Mineral Characteristics of Mica and Tourmaline and Geological Implication for the Pegmatite-Type Lithium Mineralization, Dahongliutan Area, West Kunlun
-
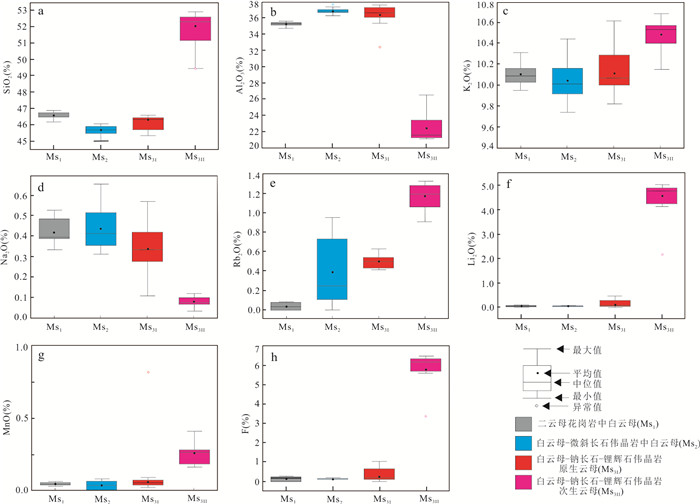
摘要: 大红柳滩二云母花岗岩被认为是白龙山等伟晶岩型锂矿的成矿母岩.为约束大红柳滩地区花岗岩‒伟晶岩的岩浆‒热液演化过程.本文选取大红柳滩岩体二云母花岗岩及不同矿化程度伟晶岩中的贯穿性矿物——云母和电气石,开展了背散射结构观察(BSE)和电子探针成分分析(EPMA).二云母花岗岩(Ms1)和白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩(Ms2)中云母结构均一、化学成分变化小;白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩(Ms3)中云母类型多样,除白云母外,还发育富锂多硅白云母、铁锂云母、锂云母,后者常交代白云母.Ms3中Li、F含量突增,其中Li2O最高可达4.68%、F可达6.47%.二云母花岗岩(Tur1)和白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩(Tur2)中电气石为碱性黑电气石,白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩中(Tur3)发育碱性锂电气石.相较于黑电气石,锂电气石具有富SiO2、Al2O3、Li2O,贫TiO2、MgO、CaO的特征.云母和电气石的成分和结构特征揭示,二云母花岗岩与白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩形成于岩浆阶段,未发生锂矿化.白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩形成于岩浆‒热液过渡期,锂元素发生了显著富集,发育锂辉石、富锂多硅白云母、铁锂云母、锂云母、锂电气石等.据此提出,岩浆‒热液转换期对于锂成矿具有重要意义.在伟晶岩型锂矿床中,锂电气石与锂云母的存在表明伟晶岩具有极高的岩浆演化程度.Abstract: The Dahongliutan two-mica granite is considered as parental rock to the adjacent pegmatite-type lithium deposits such as Bailongshan. To constrain the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of granite and associated pegmatites, we selected the penetrative minerals, mica and tourmaline, from two-mica granite and pegmatite with different degrees of mineralization, for backscattering observation (BSE) and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). In the two-mica granite (Ms1) and muscovite-microcline pegmatite (Ms2), the muscovite is homogeneous, with limited chemical variations. In muscovite-albite-spodumene pegmatite, the muscovite (Ms3) incorporates much higher Li (Li2O up to 4.68%) and F (up to 6.47%) in comparison to Ms1 and Ms2. There are additional Li-bearing phengite, zinnwaldite and lepidolite that have replaced muscovite. Tourmalines from two-mica granite (Tur1) and muscovite-microcline pegmatite (Tur2) belong to alkaline schorl, while those from spodumene pegmatite (Tur3) are alkaline elbaite. Compared to alkaline schorl, alkaline elbaite is enriched in SiO2, Al2O3, Li2O, but depleted in TiO2, MgO and CaO. The textural and compositional features of mica and tourmaline reveal that the two-mica granite and muscovite-microcline pegmatite were formed by magmatic process, without lithium mineralization. By contrast, muscovite-albite-spodumene pegmatite was formed during the magmatic-hydrothermal transition, where lithium was significantly enriched, and numerous lithium-rich minerals such as spodumene, lithium-rich polysilicon muscovite, Li-bearing phengite, zinnwaldite, lepidolite and elbaite, were precipitated. Accordingly, we propose that the magmatic-hydrothermal transition is of great significance for lithium mineralization. In pegmatite-type deposits, the presence of elbaite and lepidolite indicates high degree of magmatic evolution.
-
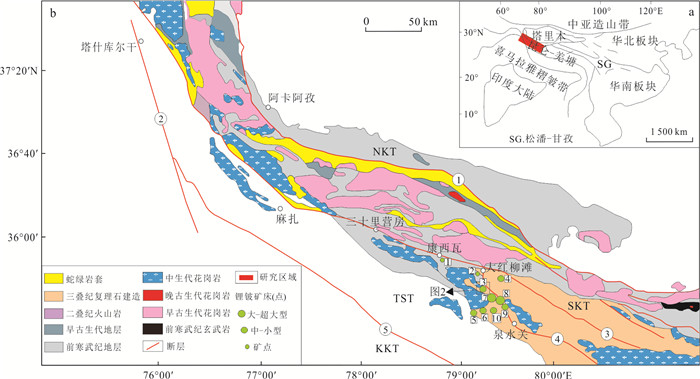
图 1 西昆仑造山带所在位置(a;据Xiao et al., 2005修编); 西昆仑造山带地质图(b;据Wang et al., 2020修编)
缝合带/区域性断裂:①奥依塔格‒库地缝合带;②喀喇昆仑断裂;③麻扎‒康西瓦缝合带;④大红柳滩断裂;⑤红山湖‒乔尔天山缝合带.地体:NKT.北昆仑地体;SKT.南昆仑地体;TST.甜水海地体;KKT.喀喇昆仑地体.矿床/矿点:1.康西瓦铍矿;2.阿克塔斯锂矿;3.大红柳滩锂矿;4.大红柳滩东锂矿床;5.俘虏沟1号脉群锂矿床;6.俘虏沟2号脉群锂矿床;7.白龙山锂矿床;8.509道班西锂矿床;9.507锂矿床;10.冰舟锂矿床
Fig. 1. Regional tectonic map showing the location of the western Kunlun Orogenic Belt (a; modified after Xiao et al., 2005); geological map of the western Kunlun Orogen (b; modified after Wang et al., 2020)
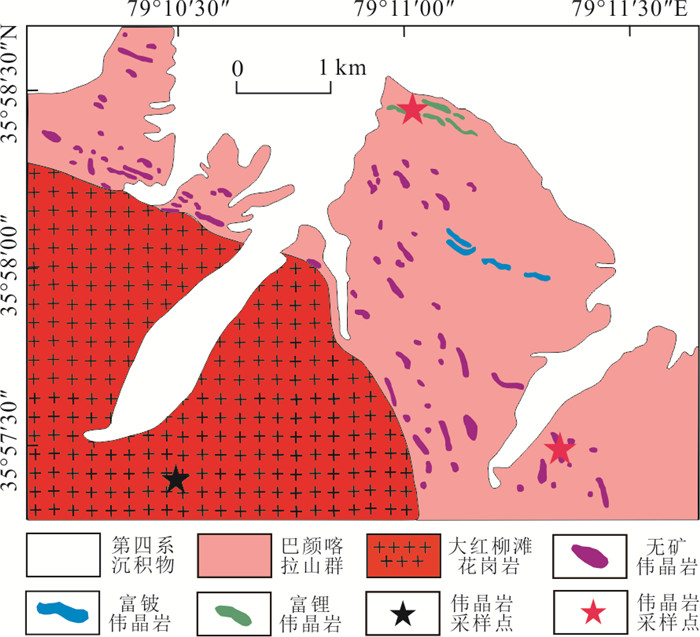
图 2 大红柳滩伟晶岩型锂矿集中区地质简图(改自Yan et al., 2018)
Fig. 2. Geological map of the Dahongliutan pegmatite-type lithium district (modified after Yan et al. 2018)
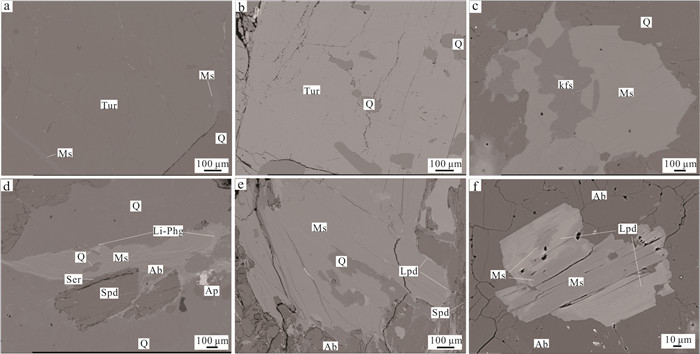
图 3 用于矿物学研究的大红柳滩花岗岩和伟晶岩样品特征
a~c.二云母花岗岩,发育石英、钾长石、斜长石、白云母、黑云母等,见白云母包裹黑云母、石英,电气石粒间可充填有石英、白云母;d~f.白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩,电气石呈黑色,见钾长石沿电气石裂隙充填;g~i.白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩,发育锂辉石晶体、锂云母(交代白云母),锂电气石呈现多色性. 矿物缩写:Ab.钠长石;Bt.黑云母;Elb.锂电气石;Grt.石榴子石;Kfs.钾长石;Lpd.锂云母;Ms.白云母;Pl.斜长石;Q.石英;Spd.锂辉石;Tur.电气石
Fig. 3. The samples used for mineralogical studies, from both the Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
图 4 大红柳滩花岗岩及伟晶岩中白云母和电气石的BSE图像
a.二云母花岗岩中电气石结构均一,沿其裂隙充填有白云母;b.白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩中电气石无结构分带,包裹有石英;c.白云母‒微斜长石伟晶岩中成分均一的白云母,被钾长石交代;d.白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩中富锂多硅白云母交代白云母,细粒绢云母沿锂辉石边缘发育;e.白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩中锂云母沿白云母边缘处产出;f.白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石伟晶岩中锂云母交代白云母. 图中缩写:Ap.磷灰石;Ab.钠长石;Li-phg.富锂多硅白云母;Lpd.锂云母;Ms.白云母;Q.石英;Tur.电气石;Ser.绢云母;Spd.锂辉石
Fig. 4. BSE photos of muscovite and tourmaline from the Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
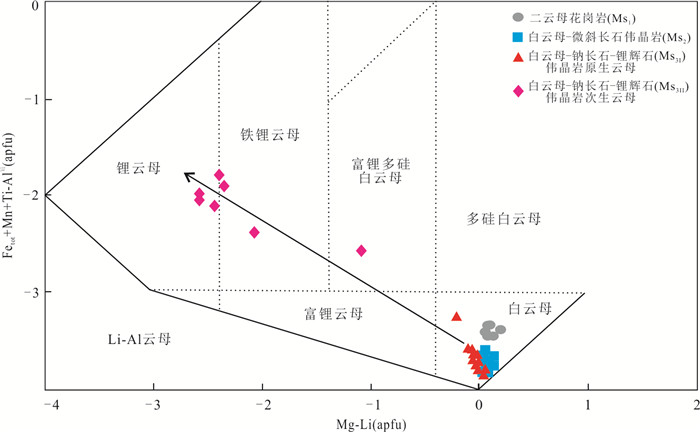
图 5 大红柳滩地区花岗岩和伟晶岩中云母的矿物分类简图
Fig. 5. The nomenclature of micas collected from the Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
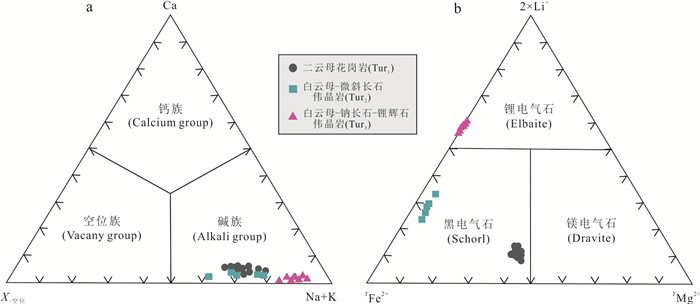
图 7 大红柳滩地区电气石类别划分图
底图据Henry and Guidotti(1985);锂辉石伟晶岩(Tur3)数据为本课题组未发表数据
Fig. 7. Classification for the tourmalines from the Dahongliutan district
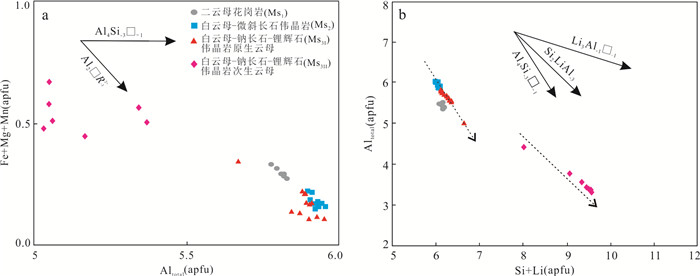
图 8 大红柳滩地区花岗岩与伟晶岩云母替代机制图解
a.云母Fe+Mg+Mn-Altotal图解,底图据Roda-Robles et al.(2006);b. Si+Li-Altotal图解,底图据Roda-Robles et al.(2006)
Fig. 8. Substitution mechanism of micas from Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
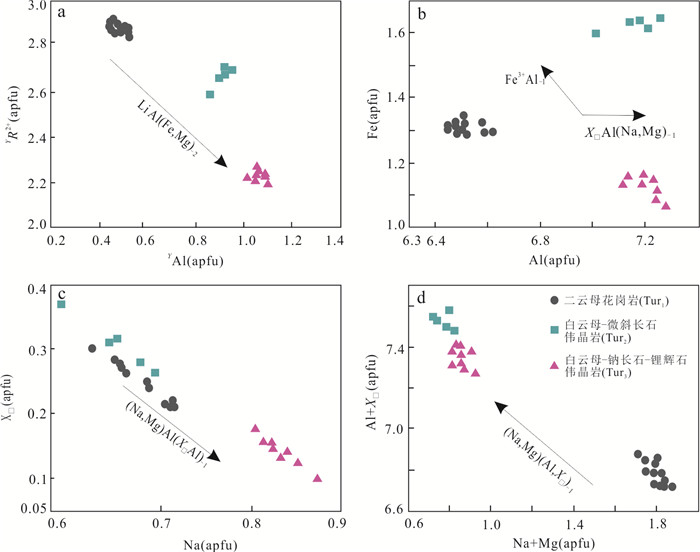
图 9 大红柳滩地区花岗岩与伟晶岩中电气石的元素替代机制图解
Fig. 9. Substitution mechanism of tourmalines from Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
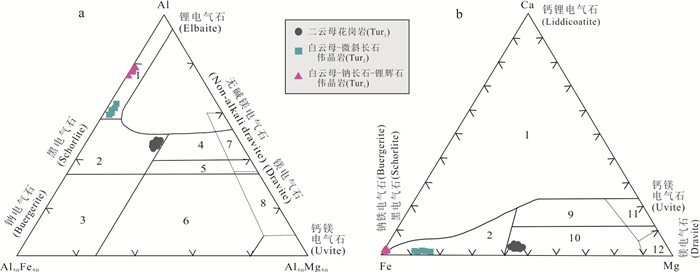
图 10 大红柳滩花岗岩和伟晶岩中电气石成分的Al-Fe-Mg和Ca-Fe-Mg三角图(据Henry and Guidotti, 1985)
1.富Li花岗岩及相关的伟晶岩、细晶岩;2.贫Li花岗岩及相关的伟晶岩、细晶岩;3.富Fe3+石英‒电气石岩(热液蚀变花岗岩);4.与Al饱和相共存的变质泥岩、变质砂岩;5.与Al饱和相不共存的变质泥岩、变质砂岩;6.富Fe3+石英‒电气石岩,钙硅酸盐及变质泥岩;7.低Ca变铁镁质岩和富Cr、V变质沉积岩;8.变质碳酸盐岩和变质灰岩;9.富Ca变质泥岩,变质砂岩及钙硅酸盐;10.贫Ca变质泥岩、变质砂岩和石英‒电气石岩;11.变质碳酸盐岩;12.变超铁镁质岩
Fig. 10. Ternary Al-Fe-Mg (a) and Ca-Mg (b) diagrams showing compositions of tourmaline from Dahongliutan granite and (after Henry and Guidotti, 1985)
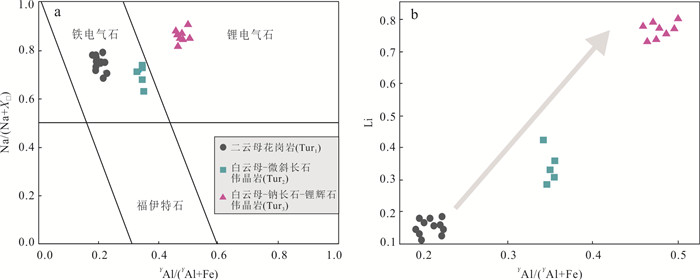
图 11 大红柳滩花岗岩和不同矿化程度伟晶岩中电气石演化图解
a. [YAl/(YAl+Fe)-Na/(Na+X□)];b. YAl/(YAl+Fe)-Li图解,据Selway et al.(2005)
Fig. 11. Evolution diagrams for tourmaline of Dahongliutan granite and pegmatite
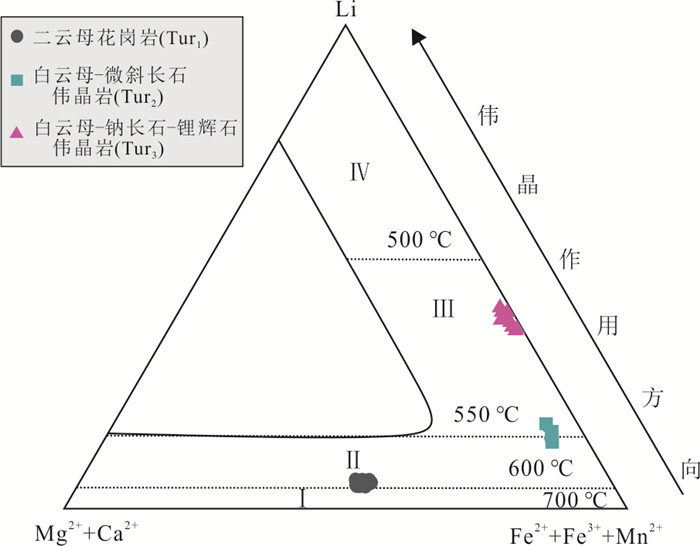
图 12 电气石类型与伟晶岩类型演化关系(底图引自邹天人和杨岳清,1996)
Ⅰ.产于二云母‒微斜长石型及白云母‒微斜长石型伟晶岩的钙镁电气石‒黑(铁)电气石系列;Ⅱ.产于白云母‒微斜长石‒钠长石型伟晶岩的钙镁电气石‒黑(铁)电气电气石系列;Ⅲ.产于白云母‒钠长石‒锂辉石型及白云母‒钠长石型伟晶岩的锂铁电气石;Ⅳ.产于锂云母钠长石型伟晶岩的锂电气石
Fig. 12. Relationship between tourmaline and pegmatite type (base map cited from Zou and Yang, 1996)
-
Bershaw, J., Garzione, C. N., Schoenbohm, L., et al., 2012. Cenozoic Evolution of the Pamir Plateau Based on Stratigraphy, Zircon Provenance, and Stable Isotopes of Foreland Basin Sediments at Oytag (Wuyitake) in the Tarim Basin (West China). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 44: 136-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.020 Cao, R., Gao, Y. B., Chen, B., et al., 2023. Pegmatite Magmatic Evolution and Rare Metal Mineralization of the Dahongliutan Pegmatite Field, Western Kunlun Orogen: Constraints from the B Isotopic Composition and Mineral-Chemistry. International Geology Review, 65(7): 1224-1242. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2021.1899062 Černý, P., Chapman, R., Teertstra, D. K., et al., 2003. Rubidium- and Cesium-Dominant Micas in Granitic Pegmatites. American Mineralogist, 88(11-12): 1832-1835. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2003-11-1226 Černý, P., London, D., Novák, M., 2012. Granitic Pegmatites as Reflections of Their Sources. Elements, 8(4): 289-294. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.8.4.289 Chen, Y. J., Xue, L. Z., Wang, X. L., et al., 2021. Progress in Geological Study of Pegmatite-Type Lithium Deposits in the World. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(10): 2971-2995 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.004 Ding, K., Liang, T., Yang, X. Q., et al., 2019. Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Dahongliutan Pluton in Western Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China. Journal of Central South University, 26(12): 3420-3435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4264-7 Ding, K., Liang, T., Zhou, Y., et al., 2020. Petrogenesis of Dahongliutan Biotite Monzogranite in Western Kunlun Orogen: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb Age and Li-Hf Isotope. Northwestern Geology, 53(1): 24-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciengine.com/doi/pdf/E98C47BD9C374B94A335EA740B582B85 Feng, J., Jia, H. X., Xu, S. Q., et al., 2021. Prospecting Model of Pegmatite Type Lithium Beryllium Deposit in Dahongliutan Ore Concentration Area of West Kunlun and Its Geological Implications. Xinjiang Geology, 39(3): 410-417 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2021.03.008 Feng, Y. G., Liang, T., Wang, M. X., et al., 2022. Geochemistry of Tourmaline from Granitic Pegmatites in East Qinling and Its Implications for Mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 38(2): 428-444 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.02.08 Feng, Y. G., Wang, Y. Q., Zhang, Z., et al., 2019. Geochemistry of Triphylite in Dahongliutan Lithium Pegmatites, Xinjiang: Implications for Pegmatite Evolution. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(6): 1405-1421 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.018 Henry, D. J., Guidotti, C. V., 1985. Tourmaline as a Petrogenetic Indicator Mineral: An Example from the Staurolite-Grade Metapelites of NW Maine. American Mineralogist, 70(1-2): 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-15-0227 Jiang, S. Y., Wang, C. L., Zhang, L., et al., 2021. In Situ Trace Element Tracing and Isotopic Dating Ofpegmatite Type Lithium Deposits: An Overview. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(10): 3017-3038 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.006 Jiang, S. Y., Yu, J. M., Ni, P., et al., 2000. Tourmaline—A Sensitive Tracer for Petrogenesis and Minerogenesis. Geological Review, 46(6): 594-604 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.06.006 Jolliff, B. L., Papike, J. J., Shearer, C. K., 1987. Fractionation Trends in Mica and Tourmaline as Indicators of Pegmatite Internal Evolution: Bob Ingersoll Pegmatite, Black Hills, South Dakota. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51(3): 519-534. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(87)90066-4 Kaeter, D., Barros, R., Menuge, J. F., et al., 2018. The Magmatic-Hydrothermal Transition in Rare-Element Pegmatites from Southeast Ireland: LA-ICP-MS Chemical Mapping of Muscovite and Columbite-Tantalite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 240: 98-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.024 Kong, H. L., Ren, G. L., Li, W. Y., et al., 2023. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Their Geological Significances of Spodumene Pegmatite Veins in the Dahongliutandong Deposit, Western Kunlun, China. Northwestern Geology, 56(2): 61-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, J. K., Li, P., Huang, Z. B., et al., 2023. Geological Features and Formation Mechanism of Pegmatite-Type Rare-Metal Deposits in the Renli Orefield, Northern Hunan, China—An Overview. Earth Science Frontiers, 30(5): 1-25 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, K., Gao, Y. B., Teng, J. X., et al., 2019. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics, Mineralization Age and Resource Potential of the Granite-Pegmatite-Type Rare Metal Deposits in Dahongliutan Area, Hetian County, Xinjiang. Northwestern Geology, 52(4): 206-221 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2019.04.016 Li, L. G., Wang, L. X., Zhu, Y. X., et al., 2023. Metallogenic Age and Process of Rare Metal-Bearing Pegmatites from the Northern Margin of Mufushan Complex, South China. Earth Science, 48(9): 3221-3244 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, W. Y., Zhang, Z. W., Gao, Y. B., et al., 2022. Tectonic Transformation of the Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan Orogenic Belt and Related Mineralization of Critical Mineral Resources of Nickel, Cobalt, Manganese and Lithium. Geology in China, 49(5): 1385-1407 (in Chinese with English abstract). Linnen, R. L., 1998. The Solubility of Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf-W in Granitic Melts with Li and Li + F; Constraints for Mineralization in Rare Metal Granites and Pegmatites. Economic Geology, 93(7): 1013-1025. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.93.7.1013 Linnen, R. L., Van Lichtervelde, M., Cerny, P., 2012. Granitic Pegmatites as Sources of Strategic Metals. Elements, 8(4): 275-280. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.8.4.275 Liu, C., Wang, R. C., Wu, F. Y., et al., 2021. Lithium Mineralization in Qomolangma: First Report of Elbaite-Lepidolite Subtype Pegmatite in the Himalaya Leucogranite Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(11): 3287-3294 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.03 London, D., Manning, D. A. C., 1995. Chemical Variation and Significance of Tourmaline from Southwest England. Economic Geology, 90(3): 495-519. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.90.3.495 Mao, J. W., Yang, Z. X., Xie, G. Q., et al., 2019. Critical Minerals: International Trends and Thinking. Mineral Deposits, 38(4): 689-698 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mattern, F., Schneider, W., 2000. Suturing of the Proto- and Paleo-Tethys Oceans in the Western Kunlun (Xinjiang, China). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(6): 637-650. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00011-0 Peng, H. L., He, N. Q., Wang, M. C., et al., 2018. Geological Characteristics and Metallogenic Regularity of West Track 509 Rare Polymetallic Deposit in Dahongliutan Region, Hetian, Xinjiang. Northwestern Geology, 51(3): 146-154 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.03.013 Qiao, G. B., Zhang, H. D., Wu, Y. Z., et al., 2015. Petrogenesis of the Dahongliutan Monzogranite in Western Kunlun: Constraints from SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemical Characteristics. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(7): 1180-1194 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.003 Roda-Robles, E., Pesquera, A., Gil-Crespo, P. P., et al., 2006. Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Micas from the Pinilla de Fermoselle Pegmatite (Zamora, Spain). European Journal of Mineralogy, 18(3): 369-377. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2006/0018-0369 Selway, J. B., 2005. A Review of Rare-Element (Li-Cs-Ta) Pegmatite Exploration Techniques for the Superior Province, Canada, and Large Worldwide Tantalum Deposits. Exploration and Mining Geology, 14(1-4): 1-30. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsemg.14.1-4.1 Tang, J. L., Ke, Q., Xu, X. W., et al., 2022. Magma Evolution and Mineralization of Longmenshan Lithium-Beryllium Pegmatite in Dahongliutan Area, West Kunlun. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 38(3): 655-675 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.03.05 Teng, J. X., Gao, Y. B., He, Y. K., et al., 2021. Metallogenic Regularity and Resource Potential of Manganese, Lithium, Lead, Zinc and Iron in West Kunlun. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Thomas, R., Davidson, P., Beurlen, H., 2012. The Competing Models for the Origin and Internal Evolution of Granitic Pegmatites in the Light of Melt and Fluid Inclusion Research. Mineralogy and Petrology, 106(1): 55-73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-012-0212-z Thomas, R., Webster, J. D., Heinrich, W., 2000. Melt Inclusions in Pegmatite Quartz: Complete Miscibility between Silicate Melts and Hydrous Fluids at Low Pressure. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 139(4): 394-401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100000120 Tischendorf, G., Gottesmann, B., Förster, H. J., et al., 1997. On Li-Bearing Micas: Estimating Li from Electron Microprobe Analyses and an Improved Diagram for Graphical Representation. Mineralogical Magazine, 61(409): 809-834. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1997.061.409.05 Trumbull, R. B., Beurlen, H., Wiedenbeck, M., et al., 2013. The Diversity of B-Isotope Variations in Tourmaline from Rare-Element Pegmatites in the Borborema Province of Brazil. Chemical Geology, 352: 47-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.021 Tu, Q. J., Han, Q., Li, P., et al., 2019. Basic Characteristics and Exploration Progress of the Spodumene Ore Deposit in the Dahongliutan Area, West Kunlun. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(11): 2862-2873 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.011 van Hinsberg, V. J., Henry, D. J., Dutrow, B. L., 2011. Tourmaline as a Petrologic Forensic Mineral: A Unique Recorder of Its Geologic Past. Elements, 7(5): 327-332. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.7.5.327 Van Lichtervelde, M., Holtz, F., Hanchar, J. M., 2010. Solubility of Manganotantalite, Zircon and Hafnon in Highly Fluxed Peralkaline to Peraluminous Pegmatitic Melts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 160(1): 17-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0462-x Veksler, I. V., 2004. Liquid Immiscibility and Its Role at the Magmatic-Hydrothermal Transition: A Summary of Experimental Studies. Chemical Geology, 210(1-4): 7-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.002 Veksler, I. V., Thomas, R., Schmidt, C., 2002. Experimental Evidence of Three Coexisting Immiscible Fluids in Synthetic Granitic Pegmatite. American Mineralogist, 87(5-6): 775-779. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2002-5-621 Wang, H., Gao, H., Ma, H. D., et al., 2020. Geological Characteristics and Pegmatite Vein Group Zoning of the Xuefengling, Xuepen, and Shuangya Lithium Deposits in Karakorum, Hetian, Xinjiang. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(1): 57-68 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, H., Li, P., Ma, H. D., et al., 2017. Discovery of the Bailongshan Superlarge Lithium-Rubidium Deposit in Karakorum, Hetian, Xinjiang, and Its Prospecting Implication. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(6): 1053-1062 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, R. C., Xie, L., Zhu, Z. Y., et al., 2019. Micas: Important Indicators of Granite-Pegmatite-Related Rare-Metal Mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(1): 69-75 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.04 Wang, W., Du, X. F., Liu, W., et al., 2022. Geological Characteristic and Discussion on Metallogenic Age of the West 509-Daoban Li-Be Rare Metal Deposit in the West Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 38(7): 1967-1980 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.10 Wang, Z., Chen, Z. Y., Li, J. K., et al., 2019. Indication of Mica Minerals for Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution of Renli Rare Metal Pegmatite Deposit. Mineral Deposits, 38(5): 1039-1052 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, H., Gao, H., Zhang, X. Y., et al., 2020. Geology and Geochronology of the Super-Large Bailongshan Li-Rb-(Be) Rare-Metal Pegmatite Deposit, West Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China. Lithos, 360-361: 105449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105449 Wei, X. P., Wang, H., Hu, J., et al., 2017. Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Dahongliutan Two-Mica Granite Pluton in Western Kunlun Orogen: Geotectonic Implications. Geochimica, 46(1): 66-80 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.006 Xiao, W. J., Han, F. L., Windley, B. F., et al., 2003. Multiple Accretionary Orogenesis and Episodic Growth of Continents: Insights from the Western Kunlun Range, Central Asia. International Geology Review, 45(4): 303-328. https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.45.4.303 Xiao, W. J., Windley, B. F., Fang, A. M., et al., 2001. Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic Accretionary Tectonics of the Western Kunlun Range, NW China. Gondwana Research, 4(4): 826-827. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70611-0 Xiao, W. J., Windley, B. F., Liu, D., et al., 2005. Accretionary Tectonics of the Western Kunlun Orogen, China: A Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic, Long-Lived Active Continental Margin with Implications for the Growth of Southern Eurasia. The Journal of Geology, 113(6): 687-705. https://doi.org/10.1086/449326 Xing, C. M., Wang, C. Y., Wang, H., 2020. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Processes Recorded by Muscovite and Columbite-Group Minerals from the Bailongshan Rare-Element Pegmatites in the West Kunlun-Karakorum Orogenic Belt, NW China. Lithos, 364-365: 105507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105507 Xu, Z. Q., Zhu, W. B., Zheng, B. H., et al., 2021. New Energy Strategy for Lithium Resource and the Continental Dynamics Research—Celebrating the Centenary of the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(10): 2937-2954 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.002 Yan, Q. H., Wang, H., Qiu, Z. W., et al., 2017. Chronology and Geological Significance of Cassiterite and Niobium-Tantalum Ore Deposits in Dahongliutan Rare Metal in West Kunlun. The 9th National Member Congress and 16th Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, Xi'an (in Chinese with English abstract). Yan, Q. H., Qiu, Z. W., Wang, H., et al., 2018. Age of the Dahongliutan Rare Metal Pegmatite Deposit, West Kunlun, Xinjiang (NW China): Constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating of Columbite-(Fe) and Cassiterite. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 561-573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.11.010 Yan, Q. H., Wang, H., Chi, G. X., et al., 2022. Recognition of a 600-km-Long Late Triassic Rare Metal (Li-Rb-Be-Nb-Ta) Pegmatite Belt in the Western Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Western China. Economic Geology, 117(1): 213-236. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4858 Yang, S. Y., Jiang, S. Y., 2012. Chemical and Boron Isotopic Composition of Tourmaline in the Xiangshan Volcanic-Intrusive Complex, Southeast China: Evidence for Boron Mobilization and Infiltration during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Processes. Chemical Geology, 312-313: 177-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.04.026 Zhang, C. L., Lu, S. N., Yu, H. F., et al., 2007. Tectonic Evolution of the West Kunlun Orogenic Belt on the Northern Margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidence from Zircon SHRIMP and LA-ICP-MS Dating. Science in China (Series D), 37(2): 145-154 (in Chinese). Zhang, C. L., Ma, H. D., Zhu, B. Y., et al., 2019. Tectonic Evolution of the Western Kunlun-Karakorum Orogenic Belt and Its Coupling with the Mineralization Effect. Geological Review, 65(5): 1077-1102 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, H., Wang, R. C., Tang, Y., 2008. How Long Does the Magma-Hydrothermal Transition Stage Last. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 27 (Suppl. ): 22-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, A. C., Wang, R. C., Jiang, S. Y., et al., 2008. Chemical and Textural Features of Tourmaline from the Spodumene-Subtype Koktokay No. 3 Pegmatite, Altai, Northwestern China: A Record of Magmatic to Hydrothermal Evolution. The Canadian Mineralogist, 46(1): 41-58. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.46.1.41 Zhang, H. J., Tian, S. H., Wang, D. H., et al., 2021a. Lithium Isotope Behavior during Magmatic Differentiation and Fluid Exsolution in the Jiajika Granite-Pegmatite Deposit, Sichuan, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 134: 104139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104139 Zhang, L., Long, X. P., Zhang, R., et al., 2017. Source Characteristics and Provenance of Metasedimentary Rocks from the Kangxiwa Group in the Western Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Implications for Tectonic Setting and Crustal Growth. Gondwana Research, 46: 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.014 Zhang, Z. Y., Jiang, Y. H., Niu, H. C., et al., 2021b. Fluid Inclusion and Stable Isotope Constraints on the Source and Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids in the Bailongshan Pegmatitic Li-Rb Deposit, Xinjiang, Western China. Lithos, 380-381: 105824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105824 Zhao, J. Z., Cao, Z. J., Zhang, Z. J., et al., 2019. Analysis of the Genesis of Tourmaline and Lithium Beryllium Ore. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 42(6): 57-60 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, B., Sun, Y. X., Kong, D. Y., 2011. Geological Features and Prospecting Potential of Rare Metallic Deposits in the Dahongliutan Region, Xinjiang. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 31(3): 288-292 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, J. S., Wang, Q., Xu, Y. G., et al., 2021. Geochronology, Petrology, and Lithium Isotope Geochemistry of the Bailongshan Granite-Pegmatite System, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Ore-Forming Potential of Pegmatites. Chemical Geology, 584: 120484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120484 Zou, T. R., Li, Q. C., 2006. Rare and Rare Earth Metallic Deposits in Xinjiang, China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Zou, T. R., Yang, Y. Q., 1996. Color and Composition of Tourmaline in China. Mineral Deposits. 15(S1): 65-68 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈衍景, 薛莅治, 王孝磊, 等, 2021. 世界伟晶岩型锂矿床地质研究进展. 地质学报, 95(10): 2971-2995. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202110004.htm 丁坤, 梁婷, 周义, 等, 2020. 西昆仑大红柳滩黑云母二长花岗岩岩石成因: 来自锆石U-Pb年龄及Li-Hf同位素的证据. 西北地质, 53(1): 24-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202001003.htm 冯京, 贾红旭, 徐仕琪, 等, 2021. 西昆仑大红柳滩矿集区伟晶岩型锂铍矿床找矿模型及意义. 新疆地质, 39(3): 410-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI202103008.htm 凤永刚, 梁婷, 王梦玺, 等, 2022. 东秦岭花岗伟晶岩中电气石地球化学特征及成矿指示意义. 岩石学报, 38(2): 428-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202202008.htm 凤永刚, 王艺茜, 张泽, 等, 2019. 新疆大红柳滩伟晶岩型锂矿床中磷铁锂矿地球化学特征及其对伟晶岩演化的指示意义. 地质学报, 93(6): 1405-1421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.018 蒋少涌, 王春龙, 张璐, 等, 2021. 伟晶岩型锂矿中矿物原位微区元素和同位素示踪与定年研究进展. 地质学报, 95(10): 3017-3038. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.006 蒋少涌, 于际民, 倪培, 等, 2000. 电气石: 成岩成矿作用的灵敏示踪剂. 地质论评, 46(6): 594-604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200006006.htm 孔会磊, 任广利, 李文渊, 等, 2023. 西昆仑大红柳滩东含锂辉石花岗伟晶岩脉年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义. 西北地质, 56(2): 61-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202302003.htm 李建康, 李鹏, 黄志飚, 等, 2023. 湘北仁里伟晶岩型稀有金属矿田的地质特征及成矿机制概述. 地学前缘, 30(5): 1-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202305001.htm 李侃, 高永宝, 滕家欣, 等, 2019. 新疆和田县大红柳滩一带花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿成矿地质特征、成矿时代及找矿方向. 西北地质, 52(4): 206-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201904020.htm 李乐广, 王连训, 朱煜翔等, 2023. 华南幕阜山北缘含稀有金属伟晶岩成矿时代及成矿过程地球科学, 48(9): 3221-3244. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.141 李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 等, 2022. 昆仑古特提斯构造转换与镍钴锰锂关键矿产成矿作用研究. 中国地质, 49(5): 1385-1407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202205003.htm 刘晨, 王汝成, 吴福元, 等, 2021. 珠峰地区锂成矿作用: 喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩带首个锂电气石‒锂云母型伟晶岩. 岩石学报, 37(11): 3287-3294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202111003.htm 毛景文, 杨宗喜, 谢桂青, 等, 2019. 关键矿产: 国际动向与思考. 矿床地质, 38(4): 689-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202303014.htm 彭海练, 贺宁强, 王满仓, 等, 2018. 新疆和田县大红柳滩地区509道班西稀有多金属矿地质特征与成矿规律探讨. 西北地质, 51(3): 146-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201803016.htm 乔耿彪, 张汉德, 伍跃中, 等, 2015. 西昆仑大红柳滩岩体地质和地球化学特征及对岩石成因的制约. 地质学报, 89(7): 1180-1194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201507003.htm 唐俊林, 柯强, 徐兴旺, 等, 2022. 西昆仑大红柳滩地区龙门山锂铍伟晶岩区岩浆演化与成矿作用. 岩石学报, 38(3): 655-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202203005.htm 滕家欣, 高永宝, 贺永康, 等, 2021. 西昆仑锰锂铅锌铁区域成矿规律与资源潜力. 北京: 地质出版社. 涂其军, 韩琼, 李平, 等, 2019. 西昆仑大红柳滩一带锂辉石矿基本特征和勘查新进展. 地质学报, 93(11): 2862-2873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201911011.htm 王核, 高昊, 马华东, 等, 2020. 新疆和田县雪凤岭锂矿床、雪盆锂矿床和双牙锂矿床地质特征及伟晶岩脉群分带初步研究. 大地构造与成矿学, 44(1): 57-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202001006.htm 王核, 李沛, 马华东, 等, 2017. 新疆和田县白龙山超大型伟晶岩型锂铷多金属矿床的发现及其意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 41(6): 1053-1062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201706005.htm 王汝成, 谢磊, 诸泽颖, 等, 2019. 云母: 花岗岩‒伟晶岩稀有金属成矿作用的重要标志矿物. 岩石学报, 35(1): 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202402008.htm 王威, 杜晓飞, 刘伟, 等, 2022. 西昆仑509道班西锂铍稀有金属矿地质特征与成矿时代探讨. 岩石学报, 38(7): 1967-1980. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202207010.htm 王臻, 陈振宇, 李建康, 等, 2019. 云母矿物对仁里稀有金属伟晶岩矿床岩浆‒热液演化过程的指示. 矿床地质, 38(5): 1039-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201905006.htm 魏小鹏, 王核, 胡军等, 2017. 西昆仑大红柳滩二云母花岗岩地球化学和地质年代学研究及其地质意义. 地球化学, 46(1): 66-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201701006.htm 许志琴, 朱文斌, 郑碧海, 等, 2021. 新能源锂矿战略与大陆动力学研究: 纪念南京大学地球科学与工程学院100周年华诞. 地质学报, 95(10): 2937-2954. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202110002.htm 闫庆贺, 王核, 丘增旺, 等, 2017. 西昆仑大红柳滩稀有金属伟晶岩矿床锡石及铌钽铁矿年代学及其地质意义. 西安: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第九次全国会员代表大会暨第16届学术年会. 张传林, 陆松年, 于海锋, 等, 2007. 青藏高原北缘西昆仑造山带构造演化: 来自锆石SHRIMP及LA-ICP-MS测年的证据. 中国科学(D辑), 37(2): 145-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200702000.htm 张传林, 马华东, 朱炳玉, 等, 2019. 西昆仑‒喀喇昆仑造山带构造演化及其成矿效应. 地质论评, 65(5): 1077-1102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201905003.htm 张辉, 王汝成, 唐勇, 2008. 岩浆‒热液过渡阶段体系究竟持续多长. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 27(增刊): 22-23. 赵建忠, 曹子健, 张子蛟, 等, 2019. 浅析电气石与锂铍矿成因联系. 新疆有色金属, 42(6): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJYS201906025.htm 周兵, 孙义选, 孔德懿, 2011. 新疆大红柳滩地区稀有金属矿成矿地质特征及找矿前景. 四川地质学报, 31(3): 288-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201103010.htm 邹天人, 李庆昌, 2006. 中国新疆稀有及稀土金属矿床. 北京: 地质出版社. 邹天人, 杨岳清, 1996. 中国电气石(碧玺)的颜色与成分. 矿床地质, 15(增刊): 65-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ1996S1025.htm -
 dqkxzx-49-3-922附表1-2.docx
dqkxzx-49-3-922附表1-2.docx

-









 下载:
下载: