Earthquake Detection Model Trained on Velocity and Acceleration Records and Its Application in Xinfengjiang Reservoir
-
摘要:
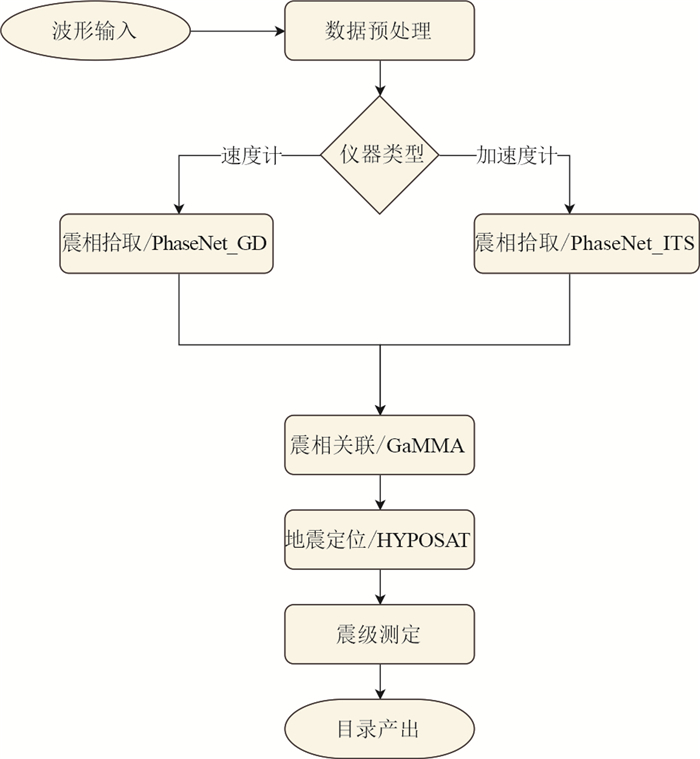
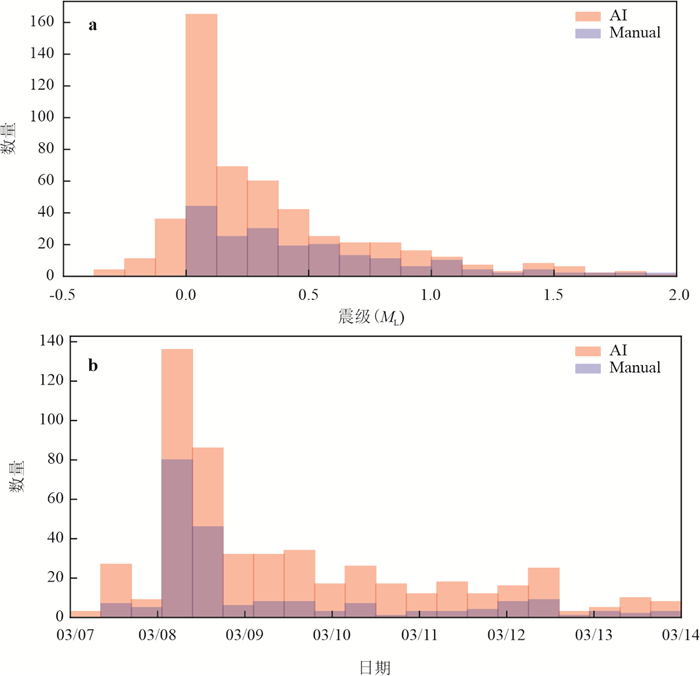
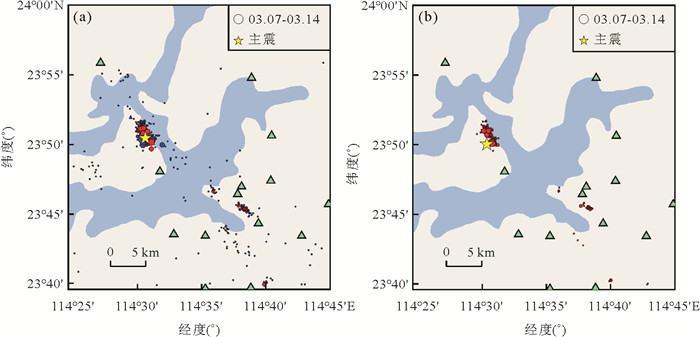
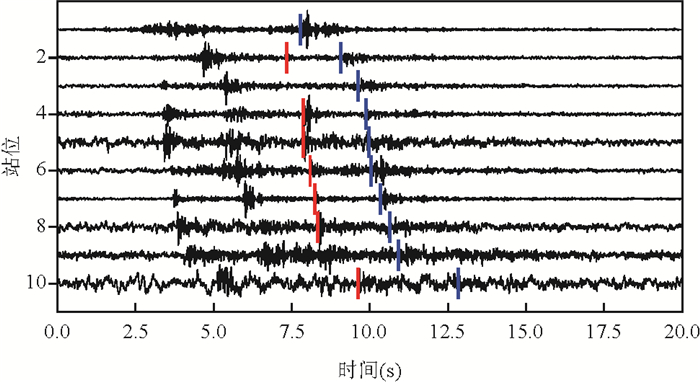
随着国家地震烈度速报与预警工程的建设,加速度记录在地震科学中将得到越来越多的应用. 但目前的地震检测模型多使用速度记录训练,对加速度记录的检测效果较差.利用广东地震台网数据,训练得到了可检测速度记录的PhaseNet_GD模型和检测加速度记录的PhaseNet_ITS模型. 在此基础上,结合GaMMA震相关联和HYPOSAT地震定位方法,发展了一套新的地震数据智能处理流程,并处理了2023年新丰江水库ML4.8地震序列,检测出的事件数量是人工目录的3.8倍,匹配率为93.2%,误检测率为0.38%.这一系统可快速产出完备性高、高精度的地震目录,为水库地震监测和区域地震台网的数据实时处理提供技术支撑.
Abstract:With the construction of the "National Seismic Intensity Rapid Reporting and Early Warning" project, acceleration records data will be increasingly applied in earthquake science research. However, most current earthquake detection models use velocity records for training, which results in poor detection performance for acceleration records. This study utilized seismic records from the Guangdong Earthquake Network to train the PhaseNet_GD model for detecting velocity records and the PhaseNet_ITS model for detecting acceleration records.Based on this, a new intelligent earthquake data processing system was developed by combining the GaMMA, phase association method, and the HYPOSAT, earthquake location method. This system was used to process the 2023 ML 4.8 earthquake sequence in XinfengjiangReservoir, Heyuan, and detected events 3.8 times more than the manual catalog, with a matching rate of 93.2% and a false detection rate of 0.38%. This system can provide technical support for reservoir seismic monitoring and real⁃time data processing of regional earthquake networks.
-
表 1 宽频带速度计震相拾取结果统计
Table 1. Statistics of phase pickup results of broadband velocimetry
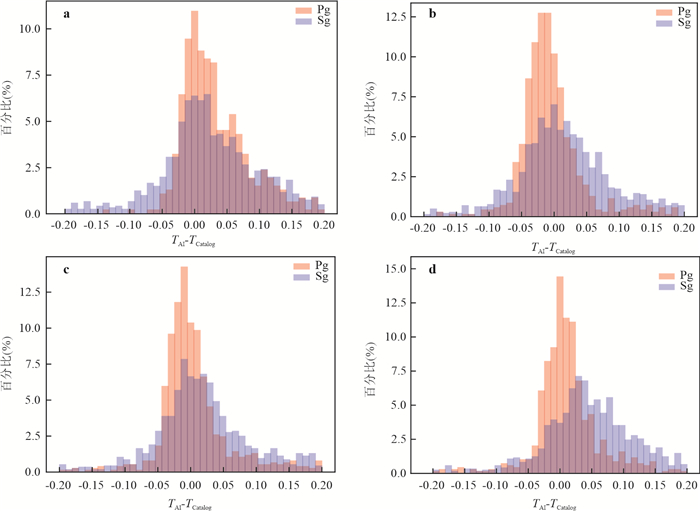
场景 Pg Sg Recall(%) Precision(%) F1 Recall(%) Precision(%) F1 PhaseNet_GD在广东 87.5 83.5 0.855 80.8 79.5 0.801 PhaseNet在广东 76.2 72.7 0.744 68.3 67.2 0.677 PhaseNet在北加州 85.7 93.9 0.896 75.5 85.3 0.801 注:残差小于0.1 s记为TP,Precision用事件波形作为基础. 表 2 加速度计震相拾取结果统计
Table 2. Statistics of accelerometer phase pickup results
训练集 Pg Sg Total Recall(%) Precision(%) Recall(%) Precision(%) Recall(%) Precision(%) PhaseNet_GD 48.4 56.3 59.8 56.8 56.1 56.7 PhaseNet_ITS1 73.5 60.4 71.2 60.5 72.0 60.5 PhaseNet_ITS2 80.2 58.4 57.4 59.5 64.8 59.0 PhaseNet 72.1 46.1 60.4 34.8 64.2 38.2 注:残差小于0.5 s记为TP. -
Allen, R. V., 1978. Automatic Earthquake Recognition and Timing from Single Traces. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 68(5): 1521-1532. https://doi.org/10.1785/bssa0680051521 Ester, M., Kriegel, H. P., Sander, J., et al., 1996. A Density⁃Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. AAAI Press, Portland, Oregon, 226-231. Fan, Y., Lin, J., Hu, R., et al., 1990. The Development of Traveltimetable for near Earthquake in South China. South China Seismological Journal, 10(2) : 1-16(in Chinese). Hu, J., Ding, Y., Zhang, H., Jin, C., et al., 2023. A Real⁃Time Seismic Intensity Prediction Model Based on Long Short⁃Term Memory Neural Network. Earth Science, 48(5): 1853-1864(in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, C., Fang, L. H., Fan, L. P., et al., 2021. Comparison of the Earthquake Detection Abilities of PhaseNet and EQTransformer with the Yangbi and Maduo Earthquakes. Earthquake Science, 34(5): 425-435. https://doi.org/10.29382/eqs⁃2021⁃0038 Kato, A., Obara, K., Igarashi, T., et al., 2012. Propagation of Slow Slip Leading up to the 2011 Mw9.0 Tohoku⁃Oki Earthquake. Science, 335(6069): 705-708. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215141 Lapins, S., Goitom, B., Kendall, J. M., et al., 2021. A Little Data Goes a Long Way: Automating Seismic Phase Arrival Picking at Nabro Volcano with Transfer Learning. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(7). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021jb021910 Li, B. R., Fan, L. P., Jiang, C., et al., 2023. CSESnet: A Deep Learning P⁃Wave Detection Model Based on UNet++ Designed for China Seismic Experimental Site. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.1032839 Liao, S., Zhang, H., Fan, L., et al., 2021. Development of a Real⁃Time Intelligent Seismic Processing System and Its Application in the 2021 Yunnan Yangbi MS6.4 Earthquake. Chinese J. Geophys, 64(10): 3632-3645(in Chinese with English abstract). Meng, X., Yang, H., Peng, Z., et al., 2018. Foreshocks, b Value Map, and Aftershock Triggering for the 2011 Mw 5.7 Virginia Earthquake. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(6): 5082-5098. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017jb015136 Mousavi, S. M., Ellsworth, W. L., Zhu, W. Q., et al., 2020. Earthquake Transformer: an Attentive Deep⁃Learning Model for Simultaneous Earthquake Detection and Phase Picking. Nature Communications, 11(1): 3952. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467⁃020⁃17591⁃w Pan, H., Yan, J., Zhang, Z., et al., 2009. Review on 1918 Nan'ao Ms 7. 3 Earthquake and Its Strong Aftershocks. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 4(1): 40-48(in Chinese with English abstract). Peng, Z. G., Zhao, P., 2009. Migration of Early Aftershocks Following the 2004 Parkfield Earthquake. Nature Geoscience, 2(12): 877-881. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo697 Ross, Z. E., Meier, M. A., Hauksson, E., et al., 2018. Generalized Seismic Phase Detection with Deep Learning. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 108(5A): 2894-2901. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120180080 Schweitzer, J., 2001. HYPOSAT: an Enhanced Routine to Locate Seismic Events. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 158(1): 277-289. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00001160 Wang, D., Chen, G. X., 2022. Seismic Wave Impedance Inversion Based on Temporal Convolutional Network. Earth Science, 47(4): 1492-1506(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J., Xiao, Z., Liu, C., et al., 2019. Deep Learning for Picking Seismic Arrival Times. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(7): 6612-6624. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019jb017536 Woollam, J., Münchmeyer, J., Tilmann, F., et al., 2022. SeisBench⁃A Toolbox for Machine Learning in Seismology. Seismological Research Letters, 93(3): 1695-1709. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220210324 Xiao, Z., Wang, J., Liu, C., et al., 2021. Siamese Earthquake Transformer: A Pair‐Input Deep‐Learning Model for Earthquake Detection and Phase Picking on a Seismic Array. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(5): e2020JB021444. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020jb021444 Yu, Z., Wang, W. 2022. LPPN: A Lightweight Network for Fast Phase Picking. Seismological Research Letters, 93(5): 2834-2846. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220210309 Zhou, Y. J., Yue, H., Kong, Q. K., et al., 2019. Hybrid Event Detection and Phase‐Picking Algorithm Using Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. Seismological Research Letters, 90(3): 1079-1087. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220180319 Zhu, W. Q., Beroza, G. C., 2019. PhaseNet: A Deep-Neural⁃Network⁃Based Seismic Arrival Time Picking Method. Geophysical Journal International, 216(1): 261-273. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggy423 Zhu, W. Q., McBrearty, I. W., Mousavi, S. M., et al., 2021. Earthquake Phase Association Using a Bayesian Gaussian Mixture Model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 127(5): 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021jb023249 范玉兰, 林纪曾, 胡瑞贺, 等, 1990. 华南地区近震走时表的研制. 华南地震, 10(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDI199002000.htm 胡进军, 丁祎天, 张辉, 等, 2023. 基于长短期记忆神经网络的实时地震烈度预测模型. 地球科学, 48(5): 1853-1864. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.338 廖诗荣, 张红才, 范莉苹, 等, 2021. 实时智能地震处理系统研发及其在2021年云南漾濞Ms6.4地震中的应用. 地球物理学报, 64: 3632-3645. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202110018.htm 潘华, 鄢家全, 张志中, 等, 2009. 1918年南澳7.3级地震与强余震之参数复核. 震灾防御技术, 4(1): 40-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY200901006.htm 王德涛, 陈国雄, 2022. 基于时间卷积网络的地震波阻抗反演. 地球科学, 47(4): 1492-1506. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.070 -










 下载:
下载: