A Large Submarine Sinkhole Group was Discovered on Ganquan Platform in Xisha Sea Area of South China Sea
-
-
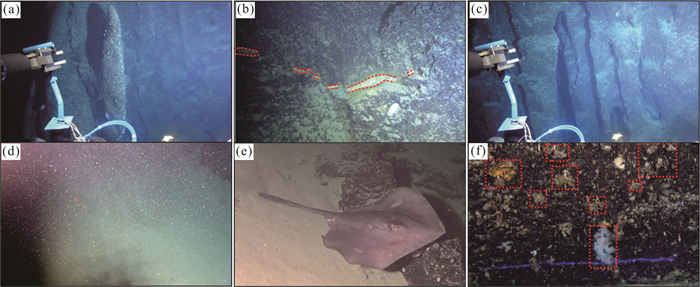
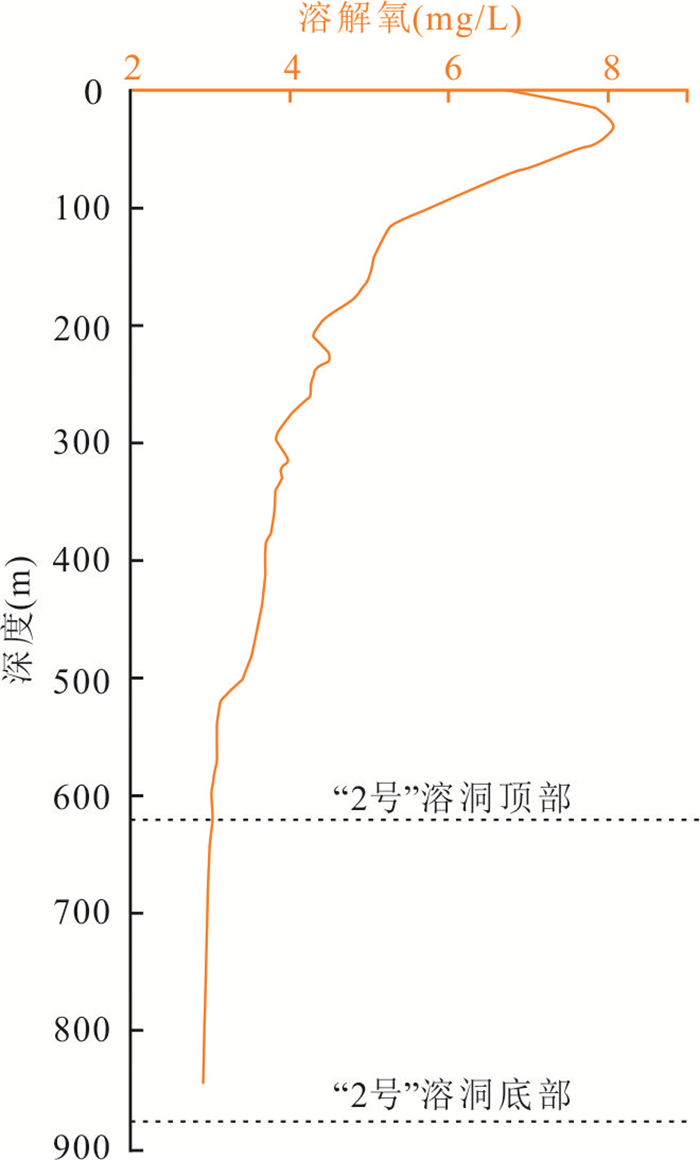
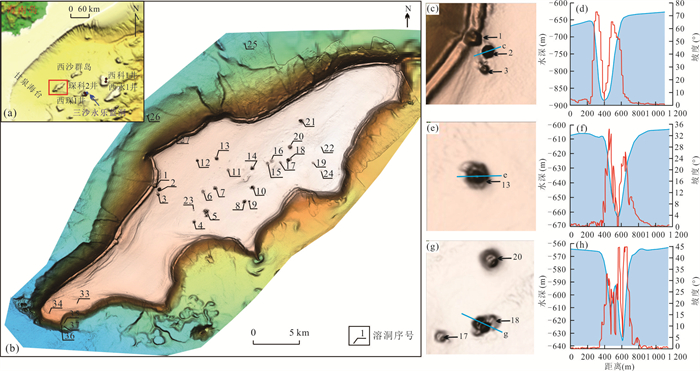
图 1 研究区位置(a), 甘泉海台溶洞群分布特征(b); 溶洞地形特征(c, e, g);溶洞地形剖面(d, f, h)
图c,e,g中蓝线为地形剖面位置. c. 2号溶洞地形特征;e. 13号溶洞地形特征;g. 18号溶洞地形特征;d. 2号溶洞地形剖面;f.13号溶洞地形剖面;h. 18号溶洞地形剖面
Fig. 1. Location of the study area(a); distribution characteristics of submarine sinkholes on the Ganquan carbonate platform(b); bathymetry maps (c, e, g); bathymetric profilescross sections of submarine sinkhole (d, f, h)
表 1 甘泉海台溶洞群的地形参数
Table 1. Geomorphologic parameters of the sinkholes on the Ganquan platform
编号 洞顶水深(m) 溶洞深度(m) 平均直径(m) 编号 洞顶水深(m) 溶洞深度(m) 平均直径(m) 1 724 54 572 20 571 56 502 2 642 241 449 21 595 81 574 3 647 46 330 22 551 5.5 172 4 591 64 441 23 597 8.5 213 5 593 90 566 24 559 3.8 267 6 598 26 465 25 1 267 15 321 7 597 54 435 26 1 242 12 338 8 586 86 459 27 821 42 264 9 586 45 252 28 776 22 207 10 573 89 501 29 584 3 268 11 599 21 320 30 590 6 214 12 613 78 339 31 593 3 148 13 609 69 468 32 601 3 180 14 580 120 487 33 704 5 144 15 582 25 416 34 794 5 145 16 580 19 519 35 1 101 14 95 17 572 22 333 36 1 089 26 66 18 571 79 550 37 1 143 16 76 19 561 14 293 -
Bastos, A. C., Amado-Filho, G. M., Moura, R. L., et al., 2016. Origin and Sedimentary Evolution of Sinkholes (buracas) in the Abrolhos Continental Shelf, Brazil. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 462: 101-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.09.009 Cavailhes, T., Gillet, H., Guiastrennec-Faugas, L., et al., 2022. The Abyssal Giant Sinkholes of the Blake Bahama Escarpment: Evidence of Focused Deep-Ocean Carbonate Dissolution. Geomorphology, 398: 108058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.108058 Chen, W. L., Wu, S. G., Wang, D. W., et al., 2023. Stratigraphic Evolution and Drowning Steps of a Submerged Isolated Carbonate Platform in the Northern South China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10: 1200788. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1200788 Humphreys, M. P., Meesters, E. H., de Haas, H., et al., 2022. Dissolution of a Submarine Carbonate Platform by a Submerged Lake of Acidic Seawater. Biogeosciences, 19(2): 347-358. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-19-347-2022 Kan, H., Urata, K., Nagao, M., et al., 2015. Submerged Karst Landforms Observed by Multibeam Bathymetric Survey in Nagura Bay, Ishigaki Island, Southwestern Japan. Geomorphology, 229: 112-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.07.032 Land, L. A., Paull, C. K., Spiess, F. N., 1999. Abyssal Erosion and Scarp Retreat: Deep Tow Observations of the Blake Escarpment and Blake Spur. Marine Geology, 160(1/2): 63-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00012-2 Mylroie, J. E., 2008. Late Quaternary Sea-Level Position: Evidence from Bahamian Carbonate Deposition and Dissolution Cycles. Quaternary International, 183(1): 61-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2007.06.030 Taviani, M., Angeletti, L., Campiani, E., et al., 2012. Drowned Karst Landscape Offshore the Apulian Margin (Southern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Journal of Cave and Karst Studies, 74(2): 197-212. https://doi.org/10.4311/2011jcks0204 Wu, S. G., Yang, Z., Wang, D. W., et al., 2014. Architecture, Development and Geological Control of the Xisha Carbonate Platforms, Northwestern South China Sea. Marine Geology, 350: 71-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2013.12.016 Yao, P., Wang, X. C., Bianchi, T. S., et al., 2020. Carbon Cycling in the World's Deepest Blue Hole. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 125(2): 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019jg005307 -









 下载:
下载: