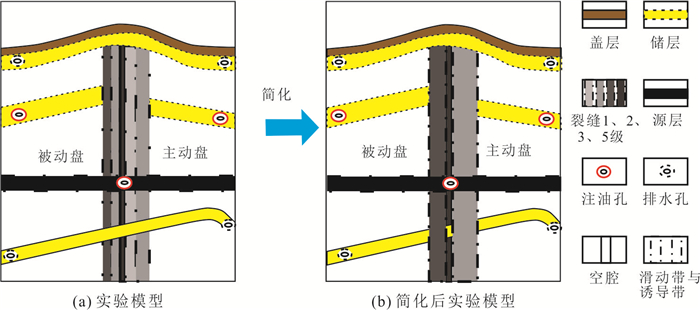
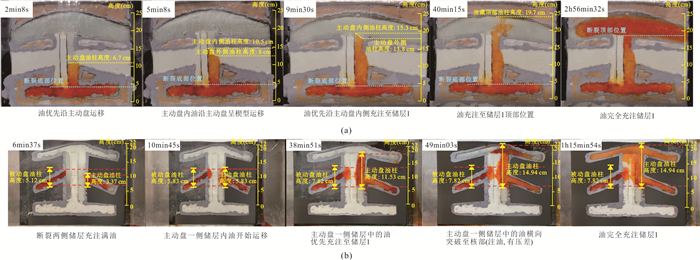
位置 烃源岩 主动盘裂缝带 被动盘裂缝带 断层核部 储层1 储层2 玻璃珠目数 60 40 80 120 30 100 玻璃珠粒径(mm) 0.25 0.425 0.18 0.125 0.6 0.15 渗透率(mD) 4 625 13 366 2 398 1 156 26 640 1 665 表 4 实验模型2各模拟内容参数
Table 4. Simulation content parameters of experimental model 2
位置 烃源岩 主动盘裂缝带 被动盘裂缝带 断层核部 储层1 储层2 玻璃珠目数 60 80 120 40 30 100 玻璃珠粒径(mm) 0.25 0.18 0.125 0.425 0.6 0.15 渗透率(mD) 4 625 2 398 1 156 13 366 26 640 1 665 表 5 实验模型3各模拟内容参数
Table 5. Simulation content parameters of experimental model 3
位置 烃源岩 主动盘裂缝带 被动盘裂缝带 断层核部 储层1 储层2 玻璃珠目数 60 40 80 120 30 60 玻璃珠粒径(mm) 0.15 0.425 0.18 0.425 0.6 0.25 渗透率(mD) 4 625 13 366 2 398 1 156 26 640 4 625 表 6 实验模型4各模拟内容参数
Table 6. Simulation content parameters of experimental model 4
位置 烃源岩 主动盘裂缝带 被动盘裂缝带 断层核部 储层1 储层2 玻璃珠目数 60 80 120 40 30 60 玻璃珠粒径(mm) 0.15 0.18 0.125 0.425 0.6 0.25 渗透率(mD) 4 625 2 398 1 156 13 366 26 640 4 625 -
Aydin, A., 2000. Fractures, Faults, and Hydrocarbon Entrapment, Migration and Flow. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(7): 797-814. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0264-8172(00)00020-9 Chen, D. C., Yang, G. L., Ma, L. C., et al., 2020. Characteristics of the Strike-Slip Fault System and Their Control Actions on the Hydrocarbon Accumulation for Weibei Sag. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(8): 2410-2421(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.017 Chen, W., Wu, Z. P., Hou, F., et al., 2010. Internal Structures of Fault Zones and Their Relationship with Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 31(5): 774-780(in Chinese with English abstract). Clauzon, V., Mayolle, S., Leonardi, V., et al., 2020. Fault Zones in Limestones: Impact on Karstogenesis and Groundwater Flow (Lez Aquifer, Southern France). Hydrogeology Journal, 28(7): 2387-2408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-020-02189-9 Crowell, J. C., 1962. Displacement along the San Andreas Fault, California. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 71: 61. Deng, S., Zuo, L., Aydin, A., et al., 2015. Permeability Characterization of Natural Compaction Bands Using Core Flooding Experiments and Three-Dimensional Image-Based Analysis: Comparing and Contrasting the Results from Two Different Methods. AAPG Bulletin, 99(1): 27-49. https://doi.org/10.1306/07071413211 Dewney, M. W., 1984. Evaluating Seals for Hydrocarbon Accumulations. AAPG Bulletin, 68: 1752-1763. https://doi.org/10.1306/ad461994-16f7-11d7-8645000102c1865d Fu, W. M., 1998. Distribution Characteristics of Fault Zone Structure and Permeability. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 3(1): 65-66(in Chinese with English abstract). Han, J. F., Su, Z., Chen, L. X., et al., 2019. Reservoir-Controlling and Accumulation-Controlling of Strike-Slip Faults and Exploration Potential in the Platform of Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(11): 1296-1310(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201911002 Harland, W. B., 1971. Tectonic Transpression in Caledonian Spitsbergen. Geological Magazine, 108(1): 27-41. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756800050937 Hu, D. S., Tong, D. J., Yang, H. Z., 2009. Progress in Research of Strike-Slip Tectonics. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 16(5): 27-30(in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, H. W., Li, H. Y., Xiao, S. G., et al., 2022. Characteristics of Strike-Slip Faults on the Western Shaleitian Uplift and Their Control over Oil and Gas Accumulation. Marine Geology Frontiers, 38(3): 36-44(in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, L., Li, C., Jin, Q. Y., et al., 2021. Experimental Analysis on Influence of Plastic Formation on Characteristics of Fault Development under Extensional Stress. Earth Science, 46(5): 1749-1757(in Chinese with English abstract) Kennedy, W. Q., 1946. The Great Glen Fault. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society, 102(1-4): 41-76. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.jgs.1946.102.01-04.04 Li, W., Meng, M. F., Chen, X. P., et al., 2021. Quantitative Characterization of Extension and Compression Derived from Bending Strike-Slip Faults and Their Petroleum Geological Significance of the Eastern Bohai Sea. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 45(5): 23-32(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.05.003 Liu, Y. J., Wu, K. Y., Liu, Y., et al., 2022. Analogue Modeling and Structural Differences of Stepovers of Strike Slip Faults: A Case from Shunbei-1 Fault of Tarim Basin. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 49(3): 363-375(in Chinese with English abstract) Luo, C. M., Liang, X. X., Huang, S. Y., et al., 2022. Three-Layer Structure Model of Strike-Slip Faults in the Tazhong Uplift and Its Formation Mechanism. Oil & Gas Geology, 43(1): 118-131, 148. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2022.01.019 Luo, Q., 2002. Fault Controlling Hydrocarbon Theory and Petroleum Exploration Practice. Earth Science, 27(6): 751-756(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.06.017 Luo, Q., 2011. Transporting and Sealing Capacity of Fault Belt and Its Controlling on Reservoir. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 33(5): 474-479(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.05.006 Ma, Q. Y., Zeng, L. B., Xu, X. H., et al., 2022. Internal Architecture of Strike-Slip Fault Zone and Its Control over Reservoirs in the Xiaoerbulake Section, Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 43(1): 69-78(in Chinese with English abstract). Moody, J. D., Hill, M. J., 1956. Wrench-Fault Tectonics. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 67(9): 1207. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1956)67[1207:WT]2.0.CO;2 Su, S. M., Jiang, Y. L., 2021. Fault Zone Structures and Its Relationship with Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation in Petroliferous Basin. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 45(4): 32-41(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.04.004 Sun, Y., Li, B. L., Liu, H. L., et al., 1999. On Layer Slip, Dip Slip and Strike Slip Fault Systems. Journal of Geomechanics, 5(3): 53-57(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.009 Sylvester, A. G., 1988. Strike-Slip Faults. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 100(11): 1666-1703. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1988)1001666:ssf>2.3.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1988)1001666:ssf>2.3.co;2 Wang, J. W., Bao, J., Cao, J. J., et al., 2022. Two Types of Strike-Slip Fault Zones and Their Tectonic Deformation Patterns in the Central Junggar Basin. Earth Science, 47(9): 3389-3400(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y., Zhang, S. N., Liu, Y. L., 2022. Controls of Strike-Slip Fault Activities on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin: A Case Study of TP 39 Fault Zone. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 44(3): 394-401(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Z. Y., Su, J. Q., Qian, M. L., et al., 2011. Control Action of Strike-Slip Faulting on Hydrocarbon Accumulation: A Case Study from Cenozioc Fault in Qikou Sag. Lithologic Reservoirs, 23(4): 35-40(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.04.007 Wu, G. H., Chen, Z. Y., Qu, T. L., et al., 2012. Characteristics of the Strik-Slip Fault Facies in Ordovician Carbonate in the Tarim Basin, and Its Relations to Hydrocarbon. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2): 219-227(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.02.001 Xiao, Y., Wu, G. H., Lei, Y. L., et al., 2017. Analogue Modeling of Through-Going Process and Development Pattern of Strike-Slip Fault Zone. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(3): 340-348(in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Z. Q., Zeng, L. S., Yang, J. S., et al., 2004. Role of Large-Scale Strike-Slip Faults in the Formation of Petroleum-Bearing Compressional Basin-Mountain Range Systems. Earth Science, 29(6): 631-643(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.06.001 Yun, L., 2021. Controlling Effect of NE Strike-Slip Fault System on Reservoir Development and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Eastern Shunbei Area and Its Geological Significance, Tarim Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 26(3): 41-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.03.004 Yun, L., Deng, S., 2022. Structural Styles of Deep Strike-Slip Faults in Tarim Basin and the Characteristics of Their Control on Reservoir Formation and Hydrocarbon Accumulation: a Case Study of Shunbei Oil and Gas Field. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 43(6): 770-787(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, J. B., Zhang, Z. P., Wang, B. F., et al., 2018. Development Pattern and Prediction of Induced Fractures from Strike-Slip Faults in Shunnan Area, Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 39(5): 955-963, 1055(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Q. L., Hou, G. T., Pan, W. Q., et al., 2012. Numerical Simulation of Structural Fractures Controlled by Piqiang Strike-Slip Fault. Journal of Geomechanics, 18(2): 110-119(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2012.02.002 Zhang, Z. T., 1987. On Strike-Slip Faults in Mid-West China. Northwest Geoscience, (1): 103-111(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, F., Jia, C. Z., Yuan, J. Y., et al., 2012. Study on Strike-Slip Fault and Its Control Effect on Oil and Gas Accumulation in Western Qaidam Basin, China. Geological Review, 58(4): 660-670(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.04.007 Zhou, Q. H., 2005. Study on Fault Closure Based on Interior Structure of Fracture Belt. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 24(6): 1-3, 103(in Chinese). 陈登超, 杨贵丽, 马立驰, 等, 2020. 潍北凹陷走滑断裂体系特征及其控藏作用. 地质学报, 94(8): 2410-2421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.017 陈伟, 吴智平, 侯峰, 等, 2010. 断裂带内部结构特征及其与油气运聚关系. 石油学报, 31(5): 774-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202104005.htm 傅文敏, 1998. 断层带结构和渗透率的分布特征. 小型油气藏, 3(1): 65-66. 韩剑发, 苏洲, 陈利新, 等, 2019. 塔里木盆地台盆区走滑断裂控储控藏作用及勘探潜力. 石油学报, 40(11): 1296-1310. doi: 10.7623/syxb201911002 胡德胜, 佟殿君, 阳怀忠, 2009. 走滑构造研究进展. 断块油气田, 16(5): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200905011.htm 胡贺伟, 李慧勇, 肖述光, 等, 2022. 沙垒田凸起西段走滑断裂发育特征及其对油气的控制作用. 海洋地质前沿, 38(3): 36-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202203004.htm 胡林, 李才, 金秋月, 等, 2021. 伸展背景下塑性地层对断裂发育特征影响的实验分析. 地球科学, 46(5): 1749-1757. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.137 李伟, 蒙美芳, 陈兴鹏, 等, 2021. 渤海海域东部弯曲走滑断裂派生伸展与挤压作用的定量表征及其油气地质意义. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 45(5): 23-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202105003.htm 刘芋杰, 吴孔友, 刘寅, 等, 2022. 走滑断裂分段叠置区物理模拟及构造差异性解析: 以塔里木盆地顺北1号断裂为例. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 49(3): 363-375. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZDX202203014.htm 罗彩明, 梁鑫鑫, 黄少英, 等, 2022. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起走滑断裂的三层结构模型及其形成机制. 石油与天然气地质, 43(1): 118-131, 148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201009.htm 罗群, 2002. 断裂控烃理论与油气勘探实践. 地球科学, 27(6): 751-756. http://www.earth-science.net/article/id/1198 罗群, 2011. 断裂带的输导与封闭性及其控藏特征. 石油实验地质, 33(5): 474-479. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201105009.htm 马庆佑, 曾联波, 徐旭辉, 等, 2022. 塔里木盆地肖尔布拉克剖面走滑断裂带内部结构及控储模式. 石油与天然气地质, 43(1): 69-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201005.htm 苏圣民, 蒋有录, 2021. 含油气盆地断裂带结构特征及其与油气运聚关系. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 45(4): 32-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202104005.htm 孙岩, 李本亮, 刘海龄, 等, 1999. 论层滑、倾滑和走滑断裂系统. 地质力学学报, 5(3): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX199903008.htm 汪洋, 张哨楠, 刘永立, 2022. 塔里木盆地塔河油田走滑断裂活动对油气成藏的控制作用: 以托甫39断裂带为例. 石油实验地质, 44(3): 394-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202203003.htm 王建伟, 鲍军, 曹建军, 等, 2022. 准噶尔盆地腹部两类走滑断裂带及其构造变形样式. 地球科学, 47(9): 3389-3400. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.032 王芝尧, 苏俊青, 钱茂路, 等, 2011. 走滑断裂作用对油气成藏的控制: 以歧口凹陷新生代断裂为例. 岩性油气藏, 23(4): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201104009.htm 邬光辉, 陈志勇, 曲泰来, 等, 2012. 塔里木盆地走滑带碳酸盐岩断裂相特征及其与油气关系. 地质学报, 86(2): 219-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201202002.htm 肖阳, 邬光辉, 雷永良, 等, 2017. 走滑断裂带贯穿过程与发育模式的物理模拟. 石油勘探与开发, 44(3): 340-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201703004.htm 许志琴, 曾令森, 杨经绥, 等, 2004. 走滑断裂、"挤压性盆-山构造" 与油气资源关系的探讨. 地球科学, 29(6): 631-643. http://www.earth-science.net/article/id/1464 云露, 2021. 顺北东部北东向走滑断裂体系控储控藏作用与突破意义. 中国石油勘探, 26(3): 41-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202103004.htm 云露, 邓尚, 2022. 塔里木盆地深层走滑断裂差异变形与控储控藏特征: 以顺北油气田为例. 石油学报, 43(6): 770-787. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202206003.htm 张继标, 张仲培, 汪必峰, 等, 2018. 塔里木盆地顺南地区走滑断裂派生裂缝发育规律及预测. 石油与天然气地质, 39(5): 955-963, 1055. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805011.htm 张庆莲, 侯贵廷, 潘文庆, 等, 2012. 皮羌走滑断裂控制构造裂缝发育的力学机制模拟. 地质 张治洮, 1987. 论我国中西部的大型走滑断裂. 西北地质科学, (1): 103-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK198701007.htm 赵凡, 贾承造, 袁剑英, 等, 2012. 柴达木盆地西部走滑相关断裂特征及其控藏作用. 地质论评, 58(4): 660-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201204007.htm 周庆华, 2005. 从断裂带内部结构探讨断层封闭性. 大庆石油地质与开发, 24(6): 1-3, 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK200506000.htm -









 下载:
下载: